Conclusions
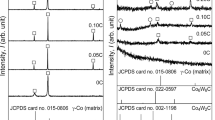
Carbon alloying of various periclase powders in an atmosphere of propane-butane at 800°C (0.5-h soaking) facilitates the incorporation in their composition of up to 4.3% C. During heating in air the carbon from the alloyed powders burns out at 480–840°C. Carbon alloying of periclase powders reduces the hydration degree.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. P. Zuev, and V. V. Mikhailov, Production of Carbon [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1970).
V. V. Kel'tsev, P. A. Tesner, Carbon: Properties, Production and Use [in Russian], Gostoptekhnizdat, Moscow (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Ogneupory, No. 9, pp. 24–26, September, 1987.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoroshavin, L.B., Perepelitsyn, V.A. Periclase powders alloyed with carbon. Refractories 28, 495–498 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01386627
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01386627