Summary
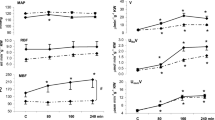
In 16 normal subjects, in 29 patients with essential hypertension and in 25 patients with renal hypertension plasma renin activity was measured together with pulse rate and blood pressure under resting conditions and 15 minutes after the intravenous administration of 5 mg d-l-propranolol subsequently.
Basal plasma renin activity (PRA) was correlated significantly to resting pulse rate in normal subjects and in patients with benign essential hypertension but not in patients with renal hypertension from chronic parenchymatous renal disease. In the normal subjects and in the patients with essential hypertension the decrease of not stimulated “basal” PRA 15 minutes after the administration of 5 mg d-l- propranolol was closely related to the initial plasma renin activity. In contrast, in the patients with well established renal hypertension the decrease of PRA was generally less pronounced or absent.
Whereas in normal subjects as well as in patients with essential hypertension the sympathetic nervous system appears to be the major determinant for basal renin release, other factors, possibly the renal baroreceptors, may determine basal renin release in renal hypertension.
This difference could possibly provide the basis for a simple biochemical test to differentiate between essential and renal hypertension.
Zusammenfassung
Bei 16 Gesunden, 29 Patienten mit benigner essentieller und 25 Patienten mit renaler Hypertonie im Rahmen chronisch parenchymatöser Nierenerkrankungen wurde die Plasmareninaktivität (PRA) nach längerer Bettruhe und anschließend 15 min nach der intravenösen Verabreichung von 5 mg d-l-Propranolol gleichzeitig mit Pulsfrequenz und Blutdruck gemessen.
Die basale PRA war bei Normalpersonen und bei Patienten mit essentieller Hypertonie, nicht aber bei Patienten mit renaler Hypertonie signifikant mit dem Ruhepuls korreliert. Während bei Gesunden und bei Patienten mit essentieller Hypertonie nach Propranolol ein deutlicher Abfall der PRA bis zu 47% gemessen wurde, dessen Ausmaß signifikant mit der basalen PRA korreliert war, zeigten Patienten mit renaler Hypertonie generell ein geringeres oder fehlendes Absinken der PRA auf Propranolol.
Die erhobenen Befunde sprechen dafür, daß bei Patienten mit essentieller Hypertonie wie bei Gesunden die nicht stimulierte „basale“ Plasmareninaktivität in erster Linie durch den Tonus des sympathischen Nervensystems bestimmt ist. Im Gegensatz dazu scheinen bei Patienten mit renaler Hypertonie andere Faktoren, eventuell die renalen Barorezeptoren, für die Aufrechterhaltung der Reninsekretion verantwortlich.
Dieser Unterschied könnte in Zukunft die Differenzierung zwischen essentieller und renaler Hypertonie auf Grund eines einfachen biochemischen Testes erlauben.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Boyd, G.W., Adamson, A.R., Fitz, A.E., Peart, W.S.: Radioimmunoassay determination of plasma-renin activity. Lancet i, 213 (1969)
Bravo, E.L., Tarazi, R.C., Dustan, H.P.: On the mechanism of suppressed plasma-renin activity during β-adrenergic blockade with propranolol. J. Lab. Clin. Med.83, 119 (1974)
Michelakis, A.M., Mc Allister, R.G.: The effect of chronic adrenergic receptor blockade on plasma renin activity in man. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab.34, 386 (1972)
Noth, R.H., Mulrow, P.J.: Serum dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity (DBH): an index of sympathetic activity. 3rd Meeting of the International Society of Hypertension, Milan, 1974
Skrabal, F., Czaykowska, W.: Half-life of plasma renin activity in normal subjects and in malignant hypertension. Klin. Wschr.52, 1173 (1974)
Sullivan, J.M., Adams, D.F., Hollenberg, N.K.: Betablockade in essential hypertension: reduced renin release despite renal vasoconstriction and reduced cardiac output. Clin. Res.21, 453 (1973)
Werner, U., Günnewig, H., Bock, K.D.: Relationship between plasma renin activity and urinary and plasma catecholamines. 3rd International Meeting of the International Society of Hypertension. Milan, 1974
Winner, N., Chokshi, S., Yoon, M.S., Freedman, A.D.: Adrenergic receptor mediation of renin secretion. J. Clin. Endocr.29, 1168 (1969)
Zimmermann, H.-D.: Persönliche Mitteilung.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Unterstützt vom Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, Österreich.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skrabal, F. Unterschiedliches Verhalten der Plasmareninaktivität nach Propranolol bei essentieller und renaler Hypertonie. Klin Wochenschr 53, 629–632 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01469683
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01469683