Summary
The follow up of brain scans in 530 consecutive patients is presented. Positive results have been obtained using Hg 203-Neohydrin in 170 out of 203 (84%), intracranial tumours in 24 out of 61 (40%) cerebrovascular disorders and in 7 out of 23 (30%) head injuries.
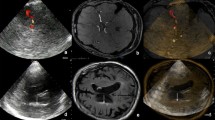
The possibility of differentiating between tumours and infarcts is discussed: for this purpose, the morphology and the intensity of the positive focus, repetition of the scan at various intervals after the onset of the disease and after the injection of the tracer are valuable.
Zusammenfassung
Bericht über die szintigraphischen Untersuchungen bei einer Serie von 530 Fällen. Es wurde Hg-203-Neohydrin verwendet. Bei 203 intrakraniellen Tumoren ergaben sich 170 (84%) positive Befunde. Unter 61 zerebrovaskulären Schädigungen waren die Befunde 24mal (40%) positiv. 23 Fälle mit Schädelverletzungen ergaben 7mal (30%) Aktivitätsanreicherungen.
Die Möglichkeit einer Differentialdiagnose zwischen Hirntumoren und zerebralen Infarkten wird diskutiert. Von Bedeutung sind dabei die Gestalt und Intensität der Aktivitätsanreicherung, Wiederholung der Szintigraphie zu verschiedenen Zeitpunkten nach Einsetzen der Krankheitserscheinungen und zu verschiedenen Zeitpunkten nach Injektion der Aktivität.
Résumé
L'étude du «scanning» de 530 malades est présent`e. Des résultats positifs ont été obtenus en utilisant le Néohydrine-Hg 203 dans 170 sur 203 (84%) tumeurs intracrâniennes, dans 24 sur 61 (40%), désordres cérébrovasculaires, et dans 7 sur 23 (30%) traumatismes crâniens.
La possibilité de différencier les tumeurs et les infarctus est discutée: dans ce but, l'aspect et l'intensité du foyer, la répétition du scanning à intervalles variés après le début de l'affection et après l'injection du traceur, ont une réelle valeur.
Riassunto
Gli Autori discutono i risultati ottenuti con la fotoseintigrafia cerebrale con Neohydrin-Hg 203 in 530 pazienti. Scintigrafie positive sono state ottenute in 170 casi di tumori endocranici su 203 (84%), in 24 vasculopatie cerebrali su 61 (40%) ed in 7 traumi eranici su 23 (30%). Gli Autori discutono anche le possibilità di diagnosi differenziale scintigrafica tra tumori cerebrali ed infarti sulla base della morfologia e dell'intensità di captazione, e sui dati ottenuti da ripetute letture nel tempo dopo la somministrazione del tracciante e dopo l'instaurarsi della malattia.
Resumen
Se presenta un estudio del “scanning” de 530 enfermos. Se obtuvieron reaultados positivos con el empleo de Neohydrina Hg 203 en 170 tumores intracraneales de los 203 estudiados (84%). En 24 de 61 (40%) se observaron trastornos cerebro-vasculares y en 7 de 23 (30%) traumatismos craneales.
Se discute la posibilidad de diferenciar los tumores de los infartos, en este sentido el aspecto y la intensidad del foco, la repetición del scanning a intervalos diferentes después del comienzo de la affección y después de la inyeeción del vector tienen un valor apreciable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Chiro, G., RISA-encephalography and conventional neuroradiological methods. A comparative study. Acta Radiol. suppl.201 (1961), 1–102.
Dregger, G. S., andF. D. Pepper, The reliability of radioisotopic encephalography. A correlation with other neuroradiological and anatomical studies. Neurology13 (1963), 1042–1053.
Glasgow, J. L., R. D. Currier, J. K. Goodrich, andF. T. Tutor, The effect of cerebrovascular accident on the brain scan. J. Nucl. Med.6 (1965), 341–342.
Goodrich, J. K., andF. T. Tutor, The isotope encephalogram in brain tumor diagnostic. J. Nucl. Med.6 (1965), 541–548.
Mastropaolo, C., eT. Daquino, L'utilità della gammaencefalografia nella diagnosi delle lesioni cerebrali. Osservazioni sulla casistica del Laboratorio di G. E. G. della Clinica delle Malattie Nervose e Mentali dell'Università di Genova. Min. Nucl.7 (1963), 153–157.
Morrison, R. T., A. K. Afifi, M. W. van Allen, andT. C. Evans, Scintiencephalography for the detection and localization of non-neoplastic intracranial lesions. J. Nucl. Med.6 (1965), 7–15.
Ojeman, R. G., S. Aronow, andW. H. Sweet, Scanning with positronemitting radioisotopes: aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation and intracerebral haemorrhage. J. Neurosurg.22 (1965), 489–498.
— — —, Scanning with positron-emitting radioisotopes. Occlusive cerebral vascular disease. Arch. Neurol.10 (1964), 218–228.
Planiol, T., andG. Gauthier, Gammaencephalographie. Bull. Schweiz. Akad. Med. Wiss.18 (1963), 425–444.
—, Gamma-encephalography after ten years of utilization in Neurosurgery — in “Progress in Neurological Surgery” (H. Krayenbuehl, P. E. Maspes, and W. H. Sweet eds.). Vol. 1, p. 93–147. Basel: S. Karger. 1966.
Paoletti, P., R. Villani, A. Castelli eM. Massarotti, La scintigrafia con Neohydrin-Hg 203 nei processi espansivi endocranici. Analisi di 100 casi. Min. Neurochir.9 (1965), 174–185.
Quinn, J. L. III, W. Hauser, andI. Ciric, Analysis of 100 consecutive abnormal brain scans using 99m Tc as pertechnetate. J. Nucl. Med.6 (1965), 333–334.
Sweet, W. H., J. Mealey jr., S. Aronow, andG. L. Brownell, Localization of focal intracranial lesions by scanning of rays from positron-emitting isotopes. Clin. Neurosurg.7 (1961), 159–197.
Wang, J., F. J. Shea, andJ. A. Rosen, Comparison of the accuracy of brain scanning and other procedures used for brain tumor detection. Neurology15 (1965), 1117–1119.
Wilcke, O., The value of positroencephalography in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of intracranial space occupying lesions. — In “Radioisotopes et affections du Système Nerveux Central — Diagnostic et Bases Biologiques” (Planiol Th. ed.), p. 7–19. Paris: Masson. 1965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castelli, A., Paoletti, P. & Villani, R. Brain scan in cerebrovascular diseases and tumours. Acta neurochir 17, 217–227 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01402540
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01402540