Summary
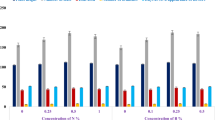
An experiment is described in which the effects were studied of deficiencies of boron, copper, manganese, molybdenum and zinc on timothy grown in solution culture.
Characteristic symptoms of copper, manganese and zinc deficiencies developed and are described.
No symptoms of boron or molybdenum deficiencies appeared; plants given no molybdenum gave bigger dry matter yields than controls.
Iron deficiency appeared fortuitously in some treatments but not in others.
These results are discussed with reference to previously published work on similar lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A. J., Molybdenum in relation to pasture improvement in South Australia. J. Council Sci. Ind. Research19, 1–15 (1946).
Anderson, A. J. and Oertel, A. C., Plant responses to molybdenum as a fertiliser II Factors affecting the responses of plants to molybdenum. C.S.I.R. Australia Bull. No. 198 (1946).
Beeson, K. C., Gray, L. and Adams, M. B., The absorption of mineral elements by forage plants. I. The phosphorus, cobalt, manganese and copper content of some common grasses. J. Am. Soc. Agron.39, 356–62 (1947).
Brenchley, W. E., The essential nature of certain minor elements for plant nutrition II. Bot. Rev.13, 169–93 (1947).
Fricke, E. F., Molybdenum deficiency in oats. J. Australian Inst. Agr. Sci.13, 75–6 (1947).
Hewitt, E. J., Relation of manganese and some other metals to the iron status of plants. Nature161, 489–90 (1948).
Hewitt, E. J. and Jones, E. W., Molybdenum as a factor in plant nutrition. II. Effect of molybdenum deficiency on someBrassica crops. Ann. Rept. Long Ashton Res. Stn. (1949).
Müller, D., Die physiologische Grundlage für die Mangelsymptome der Pflanzen. Phys. Plant2, 11–23 (1949).
Piper, C. S., Investigations on copper deficiency in plants J. Agr. Sci.32, 143–78 (1942).
Stiles, W., Trace elements in plants and animals. Cambridge. (1946).
Stephens, C. G. and Oertel, A. C., Responses of plants to molybdenum in pot experiments on the Cressey shaley clay-loam J. Council Sci. Ind. Research16, 69–73 (1943).
Stout, P. R. and Arnon, D. I., Experimental methods for the study of the role of copper, manganese and zinc in the nutrition of higher plants. Am. J. Botany26, 144–9 (1939).
Wallace, T. and Hewitt, E. J., Studies in iron deficiency of crops. I. Problems of iron deficiency and the inter-relationships of mineral elements and iron nutrition. J. Pomol.22, 153–61 (1946).
Waring, E. J., Molybdenum deficiency in Cruciferous crops. Agr. Gaz. N. S. Wales61, 15–17 (1950).
Warington, K., Molybdenum as a factor in the nutrition of lettuce. Ann. Applied Biol.33, 249–54 (1946).
Wilson, R. D., Molybdenum in relation to the scald disease of beans. Austr. J. Sci.11, 209–11 (1949).
Wood, J. G. and Sibly, P. M. The distribution of zinc in oat plants. Austr. J. Sci. Res. B3, 14–27 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, R.D. The effects of deficiencies of several trace elements on timothy (Phleum pratense L.) grown in solution culture. Plant Soil 3, 257–266 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01393980
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01393980