Summary
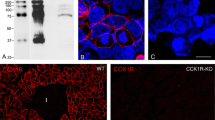
The present study reports an immunohistochemical approach for localizing the immunoreactivity of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) receptor in the human colon, by using a monoclonal antibody which recognizes the VIP-receptor of a human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line. Simultaneous demonstration of immunoreactive VIP-receptor of a human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line. Simultaneous demonstration of immunoreactive VIP-receptor and VIP was achieved by a double-labelling procedure employing immunogold silver staining for VIP-receptor, and a biotinylated secondary antibody followed by streptavidin-Texas Red, to visualize VIP.
The immunoreactive VIP receptor was found at two locations receiving dense VIP innervation: myenteric ganglia and mucosal epithelium.
Epithelial cells displayed intense labelling at the basolateral membrane, which confirmed earlier binding studies on fractionated membranes. A small number of enteroendocrine cells was also recognized by the VIP-receptor antibody. Smooth muscle and cells of the immune system were not stained by the monoclonal antibody, indicating that it recognized an epitope not common to VIP-receptors of all locations.
Thus, the immunohistochemical approach of VIP-receptor localization differs from autoradiography in (a) precise cellular localization, (b) possibility of simultaneous demonstration of receptor and ligand immunoreactivity, and (c) selectivity to a certain receptor population which, however, is presently not fully characterized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anteunis, A., Heijblum, G., Astesano, A., Marie, J.-C., Hui Bon Hoa, D., Kergoat, M., Portha, B. &Rosselin, G. (1986) Mise en évidence des récepteurs au VIP dans les cellules B du pancréas par autoradiographie ultrastructurale quantitative.C. R. Acad. Sc. Paris 303, 357–60.
Audigier, S., Barberis, C., &Jard, S. (1986) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide increases inositol phospholipid breakdown in the rat superior cervical ganglion.Brain Res. 376, 363–7.
Bitar, K. N. &Makhlouf, G. M. (1982) Relaxation of isolated gastric smooth muscle cells by vasoactive intestinal peptide.Science 216, 531–3.
Bloom, S. R., Polak, J. M. &Pearse, A. G. E. (1973) Vasoactive intestinal peptide and watery-diarrhea syndrome.Lancet 2, 14–16.
Conrath, M., Couraud, J.-Y. &Pradelles, P. (1988) Anti-idiotypic antibodies as a tool for cytochemical identification of substance P receptors in the central nervous systems.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36, 1397–1401.
Dharmsathaphorn, K., Harms, V., Yamashiro, D. J., Hughes, R. J., Binder, H. J. &Wright, E. M. (1983) Preferential binding of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide to basolateral membrane of rat and rabbit enterocytes.J. Clin Invest. 71, 27–35.
Santini, J., Martin, J. M., Luis, J., Remy, L., Tirard, A., Marvaldi, J., Pichon, J. (1988) Restricted localization of functional vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptorsin vitro differentiated human colonic adenocarcinoma cells.Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 46, 458–65.
Turness, J. B. &Costa, M. (1987)The enteric nervous system. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Grider, J. R. &Makhlouf, G. M. (1988) Transmitter of inhibitory motor neurons of the gut.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 527, 369–77.
Grider, J. R., Bitar, K. N., Said, S. I. &Makhlouf, G. M. (1983) Evidence that VIP is the neural mediator of relaxation in guinea pigtenia coli.Gastroenterology 84, 1175.
Grider, J. R., Camble, M. B., Said, S. I. &Makhlouf, G. M. (1985) Vasoactive intestinal peptide as a neural mediator of gastric relaxation.Am. J. Physiol. 248, G73–8.
Grube, D., Bargsten, G., Cetin, Y. &Yoshie, S. (1989) Chromogranins in mammalian GEP endocrine cells: Their distribution and interrelations with co-stored amines and peptides.Arch. Histol. Cytol. 52, Suppl., 91–8.
Holgate, C. S., Jackson, P., Cowen, P. N. &Bird, C. C. (1983) Immunogold-silver staining: New method of immunostaining with enhanced sensitivity.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 938–44.
Hoosein, N. M., Black, B. E., Brattain, D. E. &Brattain, M. G. (1989) Promotion of differentiation in human colon carcinoma cells by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide.Regul. Peptides 24, 15–26.
Lazarus, S. C., Basbaum, C. B., Barnes, P. J. &Gold, W. M. (1986) cAMP immunocytochemistry provides evidence for functional VIP receptors in trachea.Am J. Physiol. 251, C115–69.
Lipkin, M., Sherlock, P. &Bell, B. (1963) Cell proliferation kinetics in the gastrointestinal tract of man. II. Cell renewal in stomach, ileum, colon and rectum.Gastroenterology 45, 721–9.
