Summary
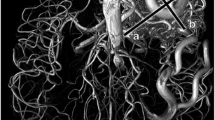
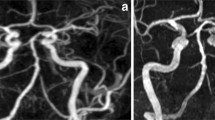
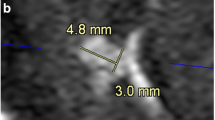
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the high resolution magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) as pre-operative angiography for the detection of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. MRA was performed on 1.5 tesla system using the 3-dimensional time of flight (3D-TOF) method. The field of view was 16 cm or 20 cm and matrix size was 192×256 or 256×512. Twenty patients with ruptured cerebral aneurysms and 35 cases of non-ruptured aneurysms (incidental aneurysm) examined by both conventional angiography and MRA were included in this study. All the ruptured aneurysms were operated on based on the information obtained from conventional angiography and MRA. Aneurysms smaller than 3 mm in size were difficult to visualize on MRA. However, most ruptured aneurysms were clearly visualized because they were generally larger than 3 mm. The image quality of MRA was satisfactory for planning surgery.
Screening for non-ruptured cerebral aneurysms using MRA is controversial. However, in ruptured aneurysms larger than 3 mm in size, MRA clearly revealed the aneurysm, and MRA findings were informative enough to plan surgery. It is concluded that this noninvasive examination can be selected as a first-choice examination especially in cases of ruptured aneurysm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan DM, Witcombe JB (1977) Intracranial extravasation of contrast medium during carotid angiography. Br J Radiol 50: 404–411
Anderson CM, Saloner D, Lee RE, Griswold VJ, Shapeero LG, Rappe JH, Nagarkar S, Pan X, Gooding GA (1992) Assessment of carotid artery stenosis by MR angiography: comparison with x-ray angiography and color-coded Doppler ultrasound. AJNR 13: 989–1003
Dell S (1988) Asymptomatic cerebral aneurysms. Assessment of its risk of rupture. Neurosurgery 10: 162–166
Dublin B, Barry N (1980) Cerebral aneurysmal rupture during angiography with confirmation by computed tomography. Surg Neurol 13: 19–26
Heiskanen O (1986) Risks of surgery for unruptured intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 65: 451–453
Jamieson KG (1954) Rupture of an intracranial aneurysm during cerebral angiography. J Neurosurg 11: 625–628
Jane JA, Kassel NA, Torner JC (1985) The natural history of aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 63: 321–323
Kido DK, Barsotti JB, Rice LZ, Rothenberg BM, Panzer RJ, Souza SP, Domoulin CL (1991) Evaluation of the carotid artery bifurcation: comparison of magnetic resonance angiography and digital subtraction arch aortography. Neuroradiology 33: 48–51
Koenig GH, Marshall WH, Poole GJ, Kramer RA (1979) Rupture of intracranial aneurysms during cerebral angiography: report of ten cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 5: 314–324
Masaryk TJ, Modic MT, Ross JS, Ruggieri PM, Laub G, Lenz G, Haacke EM, Selman W, Wiznitzer M, Harik SI (1989) Intracranial circulation: Preliminary clinical results with threedimensional (volume) MR angiography. Radiology 171: 798–799
Riles TS, Eidelman EM, Litt AW, Pinto RS, Oldford F, Schwarzenberg T (1992) Comparison of magnetic resonance angiography, conventional angiography and duplex scanning. Stroke 23: 341–346
Ross JS, Masaryk TJ, Modic MT, Ruggieri PM, Haacke EM, Selman WR (1990) Intracranial aneurysms: evaluation by MR angiography. AJR 155: 159–165
Ruggieri PM, Masaryk TJ, Ross JS (1991) Magnetic resonance angiography: Cerebrovascular application. Stroke 26: 29–36
Ruggieri PM, Masaryk TJ, Ross JS, Modic MT (1992) Intracranial magnetic angiography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 15: 71–81
Sevick RJ, Tsuruda JS, Schmalbrock P (1990) Three dimentional time-of-flight MR angiography in evaluation of cerebral aneurysms. J Comput Assist Tomogr 14: 874–881
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Houkin, K., Aoki, T., Takahashi, A. et al. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Acta neurochir 128, 132–136 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01400663
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01400663