Summary
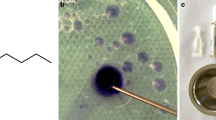
Vaporization of atheromas in 10 human aorta segments immersed under flowing blood in vitro were done using the EFF probe. No increase in packed cells of the flowing blood following atheroma vaporization were noted suggesting absence of post vaporization debris. No damage to the aorta underlying the vaporized atheroma was noted on light microscopy suggesting well localized vaporization process. This study suggests that EFF probe might be a safe tool for intravascular endarterectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boddie AW, Yamanashi WS, Frazer JW,et al (1983) Field-focusing and focal heating patterns in solid phantoms using a hybrid radio frequency systems of novel design. Med Instrum 17: 358–364
Gerrity RG, Loop FD, Golding LA, Ehrhart LA, Argenyi ZB (1983) Arterial response to laser operation for removal of atherosclerotic plaques. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 85 (3): 409–421
Geschwind HJ, Boussignac G, Teisseire B, Benhaiem N, Bittoun R, Laurent D (1984) Conditions for effective Nd-YAG laser angioplasty. Br Heart J 52 (5): 484–489
Guy AW, Webb MD, McDougall JA (1976) Critical comparison of RF field delivery method to thermal response of models and experimental animals. USAF/SAM Contract F41609-75-C-0021. Final Report
Lee G, Ikeda RM, Stobbe D, Ogata C, Theis J, Hussein H, Mason DT (1983) Laser irradiation of human atherosclerotic obstructive disease; simultaneous visualization and vaporization achieved by a dual fiberoptic catheter. Am Heart J 105 (1): 163–164
Lee G, Ikeda RM, Chan MC, Lee MH, Rink JL, Reis RL, Theis JH, Low R, Bommer WJ, Kung AH,et al (1985) Limitations, risks and complications of laser recanalization: a cautious approach warranted. Am J Cardiol 56 (1): 181–185
Patil AA, Yamanashi WS, Valentine JL, Hill D, Woosley RE, Filip OF (1986) Electromagnetic field focusing (EFF) probe in aneurysm thrombosis-Preliminary report. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 81: 72–76
Patil AA, Yamanashi WS, Valentine JL, Hill D, Filip OF (1987) Electromagnetic Field Focusing (EFF) probe—A new neurosurgical tool. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 86: 106–110
Yamanashi WS, Boddie AW, Frazer JW,et al (1984) Further observations on tissue heating patterns using an invasive ground probe with radio frequency hyperthermia system. Med Instrum 18: 200–223
Yamanashi WS, Fesen MR, Andersen DW,et al (1984) Focused hyperthermia with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) unit and an interstitial grounded probe. Physiol Chem Phys Med NMR 16: 491–498
Yamanashi WS, Fesen MR, Anderson DW,et al (1985) Fieldfocusing hyperthermia and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with a ground probe and a commercial MRI scanner. Med Instrum 19: 217–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, A., Yamanashi, W., Hill, D. et al. Electromagnetic Field Focusing (EFF) probe for intravascular endarterectomy. Preliminary feasibility study. Acta neurochir 91, 130–133 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01424568
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01424568