Summary
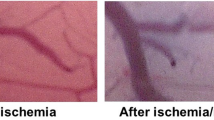
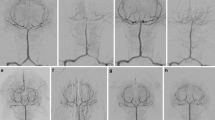
Specific antagonists to the influx of calcium, necessary for the excitation-contraction coupling process in arterial smooth muscle, are potentially useful in the treatment of cerebral vasospasm but systemic hypotension might limit their clinical applicability. We studied the effect of the calcium antagonist nimodipine (BAY e 9736) on cerebral arterial spasm, intraventricular pressure and blood pressure (BP), when administered into the cerebral ventricles of the dog. Cerebral vasospasm was produced by the injection of autologous blood into the cisterna magna. In a group of 8 dogs, 100 μg of nimodipine was injected into the lateral ventricle. The effect of the drug on the basilar artery was monitored angiographically. Nimodipine always relieved spasm, and often the relaxation surpassed the resting vessel diameter. In a control group, the injection of placebo did not relax the spastic arteries. Determinations using gas chromatography of nimodipine in CSF and blood demonstrated that a concentration of 1 μg/ml in cisternal CSF was sufficient to reduce spasm while concomitant plasma concentrations of 0.004 μg/ml did not result in significant BP reduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, G. S., Gold, L. A., Chou, S. N., French, L. A., Cerebral arterial spasm. Part 3: In vivo intracisternal production of spasm by serotonin and blood and its reversal by phenoxybenzamine. J. Neurosurg.40 (1974), 451–458.
Allen, G. S., Banghart, S. B., Cerebral arterial spasm. Part 9: In vitro effects of nifedipine on serotonin, phenylephrine and potassium induced contractions of canine basilar and femoral arteries. Neurosurgery4 (1979), 37–42.
Allen, G. S., Bahr, A. L., Cerebral arterial spasm. Part 10: Reversal of acute and chronic spasm in dogs with orally administered nifedipine. Neurosurgery4 (1979), 43–47.
Auer, L. M., Pial arterial vasodilation by intravenous nimodipine in cats. Drug Research31 (1981), 1423–1425.
Auer, L. M., Cerebrovascular activity of the Ca-antagonist nimodipine. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.2 (1982), 268 (abstract).
Bohr, D. F., Vascular smooth muscle updated. Circ. Res.32 (1973), 665–672.
Boullin, D. J., Adams, C. B. T., Mohan, J., Green, A. R., Hunt, T. M., du Boulay, G. H., Rogers, A. T., Effect of intracranial dopamine perfusion: Behavioural arousal and reversal of cerebral arterial spasm following surgery for clipping of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. Proc. roy. Soc. Med.70 (suppl. 2) (1977), 55–70.
Brandt, L., Andersson, K.-E., Bengtsson, B., Edvinsson, L., Ljunggren, B., MacKenzie, E. T., Effects of nifedipine on pial arteriolar calibre: An in vivo study. Surg. Neurol.12 (1979), 349–352.
Brandt, L., Andersson, K.-E., Edvinsson, L., Ljunggren, B., Effects of extracellular calcium and calcium antagonists on contractile responses of human pial and mesenteric arteries. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.1 (1981), 339–347.
Cohen, R. J., Allen, G. S., Cerebral arterial spasm: The role of calcium in in vitro and in vivo analysis of treatment with nifedipine and nimodipine. In: Cerebral Arterial Spasm (Wilkins, R. H., ed.), pp. 527–532. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins. 1981.
Ebner, F., Dünschede, H. B., Haemodynamics, therapeutic mechanism of action and clinical findings of Adalate use based on worldwide clinical trials. In: 3rd International Adalate Symposium (Jatena, A. D., Lichtlen, P. R., eds.), pp. 283–300. Amsterdam-Oxford: Excerpta Medica. 1976.
Fleckenstein, H., Specific pharmacology of calcium in myocardium, cardiac pacemakers, and vascular smooth muscle. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.17 (1977), 149–166.
