Abstract
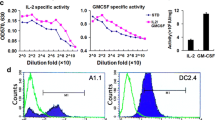
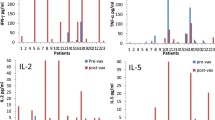
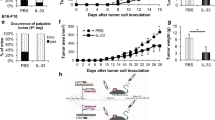
Immune cytokines are important regulators of the immune response to neoplastic cells. We previously reported that interleukin 4 (IL-4) and either tumor necrosis factor α (TNF) or interferon γ (IFN) synergistically inhibit melanoma cell growth and induce cell differentiation. In the present study we used various combinations of IL-4, IFN and TNF to enhance the antigenicity of melanoma cells. IL-4 plus TNF significantly increased the ability of melanoma cells to stimulate cytotoxic T cells (CTL) and act as targets of these CTL; IL-4 plus IFN was somewhat less effective, while TNF plus IFN was not as effective. IL-4 plus TNF also increased the expression of HLA class I and HLA-DR antigens on melanoma cells. The CTL lines examined in this study were CD3+CD4+ and oligoclonal. These preclinical results suggest that the immune response to melanoma whole-cell vaccines might be enhanced by pretreating vaccine cells with IL-4 plus TNF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertini MR, Nicklas JA, Chastenay BF, Hunter TC, Albertini JR, Clark SS, Hank JA, Sondel PM (1991) Analysis of T cell receptor β and gamma genes from peripheral blood, regional lymph node and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte clones from melanoma patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 32: 325
Anichini A, Mazzocchi A, Fossati G, Parmiani G (1989) Cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones from peripheral blood and from tumor site detect intratumor heterogeneity of melanoma cells. Analysis of specificity and mechanisms of interaction. J Immunol 142: 3692
Belldegrun A, Tso CL, Sakata T, Kim A, Chen C, Ditonno P, deKernien JP, Figlin R (1991) Characterization of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) primed in vivo with interferon-alpha as part of a combined immunotherapy protocol for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 32: 251
Bjorkman PJ, Saper MA, Samraoui B, Bennett WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1987) The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature 329: 512
De Bueger M, Bakker A, Goulmy E (1992) Existence of mature human CD4+ T cells with genuine class I restriction. Eur J Immunol 22: 875
Eisenback L, Segal S, Feldman M (1983) MHC imbalance and metastatic spread in Lewis lung carcinoma clones. Int J Cancer 32: 113
Essner R, Rhoades K, McBride WH, Morton DL, Economou J (1989) IL-4 down-regulates IL-1 and TNF gene expression in human monocytes. J Immunol 142: 3857
Gross N, Beck D, Favre S, Carrel S (1987) In vitro antigenic modulation of human neuroblastoma cells induced by IFN-gamma, retinoic acid and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Int J Cancer 39: 521
Hayashi Y, Hoon DSB, Park MS, Terasaki PI, Foshag LJ, Morton DL (1992) Induction of CD4+ cytotoxic T cells by sensitization with allogeneic melanomas bearing shared or cross-reactive HLA-A. Cell Immunol 139: 411
Hellstrom KE, Hellstrom I, Morton DL, Hoon DBS, Gupa RK, Nizze AJ, Foshag LJ, Irie RF, Bystryn JC, Wallack MK, Bash JA, Hu S-L, Kahn M, Ferrone S (1991) Melanoma cell vaccine. In: Cutaneous melanoma, Lippincott, Philadelphia, p 542
Herlyn M, Guerry D, Koprowski H (1985) Recombinant gamma-interferon induces changes in expression and shedding of antigens associated with normal human melanocytes, nevus cells, and primary and metastatic melanoma cells. J Immunol 134: 4226
Hoon DSB, Foshag LJ, Nizze AJ, Bohman R, Morton DL (1990) Suppressor cell activity in a randomized trial of patients receiving active specific immunotherapy with melanoma cell vaccine and low dosages of cyclophosphamide. Cancer Res 50: 5358
Hoon DSB, Banez M, Okun E, Morton DL, Irie RF (1991) Modulation of human melanoma cells by interleukin-4 and in combination with gamma-interferon or α-tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res 51: 2002
Hoon DSB, Okun E, Banez M, Irie RF, Morton DL (1991) Interleukin 4 alone and in combination with gamma-interferon or α-tumor necrosis factor on human renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res 51: 5687
Houghton AN, Thomson TM, Gross D, Oettgen HF, Old L (1984) Surface antigens of melanoma and melanocytes: specificity and induction of Ia antigens by human-gamma interferon. J Exp Med 160: 255
