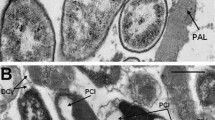
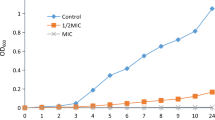
Abstract
The production, detection and the effects of iron concentration on the siderophore production ofStaphylococcus strains used as meat starter cultures were studied. Non-pathogenicStaphylococcus strains produce extracellular low molecular weight compounds which exhibited positive reactivity when measured by a universal detection method for siderophores. The production of siderophores was very closely associated with the iron concentration in the medium, and very low additions considerably reduced siderophore production. Although the production of siderophores was highly iron-dependent, the antimicrobial activity of spent medium fromStaphylococcus cultures against selected yeasts and moulds remained considerable under high iron concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander DB and DA Zuberer. 1991. Use of chrome azurol S reagents to evaluate siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria. Biol Fertil Soils 12: 39–45.
Blackburn P, J Polak, S-A Gusik and SD Rubino. 1989. Nisin compositions for use as enhanced, broad range bactericides. International patent application number PCT/US89/02625; international publication number WO89/12399. Applied Microbiology, Inc, New York.
Bruyneel B, M Vande Woestyne and W Verstraete. 1989. Lactic acid bacteria: microorganisms able to grow in the absence of available iron and copper. Biotechnol Lett 11: 401–406.
Courcol RJ, PA Lambert, P Fournier, GR Martin and MRW Brown. 1991. Effects of iron depletion and sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics on siderophore production byStaphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chromother 28: 663–668.
Cox CD. 1980. Iron uptake with ferripyochelin and ferric citrate byPseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 142: 581–587.
Crowley DE, YC Wang, CPP Reid and PJ Szaniszlo. 1991. Mechanisms of iron acquisition from siderophores by microorganisms and plants. In: Iron Nutrition and Interaction in Plants (Chen Y and Y Hadar, eds), pp 213–232, Academic Publishers Kluwer.
Domingue PAG, B Mottle, DW Morck, MRW Brown and JW Costerton. 1990. A simplified rapid method for the removal of iron and other cations from complex media. J Microbiol Meth 12: 13–22.
Drechsel H, S Freund, G Nicolson, H Haag, O Jung, H Zähner and G Jung. 1993. Purification and chemical characterization of staphyloferrin B, a hydrophilic siderophore from staphylococci. BioMetals 6: 185–192.
Evans E, MRW Brown and P Gilbert. 1994. Iron chelator, exopolysaccharide and protease production inStaphylococcus epidermidis: a comparative study of the effects of specific growth rate in biofilm and planktonic culture. Microbiology 140: 153–157.
Guerinot ML. 1994. Microbial iron transport. Annu Rev Microbiol 48: 743–772.
Haag H, H-P Fiedler, J Meiwes, H Drechsel, G Jung and H Zähner. 1994. Isolation and biological characterization of staphyloferrin B, a compound with siderophore activity from staphylococci. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115: 125–130.
Haikara A and ML Niku-Paavola. 1993. Fungisidic substances produced by lactic acid bacteria. 4th Symp. Lactic acid bacteria—genetics, metabolism and applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 12: 120.
Han D, KW McMillin, JS Godber, MT Bidner, MT Younathan, DL Marshall and LH Hart. 1993. Iron distribution in heated beef and chicken muscles. J Food Sci 58: 697–700.
Konetschny-Rapp S, G Jung, J Meiwes and H Zähner. 1990. Staphyloferrin A: a structurally new siderophore from staphylococci. Eur J Biochem 191: 65–74.
Lindsay JA, TV Riley and BJ Mee. 1995.Staphylococcus aureus but notStaphylococcus epidermidis can acquire iron from transferrin. Microbiology 141: 197–203.
Manninen M and T Mattila-Sandholm. 1994. Methods for the detection ofPseudomonas siderophores. J Microbiol Meth 19: 223–234.
Maskell JP. 1980. The functional interchangeability of enterobacterial and staphylococcal chelators. Antonie van Leeuwenhock 46: 343–351.
Mattila-Sandholm T. 1994. Nature's preservation. In: Minimal Processing of Foods (Mattila-Sandholm T and R Ahvenainen, eds), pp 103–117, VTT Symposium 142, Espoo.
Matzanke BF. 1991. Structures, coordination, chemistry and functions of microbial iron chelates. In: Handbook of Microbial Iron Chelates (Winkelmann G, ed), pp 15–64, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Meiwes J, H-P Fiedler, H Haag, H Zähner, S Konetschny-Rapp and G Jung. 1990. Isolation and characterization of staphyloferrin A, a compound with siderophore activity fromStaphylococcus hyicus DSM 20459. FEMS Microbiol Lett 67: 201–206.
Miller MJ. 1995. Synthesis and studies of microbial iron chelators (siderophores) and drug conjugates. 209th ACS National Meeting, Anaheim, Calif, April 2–6, 1995, oral presentation.
Neilands JB. 1984. Methodology of siderophores. Struct Bond 58: 1–24.
Neilands JB. 1989. Siderophore systems of bacteria and fungi. In: Metal Ions and Bacteria (Beveridge TJ and RJ Doyle, eds), pp 141–164, John Wiley and Sons, New Jersey.
Nychas GJE and JS Arkoudelos. 1990. Staphylococci: their role in fermented sausages. J Appl Bacteriol Symp Supp. 19: 167S-188S.
Raaska L, L Viikari and T Mattila-Sandholm. 1993. Detection of siderophores in growing cultures ofPseudomonas spp. J Ind Microbiol 11: 181–186.
Reigh G and M O'Connell. 1993. Siderophore-mediated iron transport correlates with the presence of specific iron-regulated proteins in the outer membrane ofRhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 175: 94–102.
Roy N, P Bhattacharyya and PK Chakrabartty. 1994. Iron acquisition during growth in an iron-deficient medium byRhizobium sp isolated fromCicer arietinum. Microbiology 140: 2811–2820.
Scher FM and R Baker. 1982. Effect ofPseudomonas putida and a synthetic iron chelator on induction of soil suppressiveness toFusarium wilt pathogens. Phytopathol 72: 1567–1573.
Schwyn B and JB Neilands. 1987. Universal chemical assay for the determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160: 47–56.
Skyttä E and T Mattila-Sandholm. 1991. A quantitative method for assessing bacteriocins and other food antimicrobials by automated turbidometry. J Microbiol Meth 14: 77–88.
Skyttä E, A Haikara and T Mattila-Sandholm. 1993. Production and characterization of antibacterial compounds produced byPediococcus damnosus andPediococcus pentosaceus. J Appl Bacteriol 74: 134–142.
Weller DM. 1988. Biological control of soilborne plant pathogens in the rhizosphere with bacteria: Annu Rev Phytopathol 26: 397–407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raaska, L., Mattila-Sandholm, T. Effects of iron level on the anatagonistic action of siderophores from non-pathogenicStaphylococcus spp. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 15, 480–485 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570018
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570018