Summary
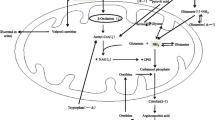
Data are reviewed on the amino acid metabolism in patients suffering from transient acute polymorphic psychoses according to ICD-10. The psychotic episodes of many of these patients are characterized by distorted sensory perceptions and intense emotional states; plasma amino acid analysis revealed a disturbed serine-glycine metabolism.
In remitted patients oral loading with serine induced the characteristic dysperceptions and psychedelic symptoms. Plasma concentrations of serine and methionine were decreased, and the concentration of taurine was increased. Fibroblast experiments suggest that the activities of the serine metabolizing enzymes serine hydroxymethyltransferase and cystathionineβ-synthase are increased in these patients.
The determination of plasma amino acid concentrations proved to be useful in discriminating these patients. The prevalence of this transient psychosis in a psychiatric in-patient population ranged between 1.4 and 3.6%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brimblecombe RW, Pinder RM (1975) Hallucinogenic agents. Wright Scientechnica, Bristol
Bruinvels J, Pepplinkhuizen L (1984) Impaired glycine-serine conversion and increased plasma taurine levels in episodic psychotic patients with psychedelic symptoms. J Psychiatr Res 18: 307–318
Bruinvels J, Pepplinkhuizen L (1985) Disturbances in serine-glycine metabolism in relation to acute psychoses with psychedelic symptoms. In: Beckmann H, Riederer P (eds) Pathochemical markers in major psychoses. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 59–73
Bruinvels J, Pepplinkhuizen L, Van Tuijl HR, Moleman P, Blom W (1980) Role of serine, glycine, and the tetrahydrofolic acid cycle in schizoaffective psychosis. A hypothesis relating porphyrin biosynthesis and transmethylation. In: Usdin E, Sourkes TL, Youdim MBH (eds) Enzymes and neurotransmitters in mental disease. John Wiley, Chicester, pp 139–154
Bruinvels J, Pepplinkhuizen L, Fekkes D (1988) Derangement of one-carbon metabolism in episodic schizoaffective psychoses. Pharmacopsychiatry 21: 28–32
DSM III-R (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd edn. Am Psychiatric Association, Washington DC
Fekkes D, Bruinvels J (1986) Serine and folate metabolism in fibroblasts from episodic psychotic patients with psychedelic symptoms. Biol Psychiatry 21: 951–959
Fekkes D, Pepplinkhuizen L, Bruinvels J (1991) Changes in serine metabolism by a serum factor present in a group of episodic psychotic patients. Biol Psychiatry 30: 966–972
Fekkes D, Pepplinkhuizen L, Verheij R, Bruinvels J (1994) Abnormal plasma levels of serine, methionine, and taurine in transient acute polymorphic psychosis. Psychiatry Res 51: 11–18
ICD-10 (1992) Classification of mental and behavioural disorders. World Health Organization, Geneva
Leonhard K (1979) The cycloid psychoses. In: Robbins E (ed) The classification of endogenous psychoses, 5th edn. Irvington Publishers Inc., New York, pp 99–139
Magnan V (1893) Leçons Cliniques, 2nd edn. Bataille éd., Paris
Meller E, Rosengarten H, Friedhoff AJ, Stebbins RD, Silber R (1975) 5-Methyltetrahydrofolic acid is not a methyl donor for biogenic amines: enzymatic formation of formaldehyde. Science 187: 171–173
Mitsuda H (1965) The concept of “Atypical Psychoses” from the aspect of clinical genetics. Acta Psychiat Scand 41: 372–377
Osmond H, Smythies J (1952) Schizophrenia: a new approach. J Ment Sci 98: 309–315
Pearson AG, Turner AJ (1975) Folate-dependent-1-carbon transfer to biogenic amines mediated by methylenetetrahydrofolic acid reductase. Nature 258: 173–174
Pepplinkhuizen L (1983) Disturbances of serine and glycine metabolism as a cause of episodic acute polymorphous psychoses. Thesis, Erasmus University Rotterdam
Pepplinkhuizen L (1988) Ritanserin in the treatment of therapy resistent psychoses: 13 pilot case reports. Janssen Res Rep 15: 109–113
Pepplinkhuizen L, Bruinvels J, Blom W, Moleman P (1980) Schizophrenia-like psychosis caused by a metabolic disorder. Lancet i: 454–456
Perris C (1974) A study of cycloid psychoses. Acta Psychiat Scand [Suppl] 253
Rijn-van den Meijdenberg JCC, Fekkes D, Wilson JHP, Pepplinkhuizen L, Verhoeven WMA, Jansen HML, Ederveen AB (1994) Acute intermittent porphyria and disturbances in amino acid metabolism in a psychiatric in-patient population. Eur Psychiatry 9: 249–253
Schröder P (1920) Degeneratives Irresein und Degenerationspsychosen. Z Gesamte Neurologie Psychiatrie 60: 119–126
Spitzer RL, Endicott J, Robins E (1978) Research diagnostic criteria. Rationale and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 35: 773–782
Wunderink AL, Pepplinkhuizen L, Bruinvels J (1986) Nutrition and psychoses. Progr Brain Res 65: 49–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fekkes, D., Pepplinkhuizen, L. Amino acid studies in transient acute polymorphic psychosis. Amino Acids 12, 107–117 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01386474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01386474