Summary
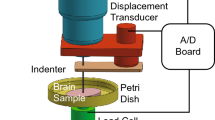
We studied the mechanical properties of the brain in anaesthetized rabbits by application of a standard external load to the exposed cerebral surface. The experimental model used allows one to eliminate potential circulatory factors. Brain oedema was produced by repeated episodes of ischaemia secondary to a decrease of the arterial blood pressure to zero. The development of brain oedema was assessed by an increase of the cerebral water content. In the course brain oedema development brain fluidity was found to steadily rise, while the brain compliance and the index of hysteresis decreased from the control value found at the onset of the experiment. Most important both, brain compliance and the index of hysteresis were already markedly elevated prior to the manifestation of brain oedema.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guyton AC, Granger HJ, Taylor AE (1971) Interstitial fluid pressure. Physiol Rev 51: 527–563
Haddy FJ, Scott JB, Grega GJ (1976) Peripheral circulation: Fluid transfer across the microvascular membrane. In: Guyton AC, Cowley AW (eds) International review of physiology. Cardiovascular physiology. Univ Park Press, Baltimore, pp 63–109
Itkis ML, Mchedlishvili GI (1979) Method ofin vivo studies of brain mechanical properties. Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov. Riga 6: 1084–1099
Marmarou A, Takagi H, Shulman K (1980) Biomechanics of brain edema and effect of local cerebral blood flow. In: Cervos-Navarra J, Ferszt R (eds). Raven Press, New York, pp 345–359
Mchedlishvili GI, Itkis ML, Sikharulidze NV (1981) Effect of circulatory factors on the mechanical properties of the brain. Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov. Riga 5: 878–882
Mchedlishvili GI, Itkis ML, Sikharulidze NV (1982) Mechanical properties of the brain during development of postischemic oedema. Voprosy Neirokhirurgii, Moscow 4: 17–20
Mchedlishvili GI, Mossakowski MI, Itkis ML, Sikharulidze NV, Januszewski S (1980) Changes in mechanical properties of brain tissue as factor of brain edema development. Neuropat Pol 18: 543–554
Mchedlishvili GI, Nikolaishvili LS, Itkis ML (1979) Pathophysiological mechanisms of brain edema development. Role of tissue factors. Stroke 10: 52–57
Voronin VV (1947) Handbook of pathological physiology, vol 1 Gruzmedgiz, Tbilisi
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mchedlishvili, G., Itkis, M. & Sikharulidze, N. Mechanical properties of brain tissue related to oedema development in rabbits. Acta neurochir 96, 137–140 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01456173
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01456173