Summary
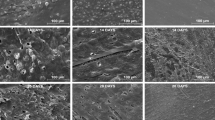
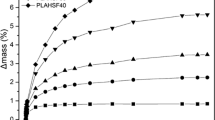
Blends of starch with polypropylene, starch with polyethylene, polycaprolactone with polyethylene, and a copolymer of β-hydroxybutyrate and β-hydroxyvalerate (PHB/V) were exposed to degrading leaves in a municipal leaf composting operation. Every month for 6 months, duplicate samples were analyzed for changes in weight and tensile properties, and many of these samples were further analyzed for changes in molecular weight and surface morphology. All results were compared to controls which were incubated for 6 months in moist, sterile leaves at a leaf compost temperature. Very little change was noted for any of the polyolefin blends over the 6-month period. In contrast, PHB/V samples showed massive deterioration with substantial weight loss. Although there was a decrease in molecular weight and a loss of tensile properties in leaf-exposed PHB/V films, the sterile control films also showed similar changes, but without weight loss. Of the microbial isolates from film surfaces, only fungi possessed PHB/V depolymerase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertsson, A.C., S.O. Anderson and S. Karlsson. 1987. The mechanism of biodegradation of polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 18: 73–87.
Austin, R. 1990. Degradation studies of polyolefins. In: Degradable Materials: Perspectives, Issues, and Opportunities. (Barenberg, S.A., J.L. Brash, R. Narayan, and A.E. Redpath, eds.), pp. 209–229, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Benedict, C.V., J.A. Cameron and S.J. Huang. 1983. Polycaprolactone degradation by mixed and pure cultures of bacteria and a yeast. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 28: 335–342.
Brandl, H., R.A. Gross, R.W. Lenz and R.C. Fuller. 1988.Pseudomonas oleovorans as a source of poly(beta-hydroxyalkkanoates) for potential applications as biodegradable plastics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 1977–1982.
Brandl, H., R.A. Gross, R.W. Lenz and R.C. Fuller. 1990. Plastics from bacteria and for bacteria: poly(beta-hydroxyalkanoates) as natural, biocompatible, and biodegradable polyesters. Adv. Biochem. Engineer. Biotechnol. 41: 77–94.
Delafield, F.P., M. Doudoroff, N.J. Palleroni, C.J. Lusty and R. Contopoulos. 1965. Decomposition of poly(beta-hydroxybutyrate) by pseudomonads. J. Bacteriol. 90: 1455–1466.
Reference deleted.
Doi, Y., Y. Kanesawa, M. Kunioka and T. Saito. 1990. Biodegradation of microbial copolyesters.: Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules 23: 26–31.
Gilmore, D.F., R.W. Lenz and R.C. Fuller. 1990. Biodegradation of poly(beta-hydroxyalkanoates). In: Degradable Materials: Perspectives Issues, and Opportunities. (Barenberg, S.A., J.L. Brash, R. Narayan and A.E. Redpath, eds.), pp. 481–507, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Glen, J. 1989. Degradables tested in compost programs. Biocycle 30: 28–32.
Holmes, P.A., K.R. Richardson, I.R. Hill and E.A. Drew. 1983. Biodegradability of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) films in soil. ICI technical publication, Billingham, UK.
Ianotti, G., N. Fair, M. Tempesta, H. Neibling, F.H. Hsieh and R. Mueller. 1990. Studies on the environmental degradation of starch-based plastics. In: Degradable Materials: Perspectives, Issues, and Opportunities. (Barenberg, S.A., J.L. Brash, R. Narayan, and A.E. Redpath, eds.), pp. 425–439, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Kenealy, W. and J.G. Zeikus. 1981. Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J. Bacteriol. 146: 133–140.
Kunioka, M., Y. Kawaguchi and Y. Doi. 1989. Production of biodegradable copolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 4-hydroxybutyrate byAlcaligenes eutrophus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30: 569–573.
Maddever, W.J. and P.D. Campbell. 1990. Modified starch based environmentally degradable plastics. In: Degradable Materials: Perspectives, Issues, and Opportunities. (Barenberg, S.A., J.L. Brash, R. Narayan and A.E. Redpath, eds.), pp. 237–255, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Miller, N.D. and D.F. Williams. 1987. On the biodegradation of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) homopolymer and poly-β-hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers. Biomaterials 8: 129–137.
Potts, J.E. 1978. Biodegradation. In: Aspects of degradation and stabilization of polymers. (Jellinek, H.H.G., ed.), pp. 617–658, Elsevier, New York.
Ramsay, B.A., J.A. Ramsay and D.G. Cooper. 1989. Production of poly-β-hydroxyalkanoic acid byPseudomonas cepacia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 584–589.
Sadun, A.G., T.F. Webster and B. Commoner. 1990. Breaking down the degradable plastics scam. a Greenpeace report. Center for the Biology of Natural Systems, Flushing, NY.
Windeatt, A.J. and J.R. Street. 1983. Assessment of the ultimate fate of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate under anaerobic conditions. ICI technical publication, Billingham, UK.
Wolin, E.A., M.J. Wolin and R.S. Wolfe. 1963. Formation of methane by bacterial extracts. J. Biol. Chem. 238: 2882–2886.
Wool, R.P., J.S. Penasky, J.M. Long and S.M. Coheen. 1990. Degradation mechanisms in polyethylene-starch blends. In: Degradable Materials: Perspectives, Issues, and Opportunities. (Barenberg, S.A., J.L. Brash, R. Narayan, and A.E. Redpath, eds.), pp. 515–537, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilmore, D.F., Antoun, S., Lenz, R.W. et al. The fate of ‘biodegradable’ plastics in municipal leaf compost. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 10, 199–206 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569767
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569767