Luis, J., Martin, J.-M., El Battari, A., Marvaldi, J. &Pichon, J. (1988) The vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptor: recent data and hypothesis.Biochimie 70, 1311–22.
Major, H. D., Hampton, J. C. &Rosario, B. (1961) A simple method for removing the resin from epoxyembedded tissue.J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 9, 909–10.
Mantyh, P. W., Catton, M. D., Boehmer, C. G., Welton, M. L., Passaro, E. P. Jr., Maggio, J. E. &Vigna, S. R. (1989) Receptors for sensory neuropeptides in human inflammatory diseases: Implications for the effector role of sensory neurons.Peptides 10, 627–45.
Marvaldi, J., Luis, J., Muller, J.-M., El Battari, A., Fantini, J., Martin, J.-M., Abadie, B., Tirard, A. &Pichon, J. (1986) Characterization of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) binding site: a biochemical and immunological approach.Peptides 7, Suppl. 1, 137–46.
Modlin, I. M., Bloom, S. R. &Mitchell, S. J. (1978) Experimental evidence for vasoactive intestinal peptide as the cause of the watery diarrhea syndrome.Gastroenterology 75, 1051–4.
Omary, M. B. &Kagnoff, M. F. (1987) Identification of nuclear receptors for VIP on a human colonic adenocarcinoma cell line.Science 238, 1578–81.
Ottaway, C. A. (1984) In vitro alteration of receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide changes the in vivo localization of mouse T cells.J. Exp. Med. 160, 1054–69.
Pichon, J., Hirn, M., Muller, J. M., Mangeat, P. &Marvaldi, J. (1983) Anti-cell surface monoclonal antibodies which antagonize the action of VIP in a human adenocarcinoma cell line (HT29).EMBO J. 2, 1017–22.
Power, R. F., Bishop, A. E., Wharton, J., Inyama, C. O., Jackson, R. H., Bloom, S. R. &Polak, J. M. (1988) Anatomical distribution of vasoactive intestinal peptide binding sites in peripheral tissues investigated by in vitro autoradiography.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 527, 314–25.
Racusen, L. C. &Binder, H. J. (1977) Alteration of large intestinal electrolyte transport by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the rat.Gastroenterology 73, 790–6.
Rindi, G., Buffa, R., Sessa, F., Tortora, O. &Solcia, E. (1986) Chromogranin A, B and C immunoreactivities of mammalian endocrine cells. Distribution, distinction from costored hormones/prohormones and relationship with the argyrophil component of secretory granules.Histochemistry 85, 19–28.
Said, S. I. &Faloona, G. R. (1975) Elevated plasma and tissue levels of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the watery-diarrhea syndrome due to pancreatic, bronchogenic and other tumors.N. Eng. J. Med. 293, 155–60.
Said, S. I. &Mutt, V. (1970) Polypeptide with broad biological activity: Isolation from small intestine.Science 169, 1217–18.
Sayadi, H., Harmon, J. W., Moody, T. W. &Korman, L. Y. (1988) Autoradiographic distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide receptors in rabbit and rat small intestine.Peptides 9, 23–30.
Stanisz, A. M., Befus, D. &Bienenstock, J. (1986) Differential effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide, substance P and somatostatin on immunoglobulin synthesis and proliferation by lymphocytes from Peyer's patches, mesenteric lymph nodes and spleen.J. Immunol. 136, 152–6.
De Waele, M., De Mey, J., Renmans, W., Labeur, C., Jochmans, K. &Van Camp, B. (1986) Potential of immunogold-silver staining for the study of leukocyte subpopulations as defined by monoclonal antibodies.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 34, 1257–63.
Wood, C. L., O'Dorisio, M. S., Vasallo, L. M., Malarkey, W. B. &O'Dorisio, T. M. (1985) VIP effects on GH3 pituitary tumor cells: high affinity binding, affinity labelling and adenylate cyclase stimulation.Regul. Peptides 12, 237–48.
Williams, J. T. &North, R. A. (1979) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide excites neurons of the myenteric plexus.Brain Res. 175, 174–7.
Yajima, Y., Akita, Y. &Saito, T. (1986) Pertussis toxin blocks the inhibitory effects of somatostin in cAMP dependent VIP and cAMP independent TRH stimulated prolactin secretion of GH3 cells.J. Biol. Chem. 261, 2684–9.
Zimmerman, R. P., Gates, T. S., Mantyh, C. R., Vigna, S. R., Boehmer, C. G. &Mantyh, P. W. (1989) Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP receptors) in the canine gastrointestinal tract.Peptides 9, 1241–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kummer, W. Simultaneous immunohistochemical demonstration of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and its receptor in human colon. Histochem J 22, 249–256 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01387180
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01387180