Abstract
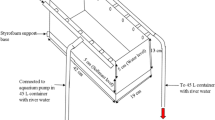
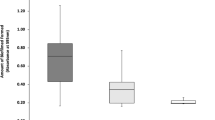
Coliphage T1 was more sensitive than its host bacterium,Escherichia coli B, to nickel (Ni). A 5-h exposure to 100 ppm Ni in nutrient broth did not adversely affect T1, whereas 10 and 20 ppm Ni extended the lag phase of growth ofE. coli B, and no growth occurred with 40 or more ppm Ni. 5 ppm Ni enhanced the survival (after 4 wk) of T1 in sea or simulated estuarine water but was toxic (i.e., reduced viral infectivity) in lake water; 50 ppm Ni was not toxic to T1 in sea water, was moderately toxic in estuarine water, but was highly toxic in lake water; and 100 ppm Ni was toxic in all systems, with the sequence of loss in viral infectivity being lake > estuarine > sea water. 100 ppm Ni was not toxic to T1 in nutrient broth, even after 3 wk of exposure, probably because of the protective effect of the organic compounds in the broth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Akin, E. W., Hill, F., Jr., Clarke, N. A. 1975. Mortality of enteric viruses in marine and other wastes, pp. 1–9. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Discharge of Sewage from Sea Outfalls. Elmsford, N.Y.: Pergamon Press.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1978. Toxicity of zinc to fungi, bacteria, and coliphages: influence of chloride ions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology36:904–913.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1979. Differential toxicities of mercury to bacteria and bacteriophages in sea and in lake water. Canadian Journal of Microbiology25:1252–1257.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1980. Environmental factors that influence the toxicity of heavy metals and gaseous pollutants to microorganisms. Critical Reviews in Microbiology8:99–145.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1980. Reductions in inactivation rates of bacteriophages by clay minerals in lake water. Water Research14:185–187.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G., 1981. Components of water hardness that reduce the toxicity of nickel to fungi. Microbios Letters18:17–24.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1982. Nickel toxicity to microbes: effect of pH and implications for acid rain. Environmental Research29:335–350.
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1982. Nickel toxicity to estuarine/marine fungi and its amelioration by magnesium in sea water. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution (in press).
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1983. Temperature, pH, salinity, hardness and particulates mediate nickel toxicity to eubacteria, an actinomycete, and yeasts in lake, simulated estuarine, and seawater. Aquatic Toxicology (in press).
Babich, H., Stotzky, G. 1983. Further studies on environmental factors that modify the toxicity of nickel to microbes. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology (in press).
Berry, S. A., Norton, B. G. 1977. Survival of bacteriophages in seawater. Water Research8:323–327.
Bitton, G., Mitchell, R. 1974. Effect of colloids on the survival of bacteriophages in seawater. Water Research8:227–229.
Blundell, M. R., Wild, D. G. 1969. Inhibition of bacterial growth by metal salts. Biochemical Journal115:207–211.
Corbett, T. H., Heidelberger, C., Dove, W. F. 1970. Determination of the mutagenic activity to bacteriophage T4 of carcinogenic and noncarcinogenic compounds. Molecular Pharmacology6:667–679.
Fishesjo, G. 1971. The effect of two mercury compounds on lysogenicE. coli K 39 (λ). Hereditas69:135–138.
Gonye, E. R., Jr., Jones, G. E. 1973. An ecological survey of open ocean and estuarine microbial populations. II. The oligodynamic effect of nickel on marine bacteria, pp. 243–257. In: Stevenson, H., Colwell, R. R. (eds.), Estuarine microbial ecology. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press.
Guha, C., Mookerjee, A. 1979. Effect of nickel on macromolecular synthesis inEscherichia coli K-12. Nucleus22:45–47.
Hermann, J. E., Kostenbader, K. D., Jr., Clive, D. O. 1974. Persistence of enteroviruses in lake water. Applied Microbiology28:895–896.
Kozloff, L. M. 1978. Properties of T4D bacteriophage grown in synthetic media containing Zn2+, Co2+, or Ni2+. Journal of Biological Chemistry253:1059–1064.
Kozloff, L. M., Lute, M., Henderson, K. 1957. Viral invasion. Rupture of thiol ester bonds in the bacteriophage tail. Journal of Biological Chemistry228:511–528.
Lo, S., Gilbert, J., Hetrick, F. 1976. Stability of enteroviruses in estuarine and marine waters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology32:245–249.
Mitchell, R., Jaanasch, H. W. 1969. Processes controlling virus inactivation in seawater. Environmental Science and Technology3:941–943.
Orgel, A., Orgel, L. E. 1965. Induction of mutations in bacteriophage T4 with divalent manganese. Journal of Molecular Biology14:453–457.
Puck, T. T., Garen, A., Cline, J. 1951. The mechanism of virus attachment to host cells. I. The role of ions in the primary reaction. Journal of Experimental Medicine93:65–88.
Schiffenbauer, M., Stotzky, G. 1982. Absorption of coliphages T1 and T7 to clay minerals. Applied and Environmental Microbiology43:590–596.
Stent, G. S. 1963. Molecular biology of bacterial viruses. San Francisco, California: W. H. Freeman and Co.
Tzagoloff, H., Pratt, D. 1964. The initial steps in infection with coliphage M13. Virology24:372–380.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babich, H., Schiffenbauer, M. & Stotzky, G. Sensitivity of coliphage T1 to nickel in fresh and salt waters. Current Microbiology 8, 101–105 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566966
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566966