Abstract
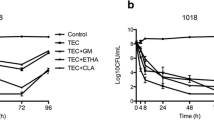
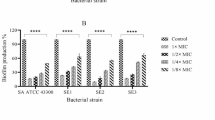
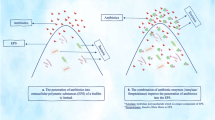
During a prospective study of indwelling vascular catheter-related infections, 134 isolates ofStaphylococcus epidermidis were grown from 700 catheter tips.In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing of these isolates to oxacillin, vancomycin and ofloxacin was performed using the standard broth microdilution technique. These results were compared to those for the same organisms grown in biofilm before the addition of antimicrobial agents. In 96-well flat bottom microtiter plates, 104–105 colony forming units ofS. epidermidis in 0.1 ml broth were grown for 18 h at 37°C, at which time a biofilm was observed for all isolates. Different concentrations of antimicrobial agents (0.1 ml) were then added to the plates. The plates were incubated for 18 h at 37°C. Since MICs could not be estimated in these plates, all the wells were subcultured after mixing the biofilm with the broth. Minimum bactericidal concentrations (MBCs) were defined as 99.9% reduction in colony forming units. For organisms grown in suspension, 100% of the isolates were susceptible to vancomycin, 81% to ofloxacin and 40% to oxacillin. MBCs of susceptible isolates were within four-fold differences for vancomycin (53%), oxacillin (50%), and ofloxacin (51%). When grown as a biofilm, 78%, 93% and 71% of isolates had MBCs of ≥2048 μg ml−1 of oxacillin, vancomycin and ofloxacin respectively. These data demonstrate the reduced bactericidal activity of antimicrobial agents againstS. epidermidis in a biofilm and a simple method for its detection in the microbiology laboratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar H, MK Dasgupta and JW Costerton. 1990. Mini review: testing the susceptibility of bacteria in biofilms to antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34: 2043–2046.
Anwar H, JL Strap and JW Costerton. 1992. Mini review: establishment of aging biofilms: possible mechanism of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 36: 1347–1351.
Archer G. 1984.Staphylococcus epidermidis: the organisms, its diseases, and treatment. Curr Clin Topic Infect Dis 5: 25–40.
Benezra D, TE Kiehn, GWM Gold, AE Brown, ADM Turnbull and D Armstrong. 1988. Prospective study of infections in indwelling central venous catheters using quantitative blood cultures. Am J Med 85: 495–498.
Christensen GD, WA Simpson, AL Bisno and EH Beachey. 1982. Adherence of slime-production strain ofStaphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun 37: 318–326.
Costerton JW. 1977. Cell envelope as a barrier to antibiotics. In: Microbiology 1977 (Schlessinger D, ed), pp. 151–157, Am Soc for Microbiol, Washington DC.
Costerton JW, KJ Cheng, GG Geesey, TI Ladd, JC Nickel, M Dasgupta and TJ Marrie. 1987. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41: 435–464.
Costerton JW, KJ Cheng, GG Deesey, TI Ladd, JC Nickel, M Dagupta and TJ Marrie. 1987. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41: 435–464.
Coulioud D, P Van Der Auwera and C Lasset. 1993. Prospective multicentric study of the etiology of 1051 bacteremias in 782 patients. Supportive Care in Cancer 1: 34–36.
Dall L, WG Barnes, JW Lane and J Mills. 1987. Enzymatic modification of glycocalyx in the treatment of experimental endocarditis due toViridans streptococci. J Infect Dis 156: 756–746.
Dasgupta MK and JW Costerton. 1989. Significance of biofilm-adherent bacterial microcolonies on Tenckhoff catheters of CAPD patients. Blood Purif 7A144–7A155.
Dasgupta MK, KB Bettcher, RA Ulan, V Burns, K Lam, JB Dossetor and JW Costerton. 1987. Relationship of adherent bacterial biofilms to peritonitis in chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Bull 7: 168–173.
Davenport DS, RM Massanari, MA Pfaller, MJ Bale, SA Streed and WJ Hierholzer, Jr. 1986. Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negativeStaphylococcus. J Infect Dis 153: 332–339.
Diaz-Mitoma FG, KM Harding, DJ Hoban, RS Roberts and DE Low. 1987. Clinical significance of a test for slime production in ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections caused by coagulase-negative. J Infect Dis 156(4): 555–560.
Dickinson GM and AL Bisno. 1989. Infections associated with indwelling devices: concepts of pathogenesis: infections associated with intravascular devices. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33: 597–601.
