Summary
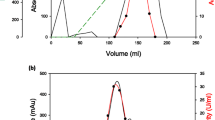
The fermentative production of amyloglucosidase (AMG) by differentAspergillus species simultaneously yields transglucosidase (TG), which is undersirable in the conversion of starch to dextrose, as it catalyses the reversion of dextrose and maltose to maltosaccharides, in turn providing disproportionately lower yields of dextrose (DX). To overcome this problem, using UV-irradiation, a novel mutant (ND-1-283) has been isolated fromAspergillus awamori, which has lost the ability to produce TG and which secretes 45% more AMG than its parent strain, giving the mutant a dual operational advantage. The inability of this mutant to produce TG was demonstrated by thin layer chromatography (TLC) of starch hydrolysate; this was substantiated by obtaining 96.0% DX (w/w) at the end of saccharification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alikhanian, S.I. 1962. Induced mutagenesis in the selection of microorganisms. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 4: 1–48.
Aunstrup, K. 1968. Improvements in or relating to the preparation of amyloglucosidase. Indian Patent No. 106059.
Barker, S.A. and J.G. Fleetwood. 1957. Studies onAspergillus niger. Part VIII. The purification of glucoamylase. J. Chem. Soc. Oct.-Dec.: 4857–4864.
Barton, L.L., C.E. Georgi and D.R. Lineback. 1972. Effect of maltose on glucoamylase formation byAspergillus niger. J. Bacteriol. 111: 771–777.
Bernfeld, P. 1955. Enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. Methods Enzymol. 1: 149–158.
Difco Manual of Dehydrated Culture Media and Reagents. 9th Edn. 1972. pp. 64–65, Difco Laboratories Inc., Detroit, MI, U.S.A.
Gutcho, S.J. 1974. Fungal enzymes. In: Microbial Enzyme Production. Chem. Tech. Review No. 28 (Gutcho, S.J., ed.), pp. 116–136, Noyes Data Corporation, New Jersey, London.
Helena Nevalainen, K.M. and E. Tapio Palva. 1979. Improvement of amyloglucosidase production ofAspergillus awamori by mutagenic treatments. J. Chem. Tech. Biotechnol. 29: 390–395.
MacDonald, K.D., J.M. Hutchinson and W.A. Gillet. 1963. Isolation of auxotrophs ofPenicillium chrysogenum and their penicillin yields. J. Gen. Microbiol. 33: 365–374.
Park, Y.K. and M.S.S. de Santi. 1977. Induction of high amyloglucosidase producing mutant fromAspergillus awamori. J. Ferment. Technol. 55: 193–195.
Pazur, J.H. and T. Ando. 1959. The action of an amyloglucosidase ofAspergillus niger on starch and malto-oligosaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 234: 1966–1970.
Redfern, S. 1947. Methods for determination of alpha amylase. IV A glass end point color standard for use in the dextrinizing method; effect of temperature and starch lot on this method. Cereal Chem. 24: 259–268.
Shah, D.N., V.D. Shah, P.N. Nehete and R.M. Kothari. 1986. Isolation ofBacillus licheniformis mutant for stable production profiles of alkaline protease. Biotechnol. Lett. 8: 103–106.
Smiley, K.L., M.C. Cadmus, D.E. Hensley and A.A. Lagoda. 1964. High potency amyloglucosidase producing mold ofAspergillus niger group. Appl. Microbiol. 12: 455.
Wing, R.E. and J.N. BeMiller. 1972. Quantitative thin-layer chromatography. Methods Carbohydr. Chem. VI: 42–53.
Wolf, A.V., M.G. Brown and P.G. Prentiss. 1978–79. Concentrative properties of aqueous solutions: Conversion tables. In: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 59th Edn. (Weast, R.C., ed.), p. D-277, CRC Press Inc., Florida.
Zajac, A. and M. Kujawski. 1979. The role of enzymes accompanying glucoamylase in the process of enzymatic saccharification of starch. Acta Alimen. Pol. V (XXIX): 207–215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, D.N., Shah, N.K. & Kothari, R.M. Isolation of a transglucosidase-nonproducing mutant ofAspergillus awamori yielding improved quality and production of amyloglucosidase preparations. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 2, 175–180 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569425
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01569425