Summary
Somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs) were recorded by stimulating the median nerve at the wrist from the skin and epidural space of the 7th cervical spine in patients suffering from cervical radiculopathy or radiculomyelopathy. The patients were divided into four subgroups according to the severity of the disease. Skin and epidural SEPs were calculated and compared with each other and with control values.
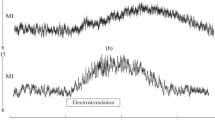
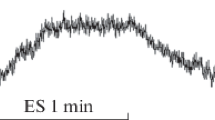
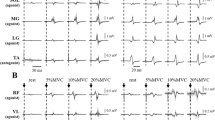
Usually only one negative potential N13 was identified in the skin recording, but two potentials N11 and N13 occurred in the epidural recording. Lower amplitudes were obtained from the skin than from the epidural space. In the skin SEPs the mean of the central latency of N13 was significantly prolonged in the severe radiculomyelopathy groups, while the mean of the amplitude N13 showed only a tendency to decrease. In contrast, in the epidural SEPs a significant decrease in the mean of the N11 and N13 amplitudes together with a significant prolongation in the mean of the central latency of N13 could be found. In the epidural recording the amplitude changes in particular increased with the severity of the disease, but the highest number of abnormalities (61%) could be seen in the central latency of N13.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anziska, B. J., Cracco, R. Q., Short latency SEPs to median nerve stimulation: comparison of recording methods and origin of components. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.52 (1981), 531–539.
Caccia, M. R., Ubiali, E., Andreussi, L., Spinal evoked responses recorded from the epidural space in normal and diseased humans. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.39 (1976), 962–972.
Cohen, A. R., Young, W., Ransohoff, J., Intraspinal localization of the somatosensory evoked potential. Neurosurg.9 (1981), 157–162.
Eisen, A., Hoirch, M., Electrodiagnostic evaluation of radiculopathies and plexopathies using somatosensory evoked potentials. Kyoto Symposia. EEG Suppl.36 (1982), 349–357.
El Negamy, E., Sedgwick, E. M., Delayed cervical somatosensory potentials in cervical spondylosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.42 (1979), 238–241.
Emerson, R. G., Pedley, T. A., Generator sources of median somatosensory evoked potentials. J. Clin. Neurophysiol.1 (1984), 203–218.
Ertekin, C., Comparison of the human evoked electrospinogram recorded from the intrathecal, epidural and cutaneous levels. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.44 (1978), 683–690.
Ganes, T., Somatosensory conduction times and peripheral, cervical and cortical evoked potentials in patients with cervical spondylosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.43 (1980), 683–689.
Ganes, T., A study of peripheral, cervical and cortical evoked potentials and afferent conduction times in the somatosensory pathway. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.49 (1980), 446–451.
Hattori, S., Saiki, K., Kawai, S., Diagnosis of the level and severity of cord lesion in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine4 (1979), 478–485.
Jones, S. J., Short latency potentials recorded from the neck and scalp following median nerve stimulation in man. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.43 (1977), 853–863.
Matsukado, Y., Yoshida, M., Goya, T., Shimoji, K., Classification of cervical spondylosis or disc protrusion by preoperative evoked spinal electrogram. J. Neurosurg.44 (1976), 435–441.
Sherwood, A. M., Characteristics of somatosensory evoked potentials recorded over the spinal cord and brain of man. Trans. Biomed.28 (1981), 481–87.
Siivola, J., Sulg, I., Heiskari, M., Somatosensory evoked potentials in diagnostics of cervical spondylosis and herniated disc. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.52 (1981), 276–282.
Spielholz, N. I., Benjamin, M. V., Engler, G. L., Ransohoff, J., Somatosensory evoked potentials during decompression and stabilization of the spine. Spine4 (1979), 500–505.
Stockard, J. J., Iragui, V. J., Clinically useful applications of evoked potentials in adult neurology. J. Clin. Neurophysiol.1 (1984), 159–202.
Stöhr, M., Buettner, U. W., Riffel, B., Koletzki, E., Spinal somatosensory evoked potentials in cervical cord lesions. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.54 (1982), 257–265.
Sulg, I., Heiskari, M., Nyström, S. H. M., Evoked somatosensory responses from cervical roots: a comparison of responses from depth and surface electrodes. IRCS Med. Sci.9 (1981), 707–708.
Tackmann, W., Radü, E. W., Observations on the application of electrophysiological methods in the diagnosis of cervical root compressions. Eur. Neurol.22 (1983), 397–404.
Yamada, T., Kimura, J., Wilkinson, T., Kayamori, R., Short- and long-latency median somatosensory evoked potentials. Arch. Neurol.40 (1983), 215–220.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heiskari, M., Tolonen, U. & Nyström, S.H.M. Comparison of somatosensory evoked responses from root and cord recorded by skin and epidural electrodes using stimulation of the median nerve in cervical radiculopathy and radiculomyelopathy. Acta neurochir 79, 114–119 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01407454
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01407454