Summary
In this study the effect of CO2 laser on spinal epidural fibrosis was examined in 24 guinea pigs which were divided into two groups. The first group was the control group, the second one the CO2 laser group.
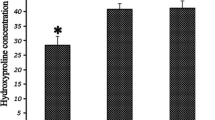
All animals had laminectomies at 3 levels. Re-exploration was performed three months after the laminectomy. In the second group the same procedure was performed but at the end of the re-exploration, CO2 laser irradiation of the epidural fibrotic tissue was done. The wounds in both groups were closed again. Four months later all animals were sacrificed, for verification and quantification of scar formation (postoperative fibrosis) light microscopic examinations and determination of hydroxyproline were done, using Bergman's spectrophotometric method. The differences which were observed between the two groups were statistically significant (U ∶ 134, p < 0.05).
This study demonstrates the reducing effect of CO2 laser irradiation on epidural scar formation. The findings encourage its use as an alternative method of prevention of epidural fibrosis after spinal surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AÇikgöz B, Turgut M, Ozean OE, Özgen T, Demirhan B, Ruacan S (1992) Delay of cranial bone regeneration by CO2 and Nd:YAG laser application: an experimental study related to craniosynostosis. Lasers Med Sci 7: 49–53
Ascher PW (1977) Der CO2 Laser in der Neurochirurgie. Molden, Wien
Beck OJ (1984) Use of the Nd:YAG laser in neurosurgery. Nerosurg Rev 7: 151–158
Beck OJ, Wilske J, Schonberger JL, Gorish W (1979) Tissue changes following application of laser to the rabbit brain. Neurosurg Rev 1: 31–36
Bergman I, Loxley R (1963) Two improved and simplified methods for the spectrophotometric determination of hydroxyproline. Anal Chem 35: 1961–1965
Boggan JE, Powers SK (1992) Use of lasers in neurological surgery. In: Youmans JR (ed) Neurological surgery, Vol 2. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 992–1004
Branch CL, Branch CL Jr (1990) Operative management of failed back syndrome. In: Youmans JR (ed) Neurological surgery. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 2731–2748
Burton CV (1985) The failed back. In: Wilkins RH, Rengechary SS (eds) Neurosurgery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 2290–2292
Burton CV, Kirkaldy-Willis WH, Young-Hing K, Heithoft KB (1981) Causes of failure of surgery on the lumbar spine. Clin Orthop 157: 191–195
Cerullo LJ (1985) Application of the laser to neurological surgery. In: Wilkins RH, Rengechary SS (eds) Neurosurgery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 478–483
Edwards MSB, Boggan JE, Fuller TA (1983) The laser in neurological surgery. J Neurosurg 59: 555–566
Gamache FW, Morgello S (1987) The histopathological effects of the CO2 versus the KTP laser on the brain and spinal cord: a canine model
Heppner F, Ascher PW (1982) The CO2 laser in neurosurgery. Int Adv Surg Oncol 5: 385–396
Jacobs RR, McClain O, Neff S (1980) Control of postlaminectomy scar formation — an experimental and clinical study. Spine 5: 223–229
Meyers AD, Denver MBA (1990) Lasers and wound healing. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116: 1128
Powers SK, Aden JT, Edwards MSB, Boggan JE, Hosobuchi Y (1984) Pain relief from dorsal root entry zone lesions made with argon and carbon dioxide microsurgical lasers. J Neurosurg 61: 841–847
Rivlin AS, Tator CH (1977) Objective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurosurg 47: 577–581
Tew JM, Tobler WD (1986) Present status of lasers in neurosurgery. In: Symon Let al (eds) Advances and technical standards in neurosurgery, Vol 13. Springer, Wien New York, pp 3–36
Walter GF, Ascher PW, Ingolitsch E (1984) The effects of carbon dioxide and neodymium-YAG laser on the central and peripheral nervous systems, and cerebral blood vessels. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47: 745–749
Wilkinson HA (1983) The failed back syndrome. Etiology and therapy. Harper and Row, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colak, A., Bavbek, M., Aydin, N.E. et al. Effect of CO2 laser on spinal epidural fibrosis. Acta neurochir 138, 162–166 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01411355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01411355