Abstract
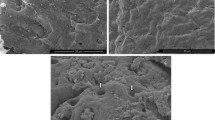
Intestinal damage caused by an enterotoxin from a coatless spore mutant ofClostridium perfringens type A (8-6) was identified by both light and scanning electron microscopy. Under the light microscope, damage to the epithelial layer of the villus and to the lamina propria was evident. Whole tissue viewed under the scanning electron microscope confirmed the two distinct forms of damage seen by light microscopy and showed that the action of the enterotoxin on an individual villus appears to occur in a specific sequence. The gross tissue damage observed contrasts with that found in previous studies of the action ofClostridium perfringens enterotoxin on rabbit ileal tissue; this suggests that the 8-6 enterotoxin may have a different mode of action on the cell, which subsequently leads to death and lysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bresson JL, Pang K, Udall J, Fritze J, Walker WA (1980) Evidence for increased enterotoxin binding to newborn microvillus membranes: a possible explanation for enhanced toxigenic diarrhea in infancy. Gastroenterology 78:1145
Genigeorgis G (1975) Public health importance ofClostridium perfringens. J Am Vet Med Assoc 167:821–827
Hennig SJ, Kretchmer N (1973) Development of intestinal function in mammals. Enzyme 15:3–23
Hobbs BC (1969)Clostridium perfringens andBacillus cereus infections. In: Rieman H (ed) Food borne infections and intoxications. New York: Academic Press, pp 131–173
Johnson LR (1981) Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. New York: Raven
Justus PG, Mathias JR, Martin JL, Carlson GM, Shields RP, Formal SB (1981) Myoelectric activity in the small intestine in response toClostridium perfringens A enterotoxin: correlation with histologic findings in an in vivo rabbit model. Gastroenterology 80:902–906
Lindsay JA, Sleigh RW, Ghitgas C, Davenport JB (1985) Purification and properties of an enterotoxin from a coatless spore mutant ofClostridium perfringens type A. Eur J Biochem 149:287–293
McClane BA, McDonel JL (1979) The effects ofClostridium perfringens enterotoxin on morphology, viability and macromolecular synthesis in vero cells. J Cell Physiol 99:191–200
McDonel JL (1979) The molecular mode of action ofClostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Am J Clin Nutr 32:210–218
McDonel JL (1980)Clostridium perfringens toxins (type A, B, C, D, E). Pharm Therm 10:617–655
McDonel JL (1980) Mechanisms of action ofClostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J Food Technol 34:91–95
McDonel JL, Chang LW, Pounds JG, Duncan CL (1978) The effect ofClostridium perfringens enterotoxin on rat and rabbit ileum. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest 39:210–218
McDonel JL, Duncan CL (1975) Histopathological effects ofClostridium perfringens enterotoxin on the rabbit ileum. Infect Immun 12:1214–1218
Merzel J, Leblond CP (1969) Origin and renewal of goblet cells in the epithelium of the mouse small intestine. Am J Anat 124:281–306
Norris HT, Majno G (1968) On the role of the ileal epithelium in the pathogenesis of experimental cholera. Am J Pathol 53:263–279
Ogra PL, Dayton DH (1979) Immunology of breast milk. New York: Raven
Ohishi I, Odargiri Y (1984) Histopathological effects of botulinum C2 toxin on mouse intestines. Infect Immun 43:54–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindsay, J.A., Dennison, J.D. Histopathological effect ofClostridium perfringens 8-6 enterotoxin on rabbit intestine. Current Microbiology 13, 61–66 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01568282
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01568282