Summary
Purpose
To evaluate the effect of Brain Tomour (BT) and Neurosurgery (NS) on the renal handling of H2O and Na, and the clinical importance of SIADH in this setting.
Methods
Fourteen patients with BT pre-op for NS and 6 controls (C) pre-op for general surgery, were assessed in a controlled prospective trial.
All patients were normovolaemic, with normal renal function. They received 400 mg of lithium carbonate (Li) 8 hours before each of two test periods (I and II) and a standard water load only before period II. Clearances studies were performed pre-op (period I) and 24 hours post-op (period II).
Results
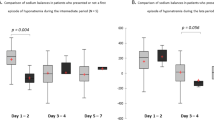
Serum Na was normal at all times. Despite normovolaemia, a 1% decrement in serum osmolality and the water load, ADH dramaticaly increased from time I to II mainly in the BT group (36.2±9.4 vs 7.1±0.6 pmol/L, p=0.02). FENa, FELi and FEUricA were significantly more elevated in the BT group pre and post-op (at time II respectively 4.6±1.6 vs 1.1±0.3%; 29.3±4.9 vs 22.6±5.5; 26.0±8.1 vs 11.3±2.2, p=0.03). Proximal and distal H2O re-absorption and distal fractional Na re-absorption were identical in both groups pre and post-operatively.
Conclusions
1-BT and NS always induce a SIADH. 2-There was a primary Na loss at the proximal tubule level not explained by ADH increment, that did not significantly changed H2O handling. 3-To prevent hyponatraemia, hypotonic I.V. fluids should be avoided, but more importantly saline must be provided to this potentially salt-wasting condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Al:
-
Aldosterone
- ADH:
-
Anti diuretic hormone
- UNa:
-
Urine sodium (mEq/l)
- SNa:
-
Serum sodium (mEq/l)
- CrCl:
-
Creatinine clearance
- LiCl:
-
Lithium clearance
- H2OCl:
-
Free water clearance
- UricACl:
-
Uric acid clearance
- NaCl:
-
Sodium clearance
- FENa:
-
Fractional excretion of sodium (NaCl/CrCl)
- FEUricA:
-
Fractional excretion of uric acid (UricACl/CrCl)
- FELi:
-
Fractional excretion of Lithium (LiCl/CrCl)
- FNa:
-
Filtered load of sodium (CrCl*SNa/1000 mEq/min)
- DistNa:
-
Distal renal tubular delivery of sodium (LiCl*SNa/1000 mEq/min)
- NaPR:
-
Proximal renal tubular reabsorption of sodium (DistNa-(UNa*Urine Volume))
- NaDR:
-
Distal renal tubular sodium reabsorption (DistNa-(UNa*Urine volume))
- H2OPR:
-
Proximal renal tubular water reabsorption (CrCl-LiCr)ml/min
- H2ODR:
-
Distal renal tubular water reabsorption (Licl-Urine volume)ml/min
- NaPFR:
-
Renal tubular proximal sodium fractional reabsorption (NaPR/FNa*100)%
- NaDFR:
-
Renal tubular distal sodium fractional reabsorption (NaDR/DistNa*100)%
References
Anderson R, Chung H, Kluge R, Shrier R (1985) Hyponatremia. A prospective analysis of its epidemiology and the pathogenetic role of vasopressin. Ann Intern Med 102: 164–168
Anderson R (1986) Hospital-associated hyponatremia. Kidney Int 29: 1237–1247
Beck L (1979) Hypouricemia in the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. N Engl J Med 301:528–530
Boer W, Koomans H, Mees E (1987) Effect of water loading on lithium clearance, electrolytes excretion and renal hemodynamics in man. Kidney Int 32: 776–779
Boer W, Hendrik A, Mees E (1987) Lithium clearance during the paradoxical natriuresis of hypotonic expansion in man. Kidney Int 32: 376–380
Born J, Hans P, Smitz S, Legros J, Kay S (1985) Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone after severe head injury. Surg Neurol 23: 383–387
Cogan E, Debieve M, Pepersack T, Abramov M (1988) Natriuresis and atrial natiuretic factor secreting during inappropriate antidiuresis. Am J Med 84: 409–418
Cogan M (1990) Atrial natriuretic peptide. Kidney Int 37: 1148–1160