Elliott TSJ. 1988. Intravascular-device infections. J Med Microbiol 27: 161–167.
Evans DJ, MR Brown, DG Allison and P Gilbert. 1991. Susceptibility ofPseudomonas aeruginosa andEscherichia coli biofilms toward ciprofloxacin: effect of specific growth rate. J Antimicrob Chemother 27: 177–184.
Farber BF, MH Kaplan and AG Clogston.Staphylococcus epidermidis extracted slime inhibits the antimicrobial action of glycopeptide antibiotics. J Infect Dis 161: 37–40.
Gray ED, G Peters, M Verstegen and WE Regelmann. 1984. Effect of extracellular slime substance fromStaphylococcus epidermidis on the human cellular immune response. Lancet 1: 365–367.
Gristina AG, CD Hobgood, LX Webb and QN Myrvik. 1987. Adhesive colonization of biomaterials and antibiotic resistance. Biomaterial 8: 423–426.
Gristina AG, RA Jennings, PT Naylor, QN Myrvik and LX Webb. 1989. Comparativein vitro antibiotic resistance of surface-colonizing coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 33: 813–816.
Hiemenz J, J Skeleton and PA Pizzo. 1986. Perspective on the management of catheter-related infections in cancer patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J 5: 6–11.
Johnson GM, DA Lee, WE Regelmann, ED Gray, G Peters and PG Quie. 1986. Interference with granulocyte functions byStaphylococcus epidermidis slime. Infect Immun 54: 13–20.
National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards 1992. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, M7-A. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Villanova, Pennsylvania.
Naylor PT, MD Quentin, N Myrvik and A Gristina. 1990. Antibiotic resistance of biomaterial-adherent coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive staphylococci. 18th Open Meeting of the Hip Society, New Orleans, Lousiana.
Nichols WW, MJ Evans, MPE Slack and HL Walmsley. 1989. The penetration of antibiotics into aggregates of mucoid and non-mucoidPseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol 135: 1291–1303.
Nickel JC, AG Gristina and JW Costerton. 1989. Electron microscopic study of an infected Foley catheter. Can J Surg 28: 50–54.
Nickel JC, J Heaton, A Morales and JW Costerton. 1986. Bacterial biofilm in persistent penile prosthesis-associated infection. J Urol 135: 586–588.
Nickel JC, I Ruseska, JB Wright and JW Costerton. 1985. Tobramycin resistance ofPseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27:619–624.
Raad II, S Davis, A Khan, J Tarrand and GP Bodey. 1992. Catheter removal affects recurrence of catheter-related coagulase-negative staphylococci bacteremia (CRCNSB). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 13: 215–221.
Sadler J, S Dietrich, R Garcia and N Khardori. 1994. Effect of glucose oxidase on the adherence ofStaphylococcus epidermidis in anin vitro model of vascular catheter colonization. Abst #148, p 122, 94th Annu Meet Am Soc Microbiol 1994.
Schaberg DR, DH Culver and RP Gaynes. 1991. Major trends in the microbial etiology of nosocomial infection. Am J Med 91: 725–755.
Selan L, F Berlutti, C Passariello, MR Comodi-Ballanti and MC Thaller. 1993. Proteolytic enzymes: a new treatment strategy for prosthetic infections? Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37: 2618–2621.
Slack MPE and WW Nichols. 1982. Antibiotic penetration through bacterial capsules and exopolysaccharides. J Antimicrob Chemother 10: 368–372.
Stillman RI, RP Wenzel and LG Donowitz. 1987. Emergence of coagulase-negativestaphylococci as major nosocomial bloodstream pathogens. Am J Infect Control 8: 108–112.
Wang EEL, CG Prober, L Ford-Jones and R. Gold. 1984. The management of central intravenous catheter infections. Pediatr Infect Dis J 3: 110–113.
Widmer AF. 1992. IV-related infections. In: Prevention and Control of Nosocomial Infections (Wenzel R, ed), pp 556–579, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
Yasuda H, Y Ajiki, T Koga, H Kawada and T Yokota. 1993. Interaction between biofilms formed byPseudomonas aeruginosa and ciarithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37: 1749–1755.
Yasuda H, Y Ajiki T Koga and T Yokota. 1994. Interaction between clarithromycin and biofilms formed byStaphylococcus epidermidis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 38: 14–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khardori, N., Yassien, M. & Wilson, K. Tolerance ofStaphylococcus epidermidis grown from indwelling vascular catheters to antimicrobial agents. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 15, 148–151 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569818
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569818