Abstract
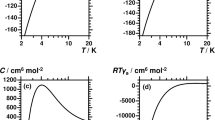
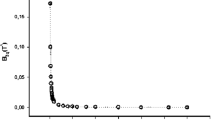
We describe methods by which all of the observable thermodynamic properties of a compressed gas, including the compressibility factor and the isochoric heat capacity, may be determined from sound speed data by numerical integration of a pair of partial differential equations. The technique may be employed over a wide range of conditions. Initial values are required. but we demonstrate that values specified on an isotherm close to the critical temperature are sufficient for application of the method to the entire homogeneous fluid region at subcritical densities. The method may also be extended to higher densities at temperatures above the critical. The effects of errors in both the initial values and the speed of sound are examined in detail by means of analytic and numerical results. The results indicate that all of the observable thermodynamic properties may be obtained with an uncertainty equal to or less than that achievable by the best available alternative techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
U. Setzmann and W. Wagner,J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 20;1061 (1991).
J. P. M. Trusler and M. P. Zarari,J. Chem. Thermodyn. 24;973 (1992).
R. B. Stewart and R. T. Jacobsen,J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 18;639 (1949).
M. P. Zarari, Ph.D. thesis (University of London, London, 1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Estrada-Alexanders, A.F., Trusler, J.P.M. & Zarari, M.P. Determination of thermodynamic properties from the speed of sound. Int J Thermophys 16, 663–673 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01438851
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01438851