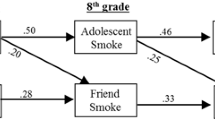
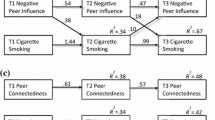
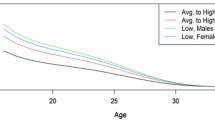
Abstract
A longitudinal sample of 3454 secondary school students in Wake County, North Carolina, was used to examine developmental changes in peer factors and their influence on marijuana initiation. Research hypotheses and questions focused on the issues of the relative influence of different types of peer factors, the causal order of peer attitudes and behaviors and respondents' behavior, and the influence of developmental changes on these relationships. Results showed that respondents perceived greater levels of use among students generally and adolescents in their neighborhoods than among their friends, but when friends' use was perceived, it was strongly related to respondents' own use. The causal order of these variables, however, was not necessarily friends influencing respondents but was probably reciprocal. Friends' drug-related behaviors, rather than attitudes, were more strongly related to respondents' likelihood of initiation. This relationship was strongest for the youngest respondents, those in the sixth grade. The strength of the relationship diminished as adolescents grew older.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, R. (1985). Social control theory and delinquency: A longitudinal test.Criminology 23: 47–61.
Akers, R. L. (1977).Deviant Behavior: A Social Learning Approach (2nd ed.). Wadsworth Publishing Co., Belmont, CA.
Akers, R. L., Krohn, M. D., Lanza-Kaduce, L., and Radosevich, M. (1979). Social learning and deviant behavior: A specific test of a general theory.Am. Sociol. Rev. 44: 636–655.
Brook, J. S., Lukoff, I. F., and Whiteman, M. (1977). Peer, family, and personality domains as related to adolescents' drug behavior.Psychol. Rep. 41: 1095–1102.
Brook, J. S., Whiteman, M., and Gordon, A. S. (1983). Stages of drug use in adolescence: Personality, peer, and family correlates.Dev. Psychol. 19: 269–277.
Burgess, R. L., and Akers, R. L. (1966). A differential association — reinforcement theory of criminal behavior.Social. Probl. 14: 128–147.
Burkett, S. R., and Warren, B. O. (1987). Religiosity, peer associations, and adolescent marijuana use: A panel study of underlying causal structures.Criminology 25: 109–131.
Elliott, D. S., Huizinga, D., and Ageton, S. S. (1985).Explaining Delinquency and Drug Use. Sage, Beverly Hills, CA.
Fisher, L. A., and Bauman, K. E. Influence and selection in the friend-adolescent relationship: Findings from studies of adolescent smoking and drinking. Unpublished manuscript.
Glynn, T. J. (ed.). (1983).Drug Abuse Prevention Research (Research Issues 33). National Institute on Drug Abuse, Washington, DC.
Hawkins, J. D., Lishner, D. M., and Catalano, R. F. (1985). Childhood predictors and the prevention of adolescent substance abuse. In Jones, C. L., and Battjes, R. J. (eds.),Etiology of Drug Abuse: Implications for Prevention. NIDA Research Monograph 56, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Washington, DC.
Hirschi, T., and Gottfredson, M. (1980). Introduction: The Sutherland tradition in criminology. In Hirschi, T., and Gottfredson, M. (eds.),Understanding Crime: Current Theory and Research. Sage, Beverly Hills, CA.
Huba, G. J., and Bentler, P. M. (1980). The role of peer and adult models for drug taking at different stages in adolescence.J. Youth Adolesc. 9: 449–465.
Johnson, R. E., Marcos, A. C., and Bahr, S. J. (1987). The role of peers in the complex etiology of adolescent drug use.Criminology 25: 323–339.
Kandel, D. B. (1974). Inter- and intragenerational influences on adolescent marijuana use.J. Social Issues 30: 107–135.
Kandel, D. B., Kessler, R. C., and Margulies, R. Z. (1978). Antecedents of adolescent initiation into stages of drug use: A developmental analysis.J. Youth Adolesc. 7: 13–40.
Kandel, D. B., and Yamaguchi, K. (1985). Developmental patterns of the use of legal, illegal, and medically prescribed psychotropic drugs from adolescence to young adulthood. In Jones, C. L., and Battjes, R. J. (eds.),Etiology of Drug Abuse: Implications for Prevention. NIDA Research Monograph 56; National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD.
Krohn, M. D., Skinner, W. F., Massey, J. L., and Akers, R. L. (1985). Social learning theory and adolescent cigarette smoking: A longitudinal study.Social Probl. 32: 455–471.
Krosnick, J. A., and Judd, C. M. (1982). Transitions in social influence at adolescence: Who induces cigarette smoking?Dev. Psychol. 18: 359–368.
Skinner, W. F., Massey, J. L., Krohn, M. D., and Lauer, R. M. (1985). Social influences and constraints on the initiation and cessation of adolescent tobacco use.J. Behav. Med. 8: 353–376.
Stafford, M. C., and Ekland-Olson, S. (1982). On social learning and deviant behavior: A reappraisal of the findings.Am. Social. Rev. 47: 167–169.
Sutherland, E. H. (1939).Principles of Criminology (3rd ed.). Lippincott, Philadelphia, PA.
Sutherland, E. H. (1947).Principles of Criminology (4th ed.). Lippincott, Philadelphia, PA.
Sutherland, E. H., and Cressey, D. (1978).Criminology (9th ed.). Lippincott, Philadelphia, PA.
Thornberry, T. P. (1987). Toward an interactional theory of delinquency.Criminology 25: 863–891.
White, H. R., Johnson, V., and Horwitz, A. (1986). An application of three deviance theories to adolescent substance use.Int. J. Addict. 21: 347–366.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by Grant Number DA 3971 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. We would like to thank Donna Albrecht and Terry Crotts for their help with analysis and manuscript preparation, and Chris Ringwalt and Richard Straw for their helpful editorial comments.
Received Ph.D. from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Current research interests are adolescent development and adolescent drug use.
Received Ph.D. from University of Michigan. Current research interests are drug use prevention and treatment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bailey, S.L., Hubbard, R.L. Developmental changes in peer factors and the influence on marijuana initiation among secondary school students. J Youth Adolescence 20, 339–360 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537401
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537401