Abstract
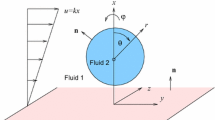
The effects of diffusion out of and into drops undergoing equatorial collision in laminar shear flow were studied. With an electric field perpendicular to the direction of flow, diffusion into undeformed drops enhanced coalescence, while diffusion from the drops inhibited it.
With marked outward diffusion, drops having a collision angle greater than 83° assumed a stable alignment in opposition to the velocity gradient for several minutes and then rotated to become a permanent head-on collision doublet. With inward diffusion the separation of drop centers increased along the paths of approach and the apparent angle of collision decreased. The phenomena were explained qualitatively on the basis of surface flow arising from concentration gradients at the drop surfaces.
Stable multiplets were formed on collision of highly deformed drops as a result of hydrodynamic forces both with and without diffusion.
Zusammenfassung
Die Wirkung der Diffusion aus den Tropfen heraus und in die Tropfen hinein auf ihr Verhalten bei äquatorialer Kollision in laminarer Scherströmung wurde untersucht. Bei Anlegen eines elektrischen Feldes senkrecht zur Fließrichtung verstärkt die Diffusion in undeformierte Tropfen die Koaleszenz, während Diffusion aus den Tropfen heraus sie verhindert.
Bei beträchtlicher Auswärtsdiffusion nehmen Tropfen, deren Kollisionswinkel größer als 83° ist, eine stabile Anordnung entgegen den Geschwindigkeitsgradienten für einige Minuten an und rotieren dann als ein dauerhaftes Dublett. Bei Einwärtsdiffusion wird der Abstand der Tropfenzentren längs der Wege der Annäherung erhöht und der scheinbare Kollisionswinkel vermindert. Das Phänomen läßt sich qualitativ auf der Basis einer Oberflächenströmung verursacht durch Konzentrationsgradienten an der Tropfenoberfläche, erklären.
Stabile Multipletts werden bei Kollision hochdeformierter Tropfen auf Grund hydrodynamischer Kräfte sowohl mit Einwärtsals auch Auswärtsdiffusion gebildet.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a, b :
-
diameter and radius of drop
- B :
-
breadth of ellipsoid
- c :
-
radius of circle of contact for touching liquid drops
- C A :
-
acetone concentration at pointA
- C :
-
spherical elliptical orbit constant
- D :
-
drop deformation=L − B/L + B
- Eo :
-
electric field strength (directed alongY-axis)
- f (Φc):
-
fraction of doublets coalescing before Φc
- F h, F:
-
hydrodynamic and total force
- G :
-
velocity gradient
- h :
-
minimum separation of two spheres
- L :
-
length of ellipsoid
- p η1/η2 :
-
viscosity ratio
- r e :
-
equivalent ellipsoidal axis ratio
- R 1, R2 :
-
radii of inner and outerCouette cylinders
- Δs :
-
linear separation of drop centers
- t :
-
time
- u, v, w :
-
velocity components alongX-, Y-, andZ-axis of shear field
- x,y,z :
-
coordinates forCouette flow
- Δx, Δy, Δz :
-
distance between two particle centers measured along coordinate axis
- β:
-
constant in equation for hydrodynamic force
- γ :
-
interfacial tension
- η 1,η2 :
-
viscosities of Phase 1 (drop) and Phase 2 (medium)
- Θ 0, Φ:
-
colatitudinal and aximuthal spherical polar coordinates(Z=polar axis)
- Θ, Φ 0 :
-
spherical polar coordinates of initial point of contact in collision of spheres (7)
- Θ0′', Φ0′:
-
spherical polar coordinates of point of separation of collision doublet of spheres
- τ :
-
rest time
- \(\bar \tau \) :
-
algebraic mean rest time
- Φ c :
-
coalescence angle
- Φ m :
-
orientation of major axis of deformed drop in shear field
- Φ r, Φr′:
-
rectilinear angles of collision and separation (7)
References
MacKay, G. D. M. andS. G. Mason (J. Colloid Sci.18, 674 (1963).
Bartok, W. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.12, 243 (1957).
Bartok, W. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.14, 13 (1959).
Jeffery, G. B., Proc. Roy. Soc. (London) A102, 161 (1922).
Taylor, G. I., Proc. Roy. Soc. (London) A146, 238 (1934).
Rumscheidt, F. D. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.16, 238 (1961).
Allan, R. S. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.17, 383 (1962).
Manley, R. St. J. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.7, 354 (1952).
Mooney, M., J. Colloid Sci.12, 575 (1957).
Charles, G. E. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.15, 236 (1960).
Bartok, W. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.13, 293 (1958).
MacKay, G. D. M. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.16, 632 (1961).
Rumscheidt, F. D. andS. G. Mason, J. Colloid Sci.16, 210 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacKay, G.D.M., Mason, S.G. Particle motions in sheared suspensions. Kolloid-Z.u.Z.Polymere 195, 138–148 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01503662
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01503662