Summary
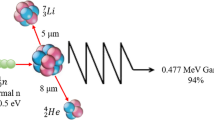
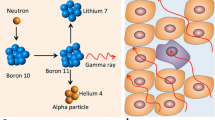
The essential feature of tumour therapy rests upon host-tumour interaction. To achieve therapeutic effects, a prerequisite to immunotherapy is the reduction of tumour cells in the host's body. Such measures should not be immunosuppressive. Cytotoxic chemotherapy is not appropriate in this regard. Supraradical surgery and non-specific radiotherapy are not desirable for preservation of nervous function, if their immunosuppression is not as severe as cytotoxic substances. Boron-neutron capture therapy is a highly specific and least immunosuppressive means of reducing tumour cells of the central nervous system. A brief introductory review of basic research is presented. The interim clinical results are: (i) Treatment of recurrent glioblastoma: Survival extension obtained by neutron capture therapy is 21.9±7.2 mos* in contrast to that obtained by conventional treatments of 6.7±0.6 mos (p<0.001), (* Total survival 26.3±6.7 mos); and (ii) only three patients including two glioblastoma cases were treated with neutron by the same surgeon who, by performing the first tumour operation, had the advantage in topographic knowledge for determining the radiation field. They survived 4, 5, and 6 years in almost fully active conditions. The new Musashi Institute of Technology Reactor Thermal Neutron Therapy Facility and the increased domestic production of boron-10 isotope have enlarged the therapeutic capacity to two dozen patients a year.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatanaka, H., Brain tumor treatment, present status and future potential. I. and II. Surgical Therapy (Gekachiryo)29 (1973), 677–683;30 (1974), 88–99.
Hatanaka, H., Sano, K., A revised boron-neutron capture therapy for malignant brain tumours. I. Experience on terminally ill patients after cobalt-60 radiotherapy. Z. Neurol.204 (1973), 309–332.
Hatanaka, H., A revised boron-neutron capture therapy for malignant brain tumours. II. Interim clinical result with the patients excluding previous treatments. J. Neurol.209 (1975), 81–94.
Hatanaka, H., Sweet, W. H., Slow-neutron capture therapy for malignant tumours, its history and recent development. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Biomedical Dosimetry, pp. 147–178. Vienna, International Atomic Energy Agency. 1975. (IAEA-SM-193/79).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatanaka, H., Amano, K., Kamano, S. et al. Boron-neutron capture therapy in relation to immunotherapy. Acta neurochir 42, 57–72 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406631
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01406631