Grubb, R. L., Jr., Raichle, M. E., Eichung, J. O., Gado, M. H., Effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage on cerebral blood volume, blood flow, and oxygen utilization in humans. J. Neurosurg.46 (1977), 446–453.
Harper, A. M., Craigen, L., Kazda, S., Effect of the calcium antagonist, nimodipine, on cerebral blood flow and metabolism in the primate. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.1 (1981), 349–356.
Jakobsen, P., Pedersen, O. L., Mikkelsen, E., Gas Chromatographic determination of nifedipine and one of its metabolites using electron capture detection. J. Chromatography162 (1979), 81–87.
Kazda, S., Hoffmeister, F., Garthoff, B., Towart, R., Prevention of the postischaemic impaired reperfusion of the brain by nimodipine (BAY e 9736). In: Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism (Gotoh, F., Nagai, H., Tazaki, Y., eds.), pp. 302–302. Copenhagen: Munksgaard. 1979.
Kuwayama, A., Zervas, N. T., Belson, R., Shintani, A., Pickren, K., A model for experimental cerebral arterial spasm. Stroke3 (1972), 49–56.
Martins, A. N., Newby, N., Doyle, T. F., Kobrine, A. I., Effect of intracisternal phentolamine on cerebral blood flow after subarachnoid injection of blood. J. Neurosurg.44 (1976), 353–358.
Sahlin, C., Brismar, J., Delgado, T., Owman, C., Salford, L. G., Svendgaard, N. Aa., The effect of a Ca-transport inhibitor on CBF and CMRO2 in late cerebral arterial spasm in baboons. Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Meeting of the Scandinavian Neurosurgical Society, Linköping, Sept. (1980), 3–6.
Symon, L., Harris, R. J., Branston, N. M., Calcium ions and calcium antagonists in ischemia. Acta Neurochir. (Wien)63 (1982), 267–275.
Takagi, T., Kamiya, K., Fukuoka, H., Mabe, H., Nagai, H., Effect of Ca antagonists on experimental cerebral vasospasm. In: Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism (Gotoh, F., Nagai, H., Tazaki, Y., eds.), pp. 486–487. Copenhagen: Munksgaard. 1979.
Tanaka, K., Gotoh, F., Muramatsu, F., Fukuuchi, Y., Amano, T., Okayasu, H., Suzuki, N., Effects of Nimodipine (BAY e 9736) on cerebral circulation in cats. Drug Research30 (1980), 1494–1497.
Towart, R., Kazda, S., The cellular mechanism of action of nimodipine (BAY e 9736), a new calcium antagonist. Brit. J. Pharmacol.67 (1979), 409–410.
Towart, R., Perzborn, E., Nimodipine inhibits carbocyclic thromboxane-induced contractions of cerebral arteries. Europ. J. Pharmacol.69 (1981), 213–215.
Voldby, B., Enevoldsen, E. M., Jensen, F. T., The pathophysiological effects of severe cerebral vasospasm following aneurysm rupture. Acta Neurochir. (Wien)56 (1981), 134–135 (abstract).
Voldby, B., Enevoldsen, E. M., Intracranial pressure changes following aneurysm rupture. Part 1: Clinical and angiographic correlations. J. Neurosurg.56 (1982), 186–196.
White, R. P., Huang, S. P., Hagen, A. I., Robertson, J. T., Experimental assessment of phenoxybenzamine in cerebral vasospasm. J. Neurosurg.50 (1979), 158–163.
White, R. P., Cunningham, M. P., Robertson, J. T., Effect of the calcium antagonist nimodipine on contractile responses of isolated canine basilar arteries induced by serotonin, prostaglandin F2a, thrombin, and whole blood. Neurosurgery10 (1982), 344–348.
Wilkins, R. H., Attempted prevention or treatment of intracranial arterial spasm: A survey. In: Cerebral Arterial Spasm (Wilkins, R. H., ed.), pp. 542–555. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins. 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voldby, B., Petersen, O.F., Buhl, M. et al. Reversal of cerebral arterial spasm by intrathecal administration of a calcium antagonist (nimodipine). Acta neurochir 70, 243–254 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406653
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406653