Summary
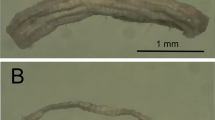
The efficacy of myosin (M)-ATPase fibre typing to differentiate fibre types in chemically (EGTA) skinned muscle fibres was investigated. Cryosections or single fibres from isolated bundles of chemically skinned rat extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and soleus (SOL) muscles were stained for M-ATPase activity. The results indicate that two major fibre types (type I and II, Brooke & Kaiser, 1970) can be indentified, as well as subgrouping of the type II fibres into types IIa and IIb. Thus, chemically skinning muscle fibres appears to have no detrimental effects on subsequent M-ATPase fibre typing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooke, M. H. &Kaiser, K. K. (1970) Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind.Archs Neurol. 23, 369–79.
Cummins, P. &Perry, S. V. (1973) The subunits and biological activity of polymorphic forms of tropomyosin.Biochem. J. 133, 765–77.
Cummins, P. &Perry, S. V. (1974) Chemical and immunochemical characteristics of tropomyosins from striated and smooth muscle.Biochem. J. 141, 43–9.
Donaldson, S. K. (1981) Single skinned skeletal fibre Ca2+ and H+ sensitivites: comparison of the various histochemical types.Biophys. J. 33, 57a.
Dubowitz, V. &Brooke, M. H. (1973) Histological and histochemical stains and reactions. InMuscle Biopsy: A Modern Approach, pp. 20–33. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders.
Eddinger, T. J., Moss, R. L. & Cassens, R. G. (1985) Fiber number and type composition in EDL, SOL and diaphragm muscles with aging in Fisher 344 rats.J. Histochem. Cytochem..In press.
Guilian, G. G., Moss, R. L. &Greaser, M. (1983) Improved methodology for analysis and quantitation of proteins on one-dimensional silver-stained slab gels.Analyt. Biochem. 129, 277–87.
Head, J. F. &Perry, S. V. (1974) The interaction of the calcium-binding protein (Troponin C) with bivalent cations and the inhibitory protein (Troponin I).Biochem. J. 137, 145–54.
Head, J. F., Weeks, S. R. &Perry, S. V. (1977) Affinity-chromatographic isolation and some properties of troponin C from different muscle types.Biochem. J. 161, 465–71.
Lowry, S. &Risby, D. (1971) Light chains from fast and slow muscle myosins.Nature, Lond. 234, 81–5.
Moss, R. L., Giulian, G. G. &Greaser, M. L. (1982) Physiological effects accompanying the removal of myosin LC2 from skinned skeletal muscle fibres.J. biol. Chem. 257, 8588–91.
Moss, R. L., Swinford, A. E. &Greaser, M. L. (1983) Alterations in the Ca2+ sensitivity of tension development by single skeletal muscle fibres at stretched lengths.Biophys. J. 43, 115–9.
Padykula, H. A. &Herman, E. (1955) Factors affecting the activity of adenosine triphosphatase and other phosphatases as measured by histochemical techniques.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 3, 161–83.
Suzuki, A. (1976) The pH stability of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase of five types in skeletal muscles of the sheep and cattle.Jap. J. Zootech. Sci. 47, 95–103.
Suzuki, A. &Cassens, R. G. (1980) pH sensitivity of myosin adenosine triphosphatase and subtypes of myofibres in porcine muscle.Histochem. J. 12, 687–93.
Van Eerd, J. P. &Takahashi, K. (1975) The amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac Troponin-C: comparison with rabbit skeletal Troponin-C.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 64, 122–7.
Weeds, A. G., Hall, R. &Spurway, N. C. S. (1975) Characterization of myosin light chains from histochemically identified fibres of rabbit psoas muscle.FEBS Lett. 49, 320–4.
Wilkinson, J. M. (1978) The components of troponin from chicken fast skeletal muscle.Biochem. J. 169, 229–38.
Zeman, R. L. &Wood, D. S. (1980) Correlative histochemical and physiological measurements in single skinned muscle fibres: heterogeneity of Ca sensitivity in type I fibres.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 28, 714–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eddinger, T.J., Moss, R.L. & Cassens, R.G. Myosin-ATPase fibre typing of chemically skinned muscle fibres. Histochem J 17, 1021–1026 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01417950
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01417950