Idzerda RL, March CJ, Mosley B, Lyman SD, Vanden Bos T, Gimpel SD, Din WS, Grabstein WS, Widmar KH, Park MB, Cosman LS, Beckmann MP (1990) Human interleukin-4 receptor confers biological responsiveness and defines a novel superfamily. J Exp Med 171: 861
Itoh K, Platsoucas C, Balch C (1988) Autologous tumor-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes in the infiltrate of human metastatic melanoma: activation by interleukin-2 and autologous tumor cells, and involvement of the T cell receptor. J Exp Med 168: 1419
Lewis GD, Aggarwal BB, Eessalu TE, Sugarman BJ, Shepard HM (1987) Modulation of the growth of transformed cells by human tumor necrosis factor-α and gamma-interferon. Cancer Res 47: 5382
Maio M, Gulwani B, Morgano A, Ferrone S (1989) Differential modulation by tumor necrosis factor and immune interferon of HLA class-II antigens expressed by melanoma cells. Int J Cancer 44: 554
Morton DL, Foshag LJ, Hoon D, Nizze JA, Famatiga E, Wanek LA, Chang C, Davtyan DG, Gupta RK, Irie RF (1992) Prolongation of long-term survival in advanced stage metastatic melanoma following active specific immunotherapy with a new polyvalent melanoma vaccine. Ann Surg 216: 463
Paliard X, Waal Malefijit R de, Yssel H, Blanchard D, Chreti en I, Abrams J, De Vries JE de, Spits H (1988) Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4 and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol 141: 849
Paul WE, Ohara J (1987) B-cell stimulatory factor/interleukin 4. Annu Rev Immunol 5: 429
Ramani P, Balkwill FR (1988) Human interferons inhibit experimental metastases of a human melanoma cell line in nude mice. Br J Cancer 58: 350
Rozschke O, Falk K (1991) Naturally-occurring peptide antigens derived from the MHC class-1-restricted processing pathway. Immunol Today 12: 447
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, 2nd edn, vol 1. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schwatzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Mancini M, Rosenberg SA (1991) Specific release of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor, tumor necrosis factor and IFN-gamma by human tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes after tumor stimulation. J Immunol 146: 3764
Sigal RK, Lieberman MD, Reynolds JV, Williams N, Ziegler MM, Daly JM (1990) Tumor immunization. Improved results after vaccine modified with recombinant interferon gamma. Arch Surg 125: 308
Stötter H, Wiebke EA, Tomita S, Belldegrun A, Topalian S, Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT (1989) Cytokines alter target cell susceptibility to lysis. II. Evaluation of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. J Immunol 142: 1767
Strassman G, Bach FH (1984) OKT4+ cytotoxic T cells can lyse targets via class 1 molecules and can be blocked by monoclonal antibodies against T molecules. J Immunol 133: 1705
Tanaka K, Isselbacher KJ, Khoury G, Jay G (1985) Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science 228: 26
Te Velde AA, Klomp JPE, Yard BA, De Vries JE, Figdor CG (1988) Modulation of phenotypic and functional properties of human peripheral blood monocytes by IL-4. J Immunol 140: 1548
Uchiyama A, Morisaki T, Torisu M (1991) Evidence that induction and regulation of lymphokine-activated (LAK) activity are mediated by changes in tumour-binding potential of lymphocytes after activation by interleukin-2 (IL-2). Immunology 74: 1
Vanky F, Wang P, Patarroyo M, Klein E (1990) Expression of the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 and major histocompatibility complex with autologous lymphocytes in vitro. Cancer Immunol Immunother 31: 19
Webb DS, Mostowski HS, Gerrard TL (1991) Cytokine-induced enhancement of ICAM-1 expression results in increased vulnerability of tumor cells to monocyte-mediated lysis. J Immunol 146: 3682
Yanagi Y, Yoshikai Y, Leggett K, Clark S, Alexander I, Mak T (1984) A human T-cell-specific cDNA clone encodes a protein having extensive homology to immunoglobulin chains. Nature 308: 145
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by grant CA 12582 from the National Cancer Institute, DHHS, and by the Joseph Drown Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoon, D.S.B., Hayashi, Y., Morisaki, T. et al. Interleukin-4 plus tumor necrosis factor α augments the antigenicity of melanoma cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 37, 378–384 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01526794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01526794