Summary
Twelve fungal cultures belonging to the genera ofAspergillus, Tricboderma, Chaetomium, Stachybotrys, andHypocrea were screened for the production of cellulolytic activity. All twelve were found to degrade xylan, avicel, and carboxymethylcellulose, More cellulolytic activity was obtained with shaken cultures than with still cultures and the addition of citrate-phosphate buffer to the media greatly depressed the levels of cellulolytic activity. Varying the composition of the mineral salts in the medium had no effect on the cellulolytic activity.
The growth ofAspergillus wentii under controlled conditions in a bioreactor showed that the cellulolytic activity was not affected by the aeration rate or the type of stirrer. The rate of stirring, however, did effect the cellulolytic activity, as at lower stirring speeds considerable wall growth occurred which resulted in low levels of cellulolytic activity.
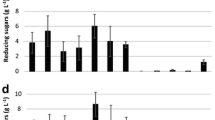
Culture supernatant fromAspergillus wentii was found to hydrolyze from 30–32% of Solka-Floc and from 2–10% of corn cobs, wheat straw, and newsprint. The extensive hydrolysis of the Solka-Floc indicates that with suitably treated cellulosic wastes and appropriate enzymes, appreciable amounts of sugars could be obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andren, R.K., Mandels, M., Modeiros, J.E. (1976). Process Biochemistry, 2–10
Crawford, D.L., McCoym, E., Harkin, J.M., Jones, P. (1973). Biotechnol. Bioeng.15, 833
Enari, T.-M., Markkanen, P. (1977). Adv. Biochem. Engg.5, 25–48
Feniksowa, R.W., Ulezlo, I.W. (1965). Prikladnaja biochimija i mikrobiologija, 1, 4, 404
Ghose, T.K., Kostick, J.A. (1969). Adv. Chemistry Series, Nr.95, 415–446
Ghose, T.K. (1969). Biotechn. Bioeng.11, 239–261
Ghose, T.K. (1977). Adv. Biochem. Engg. 6, in press
Griffin, H.L., Sloneker, J.H., Inglett, G.E. (1974). Appl. Microbiol.27, Nr. 6, 1061–1066
Han, Y.W., Callihan, C.D. (1974). Appl. Microbiol.27, 159
Linko, M. (1977). Adv. Biochem. Engg.5, 25–48
Mandels, M., Weber, J. (1969). Adv. Chemistry Series,95, 391
Mandels, M., Sternberg, D., Andreotti, R.E. (1975) Proceedings SITRA Symposium on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Cellulose, M. Bailey, T.M. Enari, and M. Linko, eds., The Technical Research Center of Finland, Helsinki 12, p. 81
Nelson, N. (1944). J. Biol. Chem.153, 375–380
Nystrom, J.M., Andren, R.K., Allen, A.L. (April 1976). Paper presented at 81 st National AIChE Meeting, Kansas City, Missouri
Peitersen, N. (1975). Biotechnol. Bioeng.17, 361
Peitersen, N. (1977). Biotechnol. Bioeng.19, 337–348
Reese, E.T., Siu, R.G.H., Levinson, H.S. (1950). J. Bacteriol.59, 485–497
Siwinska, K. (1974). Hemicellulazy plesniowe, Thesis Politechika Lodzka
Ulezlo, I.W. (1967). Fermentatiwnoje razszezeplienije celulozy, Moskwa, Izdatielstwa ‘Nauka’, 58–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pyč, R., Fiechter, A. & Galas, E. The production of cellulolytic enzymes by fungal cultures. European J. Appl Microbiol. 4, 151–158 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01390474
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01390474