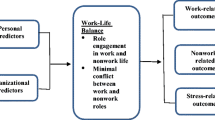
Abstract
The majority of performance appraisal systems do not result in valid and reliable evaluations of employee performance. As a consequence, conflict in the workplace may result, and a grievance procedure for employees may be necessary. This article outlines some of the problems associated with performance appraisal systems, presents the need for a grievance procedure and possible formats, and poses questions for further research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aram, J. D., & Salipante, P. F. (1981). An evaluation of organizational due process in the resolution of employee/employer conflict.Academy of Management Review, 6, 197–204.
Ash, P. (1970). The parties to the grievance.Personnel Psychology, 23, 13–37.
Ashe, R. L., Jr. & McRae, G. S. (1985). Performance evaluations go to court in the 1980s.Mercer Law Review, 36, 887–905.
Balfour, A. (1984). Five types of non-union grievance systems.Personnel, 61, 67–76.
Bassett, G. A., & Meyer, H. H. (1968). Performance appraisal based on self-review.Personnel Psychology, 21, 421–430.
Beatty, R. W., Schneier, S. E., & Beatty, J. R. (1977). An empirical investigation of perceptions of ratee behavior, frequency, and ratee behavior change using behavioral expectation scales.Personnel Psychology, 33, 647–658.
Begin, J. P. (1971). The private grievance model in the public sector.Industrial Relations, 10, 21–35.
Berenbeim, R. (1980).Nonunion Complaint Systems: A Corporate Appraisal. Conference Board Report No. 770. New York: The Conference Board.
Bernardin, H. J., & Buckley, M. R. (1981). Strategies in rater training.Academy of Management Review, 6, 205–212.
Bosco, M. L. (1985). Consensus on...nonunion grievance procedures.Personnel, 62, 61–64.
Briggs, S. (1981). The grievance procedure and organizational health.Personnel Journal, 60, 471–474.
Broden, H. E., & Taylor, E. K. (1950). The dollar criterion: Applying the cost accounting concept to criterion construction.Personnel Psychology, 3, 135–154.
Burke, R. J., & Wilcox, D. S. (1969). Characteristics of effective employee performance review and development interviews.Personnel Psychology, 22, 291–305.
Cascio, W. F., & Bernardin, H. J. (1981). Implications of performance appraisal litigation for personnel decisions.Personnel Psychology, 34, 211–226.
Condon, T. J. (1985). Use union methods in handling grievances.Personnel Journal, 64, 72–75.
Conti, A. J. (1985). Mediation of work-place disputes: A prescription for organizational health.Employee Relations Law Journal, 11, 291–310.
Dalton, D. R., & Todor, W. D. (1985). Composition of dyads as a factor in the outcomes of workplace justice: Two field assessments.Academy of Management Journal, 28, 704–712.
Denis, M. K. (1985). Subjective decision-making: Does it have a place in the employment process?Employee Relations Law Journal, 11, 269–290.
Epstein, R. K. (1975). The grievance procedure in the non-union setting.Employee Relations Law Journal, 1, 120–127.
Evan, W. M. (1961). Organization man and due process of law.American Sociological Review, 26, 540–547.
Ewing, D. W. (1982). Due process: Will business default?Harvard Business Review, 60, 114–122.
Fay, C. H., & Latham, G. P. (1982). Effects of training and rating scales on rating errors.Personnel Psychology, 35, 105–116.
Florey, P. (1985). A growing fringe benefit: Arbitration of nonunion employee grievances.Personnel Administrator, 30, 14–18.
Foulkes, F. K. (1980).Personnel Policies in Large Nonunion Companies. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Heneman, H. G. (1974). Comparisons of self and superior ratings of managerial performance.Journal of Applied Psychology, 58, 638–642.
Knowlton, W. A., & Mitchell, T. R. (1980). Effects of causal attributions on a supervisor's evaluation of subordinate performance.Journal of Applied Psychology, 65, 459–466.
