Abstract
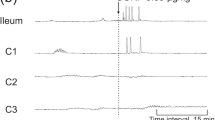
Modulation of ileal propulsive motility by different doses of neurotensin has been determined in detail. In conscious dogs neurotensin (2.5, 5, and 10 pmol/kg/min) was intravenously infused during the propulsive motor pattern induced by an acaloric viscous meal. Motor patterns were recorded by seven closely spaced strain gauge transducers and analyzed by a computerized method. Luminal transit was measured fluoroscopically. Neurotensin changed the propulsive motor pattern induced by the acaloric meal into a segmenting pattern. Effects were dose-dependent and most striking at a dose of 10 pmol/kg/min. The transit of luminal contents decreased from 20 to 8 cm/min. This was achieved by the increase in the number of stationary contractions (31 vs 55%), the reduction in the length of contraction spread (3.8 vs 1.8 cm), and the decrease in the number of contractions (11.5 vs 9.2 contractions/min). The contraction force was enhanced from 67 to 107 mN. Because of the marked effects on ileal motor patterns, neurotensin might be involved in the regulation of digestive motility in the distal small intestine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carraway R, Leemann SE: Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine and stomach. J Biol Chem 251:7045–7052, 1976
Brown DR, Miller RJ: Neurotensin. Br Med Bull 38:239–245, 1982
Buchan AMJ, Polak JM, Sullivan S, Bloom SR, Brown M, Pearse AGE. Neurotensin in the gut.In Gut Hormones. SR Bloom (ed). Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone, 1978, pp 544–549
Al-Saffar A, Rosell S: Effects of neurotensin and neurotensin analogues on the migrating myoelectrical complexes in the small intestine of rats. Acta Physiol Scand 112:203–208, 1981
Thor K, Rosell S, Rökaeus A, Kager L: (GLN4)-Neurotensin changes the motility pattern of the duodenum and proximal jejunum from a fasting-type to a fed-type. Gastroenterology 83:569–574, 1982
Blackburn AM, Bloom SR, Long RG, Fletcher DR, Christofides ND, Fitzpatrick ML, Baron JH: Effect of neurotensin on gastric function in man. Lancet 1:987–989, 1980
Hellström PM, Nylander G, Rosell S: Effects of neurotensin on the transit of gastrointestinal contents in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 115:239–243, 1982
Keinke O, Wulschke S, Ehrlein HJ: Neurotensin slow gastric emptying by a transient inhibition of gastric and a prolonged inhibition of duodenal motility. Digestion 34:281–288, 1986
Mashford ML, Nilsson G, Rökaeus A, Rosell S: The effect of food ingestion on circulating neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) in the human. Acta Physiol Scand 104: 244–246, 1978
Rosell S, Rökaeus A: The effect of ingestion of amino acids, glucose and fat on circulating neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) in man. Acta Physiol Scand 107:263–267, 1979
Schemann M, Ehrlein HJ: Effects of neurohormonal agents on jejunal contraction spread and transit in the fed dog. Gastroenterology 90:1950–1955, 1986
Thor PJ, Konturek JW, Sendur R, Konturek SJ: Comparison of neurotensin and fat on myoelectric activity pattern of the small bowel.In Gastrointestinal Motility. C Roman (ed). Lancaster, MTP Press, 1984, pp 343–348
Siegle ML, Ehrlein HJ: Interdigestive contractile patterns of the ileum in dogs. Am J Physiol 253:G452-G460, 1987
Siegle ML, Ehrlein HJ: Digestive motor patterns and transit of luminal contents in the canine ileum. Am J Physiol 254: G552-G559, 1988
Schemann M, Ehrlein HJ: Mechanical characteristics of phase II and phase III of the interdigestive migrating motor complex in dogs. Gastroenterology 91:117–123, 1986
Schemann M, Ehrlein HJ: Postprandial patterns of canine jejunal motility and transit of luminal content. Gastroenterology 90:991–1000, 1986
Wulschke S, Ehrlein HJ, Tsiamitas C: The control mechanisms of gastric emptying are not overridden by motor stimulants. Am J Physiol 251:G744-G751, 1986
Schemann M, Siegle ML, Sahyoun H, Ehrlein HJ: Computer analysis of intestinal motility: Effects of cholecystokinin and neurotensin on jejunal contraction patterns. Z Gastroenterol 24:262–268, 1986
Shaw C, Buchanan KD: Intact neurotensin (NT) in human plasma: Response to oral feeding. Regul Pept 7:145–153, 1983
Wood JD: Intrinsic neural control of intestinal motility. Annu Rev Physiol 43:33–51, 1981
Sakai Y, Daniel EE, Jury J, Fox JET: Neurotensin inhibition of canine intestinal motilityin vivo via α-adrenoceptors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 62:403–411, 1984
Williams JT, Katayama Y, North RA: The action of neurotensin on single myenteric neurones. Eur J Pharmacol 59:181–186, 1979
Bueno L, Fioramonti J, Fargeas MJ, Primi MP: Neurotensin: A central neuromodulator of gastrointestinal motility in dogs. Am J Physiol 248:G15-G19, 1985
Hellström PM: Vagotomy inhibits the effect of neurotensin of gastrointestinal transit in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 128:47–55, 1986
Fox JET, McLean J, Daniel EE, Sakai Y, Jury J: Neurotensin, evidence for multiple receptors for gastrointestinal motility action in dogs. Gastroenterology 82:1060, 1982
Huidobro-Toro JP, Zhu YX: Neurotensin receptors on the ileum of the guinea-pig: Evidence for the coexistence of inhibitory and excitatory receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 102:237–250, 1984
Wood JD: Physiology of the enteric nervous system.In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract, Vol 1, LR Johnson (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1987, pp 67
Siegle ML: Die interdigestive und digestive Motorik des Ileums beim Hund sowie die Wirkung verschiedener Hormone und Pharmaka auf die digestive Motorik. Dissertation, University of Hohenheim, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Grant Eh 64/4-2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siegle, ML., Ehrlein, HJ. Neurotensin changes the motor pattern in canine ileum from propulsive to segmenting. Digest Dis Sci 34, 1521–1527 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537104
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537104