Cort J (1954) Cerebral Salt Wasting. Lancet i: 752–754
Dóczi T, Tarjányi J, Huszka E, Kiss J (1982) Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone after head injury. Neurosurgery 10: 685–687
Ethier J, Kamel K, Magner P, Lemann J, Halperin M (1990) The transtubular potassium concentration in patients with hypokalemia and hyperkalemia. Am J Kid Dis 15: 309–315
Glantz S (1987) Alternatives to analysis of variance and the t-test based on ranks. In: Primer of biostatistics, 2nd Ed, p 101
Graber M, Corish D (1991) The electrolytes in hyponatremia. Am J Kid Dis 18: 527–545
Gross P, Ketteler M, Hausman C, Ritz E (1987) The charted and uncharted waters of hyponatremia. Kidney Int 32: S67-S75
Kennedy P, Mitchell D, Hoffbrand B (1978) Severe hyponatremia in hospital in patients. Br Med J 2: 1242–1246
Lowrance D, Garfinkel H, Schwartz W (1972) The effect of chronic hypotonic volume expansion on the renal regulation of acid-base equilibrium. J Clin Invest 51: 2928–2940
Maesaka J, Venkatesan J, Dreishback A (1990) Abnormal tubular handling of uric acid in patients with intracraneal lesion. Proceedings of the American Society of Nephrology Meeting (Abstract)
Maesaka J, Venkatesan J, Piccione J (1990) Abnormal lithium clearance induced in rats by plasma of patients with intracraneal lesions. Proceedings of the American Society of Nephrology (Abstract)
Maldonado M (1980) Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion of unknown origin. Kidney Int 17: 554–567
Manning P, Schwartz D, Katsube N (1985) Vasopressin-stimulated release of atriopeptin. Science 229: 395–397
Meisel A, Diamond H (1976) Effect of vasopressin on uric acid excretion. Clin Sci Mol Med 51: 33–40
Nelson P, Seif S, Maroon J, Robinson A (1981) Hyponatremia in intracraneal disease. J Neurosurg 55: 938–941
Nolph K, Shrier R (1970) Sodium, potassium and water metabolism in the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Am J Med 49: 534–545
Rabelink T, Koomans H Stolpe A, Bijlema J, Mees E (1990) Effects of atrial natriuretic peptide on distal tubule function in humans. Kidney Int 37: 996–1001
Rosenfeld J, Barnett G, Sila C (1989) The effect of subarachnoid hemorrhage on blood and CSF atrial natriuretic factor. J Neurosurg 71: 32–37
Samson W (1985) Atial natriuretic factor inhibits dehydration and hemorrhage-induced vasopressin release. Neuroendocrinology 40: 277–279
Schwartz W, Bennett W, Curelop S, Bartter F (1957) A syndrome of renal sodium loss and hyponatremia probably resulting from inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med 23: 554–567
Thomson K (1990) Lithium clearance as a measure of sodium and water delivery from the proximal tubules. Kidney Int 37: 510–515
Vingerhoets F, Tribolet N (1988) Hyponatremia hypoosmolarity in neurosurgical patients. Appropriate secretion of ADH and cerebral salt wasting syndrom. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 91: 50–54
Weinand M, O'Boynick P, Goetz K (1989) A study of serum antidiuretic hormone and atrial natriuretic peptide levels in a series of patients with intracraneal disease and hyponatremia. Neurosurgery 25: 781–785
Weiss N, Robertson G (1984) Water metabolism in endocrine disorders. Seminars Nephr 4: 303–313
Zusman R, Vinci J, Bourden R (1979) Effect of indomethacin and adrenocorticotropic hormone on renal function in man. Kidney Int 15: 62–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ponce, P., Travassos, J., Cruz, J. et al. Renal tubular sodium and water metabolism in brain tumour patients submitted to craniotomy. Acta neurochir 125, 86–91 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401833
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401833