Abstract
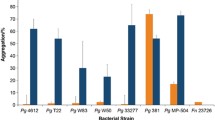
Streptococcus gordonii DL1 (Challis) bears coaggregation-mediating surface adhesins which recognize galactoside-containing surface polysaccharides onStreptococcus oralis 34,Streptococcus oralis C104, andStreptococcus SM PK509. Fifty-nine spontaneously-occurring coaggregation-defective (Cog−) mutants ofS. gordonii DL1 unable to coaggregate with partner streptococci were isolated. Six representative Cog− mutants were characterized by their coaggregation properties with fourActinomyces naeslundii strains (T14V, PK947, PK606, PK984),Veillonella atypica PK1910, andPropionibacterium acnes PK93. The six representative Cog− mutants showed altered coaggregation with their streptococcal partners,A. naeslundii PK947, andP. acnes PK93. Based on the coaggregation phenotypes of these mutants, a model for the lactose-inhibitable coaggregation betweenS. gordonii DL1 and its partner bacteria is proposed. The potential use of these mutants in studies of oral biofilms is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeygunawardana C, CA Bush and JO Cisar. 1991. Complete structure of the cell surface polysaccharide ofStreptococcus oralis C104: a 600 MHz NMR study. Biochemistry 30: 8568–8577.
Ciardi JE, GFA McCray, PE Kolenbrander and A Lau. 1987. Cell-to-cell interaction ofStreptococcus sanguis andPropionibacterium acnes on saliva-coated hydroxyapatite. Infect Immun 55: 1441–1446.
Gibbons RJ, DI Hay and DH Schlesinger. 1991. Delineation of a segment of absorbed salivary acidic proline-rich proteins which promotes adhesion ofStreptococcus gordonii to apatitic surfaces. Infect Immun 59: 2948–2954.
Hsu SD, JO Cisar, AL Sandberg and M Kilian. 1994. Adhesive properties of viridans streptococcal species. Microb Ecol Health Dis 7: 125–137.
Hughes CV, PE Kolenbrander, RN Andersen and LVH Moore. 1988. Coaggregation properties of human oralVeillonella spp: relationship to colonization site and oral ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 54: 1957–1963.
Jenkinson HF. 1987. Novobiocin-resistant mutants ofStreptococcus sanguis with reduced cell hydrophobicity and defective in coaggregation. J Gen Microbiol 133: 1909–1918.
Kolenbrander PE. 1982. Isolation and characterization of coaggregation-defective mutants ofActinomyces viscosus. Actinomyces naeslundii, andStreptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun 37: 1200–1208.
Kolenbrander PE. 1989. Surface recognition among oral bacteria: multigeneric coaggregation and their mediators. Crit Rev Microbiol 17: 137–159.
Kolenbrander PE and RN Andersen. 1990. Characterization ofStreptococcus gordonii (S. sanguis) PK488 adhesin-mediated coaggregation withActinomyces naeslundii PK606. Infect Immun 58: 3064–3072.
Kolenbrander PE and RN Andersen. 1986. Multigeneric aggregations among oral bacteria: a network of independent cell-to-cell interactions. J Bacteriol 168: 851–859.
Kolenbrander PE, RN Andersen and LVH Moore. 1989. Coaggregation ofFusobacterium nucleatum, Selenomonas flueggei, Selenomonas infelix, Selenomonas noxia, andSelenomonas sputigena with strains from 11 genera of oral bacteria. Infect Immun 57: 3194–3203.
Kolenbrander PE, RN Andersen and LVH Moore. 1990. Intrageneric coaggregation among strains of human oral bacteria: potential role in primary colonization of the tooth surface. Appl Environ Microbiol 56: 3890–3894.
Kolenbrander PE and J London. 1993. Adhere today, here tomorrow: oral bacterial adherence. J Bacteriol 175: 3247–3252.
Kolenbrander PE and J London. 1992. Ecological significance of coaggregation among oral bacteria. Adv Microb Ecol 12: 183–217.
Maryanski JH and CL Wittenberger. 1975. Mannitol transport inStreptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol 124: 1475–1481.
McIntire FC, CA Bush, SS Wu, SC Li, YT Li, M McNeil, SS Tjoa and PV Fennessey. 1987. Structure of a new hexasaccharide from the coaggregation polysaccharide ofStreptococcus sanguis 34. Carbohydrate Research 166: 133–143.
Nyvad B and M Kilian. 1990. Comparison of the initial stretococcal microflora on dental enamel in caries-active and in caries-inactive individuals. Caries Res 24: 267–272.
Nyvad B and M Kilian. 1987. Microbiology of the early colonization of human enamel and root surfacesin vivo. Scand J Dent Res 95: 369–380.
Scannapieco FA, EJ Bergey, MS Reddy and MJ Levine. 1989. Characterization of salivary α-amylase binding toStreptococcus sanguis. Infect Immun 57: 2853–2863.
Wolfaardt GM, JR Lawrence, RD Robarts, SJ Caldwell and DE Caldwell. 1994. Multicellular organization in a degradative biofilm community. Appl Environ Microbiol 60: 434–446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemans, D.L., Kolenbrander, P.E. Isolation and characterization of coaggregation-defective (Cog−) mutants ofStreptococcus gordonii DL1 (Challis). Journal of Industrial Microbiology 15, 193–197 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569825
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569825