Conclusions
The wear of alumina-graphite immersion nozzles is greatly affected by the amount and type of fluxes in the composition of the slag-forming protective mixtures. In terms of the increasing corrosion capacity, fluxes are arranged as follows: calcium chloride, fluorspar, cryolite, sodium nitrate. With a content of more than 6–8% fluxes, the degree of wear sharply increases.
With a rise in the fabrication pressure and hence a reduction in the porosity, the resistance of the refractories increases.
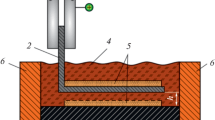
In the contact zone for slag and refractory, penetration of slag into the refractory occurs, as well as oxidation of the carbon by active oxidizing agents (FeO, MnO), and the formation of fusible eutectics. The solution rate of refractory in slag melt increases with a change from a fixed specimen to a rotating one.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. D. Mel'nikov et al., Zavod. Lab., No. 11, 1365–1367 (1978).
G. A. Sokolov, Out-of-Furance Refining of Steel [in Russian], Moscow (1977).
A. V. Leites et al., Stal', No. 5, 371–372 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Ogneupory, No. 9, pp. 35–38, September, 1981.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ermolaeva, E.I., Manyugin, A.P., Kukartsev, V.M. et al. Reaction of slag coating on the metal surface in a crystallizer with submerged nozzles. Refractories 22, 473–476 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406883
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406883