Abstract
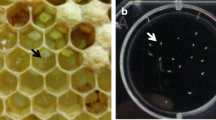
The honeybee pathogen,Spiroplasma melliferum, growing on 1.2% agar medium, forms fried egg (umbonate) colonies surrounded by large numbers of satellite colonies. In liquid media, these helical, cell wall-free prokaryotes flex, twist, and rotate rapidly. A motility mutant was isolated as an umbonate colony without satellites after nitrous acid mutagenesis and an enrichment procedure with chemotaxis. The development of an efficient motility mutant enrichment procedure, easily applied to spiroplasmas, which is described here, will not only greatly expedite the accumulation of motility mutants, but will also be extremely useful for isolating chemotactic mutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Armstrong JB, Adler J, Dahl MM (1967) Nonchemotactic mutants ofEscherichia coli. J Bacteriol 93:390–398
Clark TB, Whitcomb RF, Tully JG, Mouches C, Saillard C, Bove JM, Wroblewski H, Carle P, Rose DL, Henegar RB, Williamson DL (1985)Spiroplasma melliferum, a new species from the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Int J Sys Bacteriol 35:296–308
Clarke CH (1970) Repair systems and nitrous acid mutagenesis inE. coli B/r. Mutat Res 9:359–368
Daniels MJ, Longhand JM, Gilbert J (1980) Aspects of motility and chemotaxis in spiroplasmas. J Gen Microbiol 118: 429–436
Davis RE, Worley, JF (1973) Spiroplasma: helical microorganism asociated with corn stunt disease. Phytopathology 63:403–408
DePamphilis ML, Adler J (1971) Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella fromEscherichia coli andBacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 105:384–395
Holt S (1978) Anatomy and Chemistry of Spirochetes. Microbiol Rev 42:114–160
Lee IM, Davis RE (1983) Chemically defined medium for the cultivation of several epiphytic and phytopathogenic spiroplasmas. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:1247–1251
Orgel LE (1965) The chemical basis of mutation. Adv Enzymol 27:289–346
Townsend R, Plaskitt KA (1985) Immunogold localization of p55-fibril protein and p25-spiralin in spiroplasma cells. J Gen Microbiol 131:983–992
Townsend R, Markham PG, Plaskitt KA, Daniels MJ (1977) Isolation and characterization of a non-helical strain ofSpiroplasma citri. J Gen Microbiol 100:15–21
Townsend R, Archer DB, Plaskitt KA (1980) Purification and characterization of spiroplasma fibrils. J Bacteriol 142: 694–700
Tully JG (1983) Cloning and filtration techniques for mycoplasmas. In: Razin S, Tully JG (eds) Methods in mycoplasmology, vol 1. New York: Academic Press pp 173–177
Whitcomb RF (1983) Culture media for spiroplasmas. In: Razin S, Tully JG (eds) Methods in mycoplasmology, vol 1. New York: Academic Press, pp 147–158
Whitcomb RF, Tully JG. The genusSpiroplasma. In: Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, ninth edn. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins, pp 781–787
Williamson DL (1974) Unusual fibrils from the spirochetelike sex ratio organism. J Bacteriol. 117:904–906
Williamson DL, Whitcomb RF, Tully JG (1978) The spiroplasma deformation test, a new serological method. Curr Microbiol 1:203–207
Williamson DL, Brink PR, Zieve GW (1984) Spiroplasma fibrils. Isr J Med Sci 20:829–835
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, A.J., Williamson, D.L. & Brink, P.R. A motility mutant ofSpiroplasma melliferum induced with nitrous acid. Current Microbiology 18, 219–222 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570295
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570295