Summary
In adult cats experimental brain tumours were produced by stereotactical xenotransplantation of the rat glioma clone F 98 into the internal capsule of the left hemisphere. Two to four weeks after transplantation tumours and peritumoural oedema were investigated by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electrophysiological recording and analysis of tissue content of water, electrolytes and extravasated serum proteins.
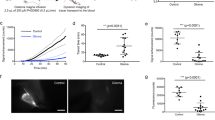
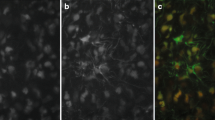
Spherical tumours with a diameter of about 10 mm developed at the injection site and were surrounded by massive white matter oedema. Water content in peritumoural white matter increased from 2.63 ± 0.17 to 3.65 ± 0.19 ml/g d.w. (means ± SD), sodium from 187±11 to 351±55 μeq/g d.w. and calcium from 7.4±1.1 to 13.3 ± 1.3 ± 1.3 μeq/g d.w. Potassium and magnesium did not change. Oedema development was associated with the extravasation of 18.0 ± 16.8mg/g d.w. albumin and 15.8 ± 12.2 mg/g d.w. immunoglobulin. The calculated electrolyte content of oedema fluid approximated that of plasma but the serum protein content was about 40% lower. The ratio of low (albumin) to high (immunoglobulin) molecular weight proteins was the same in blood and oedema fluid. It is, therefore, concluded that peritumoural oedema consist of two components,a whole plasma extravasate and a protein-free ultra-filtrate.
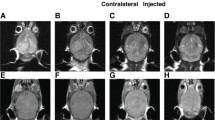
Peritumoural oedema could be clearly detected by MRI but differentiation between tumour and oedema was only possible after contrast enhancement with gadolinium-DTPA. The ratios of the intensities of the MR signal correlated linearly with the water content within white matter. MRI, in consequence, allows quantification of oedema provided a reference area with normal water content is present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borle AB (1981) Control, modulation and regulation of cell calcium. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 90: 13–153
Bothe H-W, Bodsch W, Hossmann K-A (1984) Relationship between specific gravity, water content, and serum protein extravasation in various types of vasogenic brain edema. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 64: 37–42
Carr DH, Gadian DG (1985) Contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Radiol 36: 561–568
Clasen RA, Bekorovainy A, Pandolfi S (1982) Protein and electrolyte changes in experimental cerebral edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 41: 113–128
Ebhardt G, van den Kerckhoff W, Matsuoka Y, Hossmann K-A (1982) Morphologische Befunde bei experimentell erzeugten Gliomen in Katzen. Neurochirurgia 25: 177–185
Elliott KAG, Jasper HH (1949) Measurement of experimentally induced brain swelling and shrinkage. Am J Physiol 157: 122–129
Gadian DG, Payne JA, Bryant DJ, Young IR, Carr DH, Bydder GM (1985) Gadolinium-DTPA as a contrast agent in MR imaging-theoretical projections and practical observations. J Cornput Assist Tomogr 9: 242–251
Gastaut JL, Michel B, Hassan SS, Cerda M, Bianchi L, Gastaut H (1979) Electroencephalography in brain edema (127 cases of brain tumor investigated by cranial computerized tomography). Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 46: 239–255
Gazendam J, Go KG, van Zanten AK (1979) Composition of isolated edema fluid in cold-induced brain edema. J Neurosurg 51: 70–77
Gloor P, Ball G, Schaul N (1977) Brain lesions that produce delta waves in the EEG. Neurology (Minneap) 27: 326–333
Go KG, van der Veen PH, Ebels EJ, van Woundenberg F (1972) A study of electrical impedance of oedematous cerebral tissue during operations. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 27: 113–124
Gotman J, Skuce DR, Thompson CJ, Gloor P, Ives JR, Ray WF (1973) Clinical applications of spectral analysis and extraction of features from electroencephalograms with slow waves in adult patients. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 35: 225–235
Harris RJ, Symon L, Branston NM, Bayhan M (1981) Changes in extracellular calcium activity in cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 1: 203–209
Hoiby N, Axelsen NH (1983) Crossed immunoelectrophoresis as modified for quantitative purpose. Scand J Immunol 17: 125–134
Hossmann K-A, Wechsler W, Wilmes F (1979) Experimental peritumorous edema. Morphological and pathophysiological observations. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 45: 195–203
Hossmann K-A, Hürter T, Oschlies U (1983) The effect of dexamethasone on serum protein extravasation and edema development in experimental brain tumors of cat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 60: 223–231
Hossmann K-A, Mies G, Paschen W, Szabo L, Dolan E, Wechsler W (1986) Regional metabolism of experimental brain tumors. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 69: 139–147
Klatzo I (1967) Neuropathological aspects of brain edema. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 26: 1–14
Klatzo I, Wisniewski H, Steinwall O, Streicher E (1967) Dynamics of cold injury edema. In: Klatzo I, Seitelberger F (eds) Brain edema. Springer, New York, pp 554–563
Linn F, Seo K, Hossmann K-A (1989) Experimental transplantation gliomas in the adult cat brain. 3. Regional biochemistry Acta Neurochir (Wien) (in press)
Matsuoka Y, Hossmann K-A (1981) Corticosteroid therapy of experimental tumour oedema. Neurosurg Rev 4: 185–190
Mennel HD (1978) Transplantation of tumors of the nervous system induced by resorptive carcinogens. I. Histological investigation of intracerebrally transplanted tumors of the central nervous system. Neurosurg Rev 1: 123–131
Mills CM, Crooks LE, Kaufman L, Brant-Zawadzki M (1984) Cerebral abnormalities: Use of calculated T 1 and T 2 magnetic resonance images for diagnosis. Radiology 150: 87–94
Neuwelt EA (1984) Therapeutic potential for blood-brain barrier modification in malignant brain tumor. Prog Exp Tumor Res 28: 51–66
Nicholson C, Bruggencate GT, Steinberg R, Stoeckle H (1977) Calcium modulation in brain extracellular microenvironment demonstrated with ion-selective micropipette. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 1287–1290
Reulen HJ, Graham R, Spatz M, Klatzo I (1977) Role of pressure gradients and bulk flow in dynamics of vasogenic brain edema. J Neurosurg 46: 24–35
Wechsler W, Szymas J, Bilzer T, Hossmann K-A (1989) Experimental transplantation gliomas in the adult cat brain. 1. Experimental model and neuropathology. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 98: 77–89
Wilmes F, Hossmann K-A (1979) A specific immunofluorescence technique for the demonstration of vasogenic brain edema in paraffin embedded material. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 45: 47–51
Zülch KJ (1986) Brain tumors. Their biology and pathology (3rd ed). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hossmann, K.A., Szymas, J., Seo, K. et al. Experimental transplantation gliomas in the adult cat brain. Acta neurochir 98, 189–200 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01407347
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01407347