Abstract
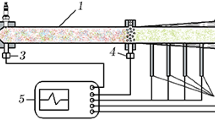
The cloud of products formed following the detonation of lead azide (LA) contains gaseous species and solid particles. The dynamics of the detonation products expanding freely or through a supersonic nozzle into vacuum is unraveled via the temporal profiles of the pressure, the emission from Pb atoms and the attenuation of a He-Ne beam. The velocity of the fastest gaseous species is found from the onset of the pressure rise and the emission at a given distance from the LA sample, and the velocity of the fastest solid particles from the attenuation. In the free expansion, the respective velocities are 4.5±0.1 and 3.8±0.2 km/s and in the nozzle expansion 5.1±0.2 and 1.4±0.2 km/s. The expansion into atmospheric pressure air is also monitored and found to be much slower than that into vacuum. The utilization of nozzles as a means for obtaining a particle free, transparent medium of detonation products is stressed in the context of exploiting explosives for achieving chemical lasers in the visible wavelength region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar I, Cohen A, Heflinger D, Tzuk Y, Rosenwaks S (1991) Preferential excitation and enhanced emission of Pb atoms following detonation of lead azide. Appl Phys Lett 58:322
Grisch F, Péalat M, Bouchardy P, Taran JP, Bar I, Heflinger D, Rosenwaks S (1991) Real time diagnostics of detonation products from lead azide using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering. Appl Phys Lett 59:3516
Heflinger D, Bar I, Ben-Porat T, Erez G, Rosenwaks S (1993) Dynamics of the detonation products of lead azide. II. Formation of charged particles. J Appl Phys 73:2178
Miron G, Bar I, Heflinger D, Tzuk Y, Rosenwaks S (1989) Multiple charge reaction cell for studies of primary explosives. Rev Sci Instrum 60:132
Tzuk Y, Bar I, Ben-Porat T, Rosenwaks S (1992) Dynamics of the detonation products of lead azide. I. Hydrodynamics. J Appl Phys 71:4693
Tzuk Y, Bar I, Rosenwaks S (1993a) Dynamics of the detonation products of lead aside. IV. Laser shadowgraphy of expanding species. J Appl Phys 74:5360
Tzuk Y, Barmashenko BD, Bar I, Rosenwaks S (1993b) Dynamics of the detonation products of lead azide. III. Laser induced hole burning and flow visualization. J Appl Phys 74:45
Zel'dovich YaB, Raizer YuP (1966) Physics of shock waves and high temperature hydrodynamic phenomena. Academic Press, New York, pp 93–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article was processed using Springer-Verlag TEX Shock Waves macro package 1.0 and the AMS fonts, developed by the American Mathematical Society.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzuk, Y., Bar, I. & Rosenwaks, S. Expansion of the detonation products of lead azide via a supersonic nozzle. Shock Waves 4, 11–14 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414627
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414627