Kothe, C. A. (1967).Individual Freedom in the Non-union Plant. New York: National Association of Manufacturers.
Landy, F. J., & Farr, J. L. (1980). Performance rating.Psychological Bulletin, 87, 72–107.
Latham, G. P., & Wexley, K. N. (1981).Increasing Productivity Through Performance Appraisal. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Latham, G. P., Wexley, K. N., & Pursell, E. D. (1975). Training managers to minimize rating errors in the observation of behavior.Journal of Applied Psychology, 60, 550–555.
McCollum, J. K., & Norris, D. R. (1984). Nonunion grievance machinery in southern industry.Personnel Administrator, 29, 106–109.
Michael, S. R. (1978). Due process in nonunion grievance systems.Employee Relations Law Journal, 3, 516–527.
Murphy, K. R., Martin, C., & Garcia, M. (1982). Do behavioral observation scales measure observation?Journal of Applied Psychology, 67, 562–567.
Nash, A. N., & Carroll, S. J., Jr., (1975).The Management of Compensation. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole.
O'Brien, F. P., & Drost, D. A. (1984). Non-union grievance procedures: Not just an antiunion strategy.Personnel, 61, 61–69.
Olson, F. C. (1984). How peer review works at Control Data.Harvard Business Review, 62, 58–66.
Panken, P. M. (1984). What every company should have: A formal employee complaint procedure.Management Review, 73, 42–45.
Porter, L. W., Lawler, E. E., III, & Hackman, J. R. (1975).Behavior in Organizations. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Pursell, E. D., Dossett, D. L., & Latham, G. P. (1980). Obtaining validated predictors by minimizing rating errors in the criterion.Personnel Psychology, 33, 91–96.
Rozelle, R. M., & Baxter, J. C. (1981). Influence of role pressures on the perceiver.Journal of Applied Psychology, 66, 437–441.
Schneider, D. J. (1973). Implicit personality theory: A review.Psychological Bulletin, 79, 294–309.
Scott, W. G. (1965).The Management of Conflict: Appeal Systems in Organization. Irwin-Dorsey Series in the Behavioral Sciences.
Scott, W. G., Mitchell, T. R., & Peery, N. S. (1981). Organizational Governance. In Nystrom, D. C., & Starbuck, W. H. (Eds.),Handbook of Organizational Deisgn, 2, 135–151.
Shaw, R. L. (1959). A grievance procedure for non-unionized employees.Personnel, 36, 66–70.
Silver, I. (1967). The corporate ombudsman.Harvard Business Review, 46, 77–87.
Smith, P. C. (1976). Behaviors, results, and organizational effectiveness: The problem of criteria. In: M. D. Dunnette (Ed.),Psychology, Chicago: Rand-McNally.
Tenopyr, M. L., & Oeltjen, P. D. (1982). Personnel selection and classification. In Porter, L. W. (Ed.),Annual Review of Psychology. Palo Alto, CA: Annual Reviews, Inc.
Venture. (1985). Dealing with complaints.45, 25–26.
Vollmer, H. M. (1960).Employee Rights and the Employment Relationship. Berkeley/Los Angeles: University of California Press.
Watkins, T. L. (1985). Why grievance systems fail.Training and Development Journal, 39, 20.
Westin, A. F. (1983). Fair procedure: Grievance systems that work for nonunion employees.World of Work Report, 8, 17.
Wexley, K. N. (1984). Personnel training.Annual Review of Psychology, 35, 519–551.
Wherry, R. J., Sr., & Bartlett, C. J. (1982). The control of bias in ratings: A theory of rating.Personnel Psychology, 35, 521–552.
Yenney, S. L. (1977). In defense of the grievance procedure in a non-union setting.Employee Relations Law Journal, 2, 434–443.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stratton, K. Performance appraisal and the need for an organizational grievance procedure: A review of the literature and recommendations for future research. Employ Respons Rights J 1, 167–179 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01384979
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01384979