Abstract
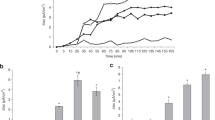
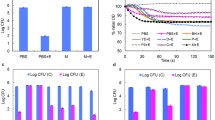
The basis for cytotoxicity to intact HeLa cells by culture filtrates ofClostridium difficile has been investigated. Decrease in intracellular K+ levels and inhibition of α-aminoisobutyric acid uptake were detected first after exposure to filtrates, followed by inhibition of macromolecular synthesis. Twenty-five percent of the K+ remained associated with the cell monolayer, and amino acid uptake and macromolecular synthesis were not totally abolished. These results indicate thatC. difficile culture filtrates preferentially inhibited membrane functions, either by exhausting ATP supplies or by disrupting the permeability barrier of the cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abrams, G. D., Allo, M., Rifkin, G. D., Fekety, R., Silva, J. 1980. Mucosal damage mediated by clostridial toxin in experimental clindamycin-associated colitis. Gut21:493–499.
Aswell, J. E., Ehrich, M., Van Tassell, R. L., Tsai, C.-C., Holdeman, L. V., Wilkins, T. D. 1979. Characterization and comparison ofClostridium difficile and other clostridial toxins, pp. 272–275. In: Schlessinger, D. (ed.), Microbiology-1979. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology.
Bartlett, J. G., Onderdonk, A. B., Cisneros, R. L., Kasper, D. L. 1977. Clindamycin-associated colitis due to a toxinproducing species ofClostridium in hamsters. Journal of Infectious Diseases136:701–705.
Brown, J. E., Rothman, S. W., Doctor, B. P. 1980. Inhibition of protein synthesis in intact HeLa cells byShigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Infection and Immunity29:98–107.
Chang, T.-W., Lauermann, M., Bartlett, J. G. 1979. Cytotoxicity assay in antibiotic-associated colitis. Journal of Infectious Diseases140:765–770.
Chang, T.-W., Lin, P.-S., Gorbach, S. L., Bartlett, J. G. 1979. Ultrastructural changes of cultured human amnion cells byClostridium difficile toxin. Infection and Immunity23:795–798.
Donta, S. T., Shaffer, S. J. 1980. Effects ofClostridium difficile toxin on tissue-cultured cells. Journal of Infectious Diseases141:218–222.
Hall, I. C., O'Toole, L. M. 1935. Intestinal flora in newborn infants with description of a new pathogenic anaerobe,Bacillus difficilis. American Journal of Diseases of Children49:390–402.
Humphrey, C. D., Condon, C. W., Cantey, J. R., Pittman, F. E. 1979. Partial purification of a toxin found in hamsters with antibiotic-associated colitis. Gastroenterology76:468–476.
Larson, H. E., Price, A. B. 1977. Pseudomembranous colitis: Presence of clostridial toxin. Lancetii:1312–1314.
Libby, J. M., Sullivan, N. M., Van Tassell, R. L., Wilkins, T. D. 1981. Relationship of two toxins ofClostridium difficile. Abstracts of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology1981:22.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry193:265–275.
Madsen, G. L., Knoop, F. C. 1981. Alteration of membrane permeability byClostridium difficile toxin. Abstract of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology1981:22.
Rifkin, G. D., Fekety, F. R., Silva, J. 1978. Neutralization byClostridium sordellii antitoxin of toxins implicated in clindamycin-induced cecitis in the hamster. Gastroenterology75:422–424.
Rifkin, G. D., Fekety, F. R., Silva, J., Sack, R. B. 1977. Antibiotic-induced colitis. Implication of a toxin neutralized byClostridium sordellii antitoxin. Lancetii:1103–1106.
Rothman, S. W. 1981. Presence ofClostridium difficile toxin in guinea pigs with penicillin-associated cohtis. Medical Microbiology and Immunology169:187–196.
Rothman, S. W., Brown, J. E., Gemski, M. J. 1980. Cytotoxicity ofClostridium difficile toxin in HeLa cells. Abstracts of the Annual Meeting of the American Society for Microbiology1980:28.
Taylor, N. S., Thorne, G. M., Bartlett, J. G. 1980. Separation of an enterotoxin from the cytotoxin ofClostridium difficile. AFCR Gastroenterology (Abstract)1980:285A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothman, S.W., Edward Brown, J. Inhibition of membrane functions in intact HeLa cells byClostridium difficile cytotoxic culture filtrates. Current Microbiology 6, 221–224 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566976
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566976