Abstract
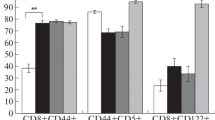
Regulatory T cells can be obtained from primary mixed lymphocyte cultures of CBA spleen cells responding to BALB/c stimulators. At day 3 of culture, T cells are generated which can either help or suppress the generation of cytotoxic T cells in a second primary MLC culture. The regulatory activity observed depends on the conditions employed in the assay system allowing independent assay of different functional cell types which coexist in the cultures. Both the helper activity and the suppressor activity are mediated by differentiated antigen-specific T cells whose function is radioresistant. The Ly phenotype of these regulatory cells was tested. At day 3 of the first-step culture, the phenotype of the helper cells is Ly 1.1+ Ly 2.1−, whereas the inhibitory cells are Ly 1.1+ Ly 2.1+. At day 5 of MLC culture, suppressor activity and helper activity are also observed. However, at this point, a suppressor cell which is Ly 1.1− Ly 2.1+ represents the major inhibitory activity. It is not clear whether this change in suppressor cell phenotype as a function of time in culture represents one differentiation pathway or cells derived from two different precursor cells. The Ly phenotype of helper or cytotoxic T cells did not change as a function of time in culture. In day 5 first-step cells, the cytotoxic cells were typed as Ly 1.1+ 2.1+, whereas the inhibitory cells present in aliquots of the same treated cell population expressed the Ly 1.1− Ly 2.1+ phenotype. Taken together, these observations show that the antigen-specific suppressor cells and helper cells which regulate the generation of cytotoxicity, and the cytotoxic cells themselves represent physically distinct subclasses of T cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Adra, A. R. and Pilarski, L. M.: Antigen-specific suppression of cytotoxic T cell responses. I. Suppressor T cells are not cytotoxic cells.Eur. J. Immunol. 8: 504–511, 1978
Baum, L. L. and Pilarski, L. M.: In vitro generation of antigen specific helper T cells that collaborate with cytotoxic T cell precursors.J. Exp. Med. 148: 1579–1591, 1978
Beverley, P. C. L., Woody, J., Bunkley, M., Feldman, M., and McKenzie, I.: Separation of suppressor and killer T cells by surface phenotypes.Nature 262: 495–497, 1976
Boyse, E. A., Miyazawa, M., Aoki, T., and Old, L. J.: Ly-A and Ly-B: two systems of lymphocyte isoantigens in the mouse.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (Biol.) 170: 174–193, 1968
Cantor, H. and Boyse, E. A.: Functional subclasses of T lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen.J. Exp. Med. 141: 1376–1389, 1975
Cantor, H. and Boyse, E. A.: Regulation of the immune response by T cell subclasses. In O. Stutman (ed.):Contemporary Topics in Immunobiology, Volume 7, p. 47, Plenum Press, New York, 1977
Feldman, M., Beverly, P. C. L., Woody, J., and McKenzie, I. F. C.: T-T interactions in the induction of suppressor and helper T-cells; analysis of membrane phenotype of precursor and amplifier cells.J. Exp. Med. 145: 793–801, 1977
Herzenberg, L. A., Okamura, K., Cantor, H., Sato, N., Shen, F. W., Boyse, E. A., and Herzenberg, L. A.: T cell regulation of antibody responses: demonstration of allotype-specific helper T cells and their specific removal of suppressor T cells.J. Exp. Med. 144: 330–344, 1976
Pilarski, L. M. and Borshevsky, L. V.: A new system for highly efficient generation of alloantigen-specific cytotoxic T cells.Eur. J. Immunol. 6: 906–909, 1976
Shaw, J., Caplan, B., Paetkau, V., Pilarski, L., Delovitch, T., and McKenzie, I. F. C: Cellular origins of costimulator and its activity in cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses.J. Immunol., in press, 1980
Shen, F. W., Boyse, E. A., and Cantor, H.: Preparation and use of Ly antisera.Immunogenetics 2: 591–595, 1975
Shiku, H., Kisielow, P., Bean, M. A., Takahashi, T., Boyse, E. A., Oettgen, H. F., and Old, L. J.: Expression of T-cell differentiation antigens on effector cells in cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Evidence for functional heterogeneity related to the surface phenotype of T cells.J. Exp. Med. 141: 227–241, 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Adra, A.R., Pilarski, L.M. & McKenzie, I.F.C. Surface markers on the T cells that regulate cytotoxic T-cell responses. Immunogenetics 10, 521–533 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01572587
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01572587