Summary
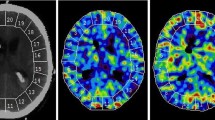
Changes in cerebral blood flow (CBF) after CT guided stereotactic aspiration of putaminal haematoma were investigated in 13 patients with Xe-133 inhalation and single photon emission computed tomography. The interval from onset to operation ranged from 13 to 82 days (mean 30 days). The mean estimated haematoma volume ranged from 20 to 50 ml (mean 31.9 ml). The percentage of haematoma aspirated ranged from 75 to 98% (mean 86.8%). Postoperative CBF in two thirds of the patients was improved even though all cases were operated on in the subacute stage. Both the mean hemispheric and regional CBF in the anterior territory of the middle cerebral artery and in the region of the thalamus and basal ganglia in the affected hemisphere were increased postoperatively. Also in the nonaffected hemisphere, regional CBF in the region of the thalamus and basal ganglia was improved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnoli A, Fieschi C, Prencipe M, Battistini N, Bozao L (1970) Relationships between regional hemodynamics in acute cerebrovascular lesions and clinico-pathological aspect. In: Meyer JS,et al (eds) Research on the cerebral circulation, Forth International Salzburg Conference. Ch C Thomas, Springfield, Ill., pp 148–154
Backlund E, von Holst H (1978) Controlled subtotal evacuation of intracerebral haematomas by stereotactic technique. Surg Neurol 9: 99–101
Baron JC (1981) Crossed cerebellar diaschisis: A remote functional depression secondary to supratentorial infarction of man. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1 [Suppl 1]: S 500-S 501
Broseta J, Gonzalez-Darder J, Barcia-Salorio JL (1982) Stereotactic evacuation of intracerebral hematomas. Appl Neurophysiol 45: 443–448
Celsis P, Goldman T, Henriksen L, Lassen NA (1981) A method for calculating regional cerebral blood flow from emission computed tomography of inert gas concentrations; Practical approach. J Comput Assist Tomogr 5: 641–645
DeLaPaz RL, Patromas NJ, Brooks RA, Smith BH, Kornblith PL, Milam H, DiChiro G (1983) A PET study of suppression of glucose utilization in cerebral gray matter associated with brain tumor. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 3 [Suppl 1]: 21–22
Doi E, Moriwaki H, Komai N, Iwamoto N (1982) Stereotactic evacuation of intracerebral hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 22: 461–467
Fieschi C, Agnoli A, Bozzao L, Battistini N, Prencipe M (1968) Derangement of regional cerebral blood flow and of its regulatory mechanisms in acute cerebrovascular lesions. Neurology (Minneap) 18: 1166–1179
Furuse M, Brock M, Hasuo M, Dietz H (1981) Relationship between brain tissue pressure gradients and cerebral blood flow distribution studied in circumscribed vasogenic oedema. Neurochirurgica 24: 10–14
Jaffe ME, McHenry LC Jr, Goldberg HI (1970) Regional cerebral blood flow measurement with small probes. II, Applications of the method. Neurology (Minneap) 20: 225–237
Hasuo M, Furuse K, Kuchiwaki H, Brock M, Dietz H (1980) An experimental study on correlation between intracranial pressure/volume curves and changes in cerebral blood flow. Brain and Nerve 32: 171–177
Ishii R, Takeuchi S, Ohsugi S, Tanaka R, Arai H (1982) Cerebral blood flow in patients with putaminal hemorrhage: Using Xe-133 inhalation method. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 22: 813–821
Kanaya H, Endo H, Sugiyama T, Kuroda K (1983) “Crossed cerebellar diaschisis” in patients with putaminal hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 3 [Suppl 1]: S 27-S 28
Kawakami H, Kutuzawa T, Uemura K, Sakurai Y (1974) Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 5: 207–212
Koslow M, Abele MG, Griffithe RC, Mair GA, Chase NE (1981) Stereotactic surgical system controlled by computed tomography. Neurosurgery 8: 72–82
Kuroda K (1982) Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage-Patients with putaminal hemorrhage treated surgically. Brain and Nerve 34: 561–569
Lassen NA, Henriksen L, Paulson O (1981) Regional cerebral blood flow in stroke patients by133Xe inhalation and emission tomography. Stroke 12: 284–288
Lenzi GL, Frackowiak RSJ, Jones T (1982) Cerebral oxygen metabolism and blood flow in human cerebral infarction. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 2: 321–335
Mathew NT, Meyer JS, Hartmann A (1973) Diagnosis and treatment of subarachnoid and intracerebral hemorrhage analyzed by regional cerebral blood flow measurements. In: Meyer JS,et al (eds) Cerebral vascular disease. G Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 176–183
Matsumoto K, Hondo H (1984) CT-guided stereotaxic evacuation of hypertensive intracerebral hematomas. J Neurosurg 61: 440–448
Mickey B, Vorstrup S, Voldby B, Lindewald H, Harmsen A, Lassen NA (1984) Serial measurement of regional cerebral blood flow in patients with SAH using133Xe inhalation and emission computed tomography. J Neurosurg 60: 916–922
Nagai H, Furuse M, Banno K, Ikeyama A, Maeda S, Kuchiwaki H (1972) Some adjustment mechanisms of brain metabolism during increased intracranial pressure. In: Brock M, Dietz H (eds) Intracranial pressure. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 75–78
Perry JE, Rosenbaum AE, Lunsford LD, Swink C, Zorub DS (1980) Computed tomography-guided stereotactic surgery. Conception and development of a new methodology. Neurosurgery 7: 376–381
Stokely EM, Sveinsdottir E, Lassen NA, Rommer P (1980) A single photon dynamic computer assisted tomograph (DCAT) for imaging brain function in multiple cross sections. J Comput Assist Tomogr 4: 230–240
Sugiyama H (1984) Cerebral blood flow in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage: With regard to difference in the mechanism of flow reduction between putaminal and thalamic hemorrhages. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 24: 564–572
Tanikawa T, Amano K, Kawamura H, Kawabatake H, Notani M, Iseki H, Shiwaku T, Nagano T, Iwata Y, Taira T, Umezawa Y, Shimizu T, Kitamura K (1985) CT-guided stereotactic surgery for evacuation of hypertensive intracerebral hematoma. In: Tasker RR, Turnbull IM, Gildenberg Phl, Franklin PO (eds) Proc 9th Meeting World Soc Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Toronto 1985. Appl Neurophysiol 48: 431–439
Tanizaki Y, Sugita K, Toriyama T, Hokama M (1985) New CT-guided stereotactic apparatus and clinical experience with intracerebral hematomas. In: Tasker RR, Turnbull IM, Gildenberg Phl, Franklin PO (eds) Proc 9th Meeting World Soc Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery, Toronto 1985. Appl Neurophysiol 48: 11–17
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanizaki, Y. Improvement of cerebral blood flow following stereotactic surgery in patients with putaminal haemorrhage. Acta neurochir 90, 103–110 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01560562
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01560562