Conclusion
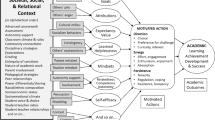
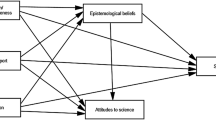
The significance of this study is reflected in the interdependence of the variables involved as shown by the emergence of total and indirect effects. Elsewhere, the importance of obtaining “ecological” maps of classroms to provide a macro level understanding of what is happening has been stressed (Clarke and Dart, 1991b). This study has illustrated how the LISREL procedure provides the facility to obtain an insight into the complex of inter-relationships that exist in ecological maps.
The study provides reasonable support for the revised structural model. It also indicates ways in which lecturers may intervene in the classroom to increase the likelihood that students will use learning strategies associated with a deep approach to learning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, C. (1992). ‘Classrooms: Goals, Structures, and student motivation’,Journal of Educational Psychology 84, 262–271.
Ames, C., and Ames R. (1984). ‘Systems of student and teacher motivation: Towards a qualitative definition’,Journal of Educational Psychology 76, 535–556.
Ames, C., and Archer, J. (1988). ‘Achievement goals in the classroom: Students' learning strategies and Motivation Processes’,Journal of Educational Psychology 80, 260–267.
Anderson, J., and Gerbing, D. (1988). ‘Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach’,Psychological Bulletin 103, 411–423.
Archer, J. (1992). ‘Students' perceptions of classroom climate: Implications for motivation’. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Australian Association for Research in Education, Deakin University, Australia.
Archer, J., Scevak, J., and Monfries, M. (1991). ‘Motivational patterns and use of effective learning strategies among first-year university students’. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Australian Association for Research in Education, Gold Coast, Australia.
Bentler, P., and Bonett, D. (1980). ‘Significance tests and goodness of fit in the analysis of covariance structures’.Psychological Bulletin 88, 588–606.
Biggs, J. (Ed.) (1991).Teaching for Learning: The View from Cognitive Psychology, Hawthorne, Vic: ACER.
Biggs, J. (1987).Student Approaches to Learning and Studying. Hawthorn. Vic.: Australian Council for Educational Research.
Biggs, J., and Moore, P. (1993).The Process of Learning. (3rd ed.). New York: Prentice Hall.
Blumenfeld, P., Puro, P., and Mergendoller, J. (1992). ‘Translating motivation into thoughtfulness, in H. Marshall (ed.),Redefining Student Learning: Roots of Educational Change Norwood, NJ: Ablex Pub. Corp. (pp 207–239).
Bollen, K. (1989). ‘A new incremental fit index for general structural equation models’,Sociological Methods and Research, 17, 303–316.
Brown, A. (1988). ‘Motivation to learn and understand: On taking charge of one's own learning’,Cognition and Instruction 5, 311–322.
Burnett, P. (1993).Personal Communication.
Clarke, J.A., and Dart, B.C. (1991a). ‘Tertiary learning’. Symposium presented at the annual conference of the Australian Association for Research in Education, Gold Coast, Australia.
Clarke, J.A., and Dart, B.C. (1991b). ‘Improving the learning of tertiary students: A theoretical model and its implementation’. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Higher Education Research and Development Association, Victoria University, Wellington, N.Z.
Coovert, M., Penner, L., and MacCallum, R. (1990). ‘Covariance structure modeling in personality and social psychological research’, in C. Hendrick and M. S. Clark (eds.),Research Methods in Personality and Social Psychology. Newbury Park, Calif.: Sage Publications.
Dahlgren, L. (1984). ‘Outcomes of learning’, in F. Marton, D. Hounsell and N. Entwistle (eds.),The Experience of Learning, Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press, (pp 19–35).
Dart, B.C. (1992). ‘Postgraduate students' perceptions of their learning’. Unpublished Manuscript. School of Learning and Development, Queensland University of Technology.
Dart, B.C., and Clarke, J.A. (1991): ‘Helping students become better learners: A case study in teacher education.’Higher Education 2, 317–335.
Dart, B.C., and Clarke, J.A. (1992). ‘Learning and learning environments’. Paper presented at the annual conference of the Higher Education Research and Development Association, Churchill Campus, Monash University.
Dweck, C. (1986). ‘Motivational processes affecting learning’,American psychologist 41, 1040–1048.
Elliott, E., and Dweck, C. (1988). ‘Goals: An approach to motivation and achievement’Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 54, 5–12.
Entwistle, N. (1987)Understanding Classroom Learning. London: Hodder and Stoughton.
Hoyle, R.H. (1991). ‘Evaluating measurement models in clinical research: Covariance Structure Analysis of latent variable models of self-conception’,Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 59, 67–76.
Joreskog, K.G., and Sörbom, D. (1989).LISREL 7: A Guide to the Program and Applications. Chicago: SPSS Inc.
Marsh, H. (1991). ‘Multidimensional students' evaluations of teaching effectiveness: A test of alternative higher-order structures.Journal of Educational Psychology 62, 17–34.
Marsh, H., Balla, J., and Mcdonald, R. (1988). ‘Goodness-of-fit indexes in confirmatory factor analysis: The effect of sample size’Psychological Bulletin, 103, 391–410.
Marsh, H., and Hocevar, D. (1985). ‘Application of confirmatory factor analysis to study of selfconcept: First- and higher order factor models and their invariance across groups’,Psychological Bulletin 102, 562–582.
McDonald, r., and Marsh, H. (1990). ‘Choosing a multivariate model: Noncentrality and goodness of fit’,Psychological Bulletin 107, 247–255.
Meece, J., Blumenfeld, P., and Hoyle, R. (1988). ‘Factors influencing students' goal orientation and cognitive engagement in classroom activities’,Journal of Educational Psychology 80, 514–523.
Miller, R., Behrens, J., Greene, B., and Newman, D. (1993). ‘Goals and perceived ability: Impact on student valuing, self-regulation, and persistence’,Contemporary Educational Psychology, 62, 17–34.
Nicholls, J. (1992). ‘Students as educational theorists’, in D. Schunk and J. Meece (eds.),Student Perceptions in the Classroom: Causes and Consequences, Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. pp. 267–286.
Nicholls, J., (1984). ‘Conceptions of ability and achievement motivation’, in R. Ames and C. Ames (eds.),Research on Motivation in Education (Vol. 1). San Diego Ca.: Academic Press, pp. 39–73.
Nolen, S.B. (1988). ‘Reasons for studying: motivational orientations and study strategies’,Cognition and Instruction, 269–287.
Nolen, S.B., and Haladyna, T. (1990). ‘Personal and environmental influences on students' beliefs about effective study strategies’,Contemporary Educational Psychology 15, 116–130.
Pintrich, P., and De Groot, E. (1990). ‘Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance’,Journal of Educational Psychology, 82, 33–40.
Pintrich, P., and Garcia, T. (1991). ‘Student Goal Orientation and self-regulation in the college classroom, in M. Maehr and P. Pintrich (eds.),Advances in Motivation and Achievement (Vol. 7, 371–402) Greenwich: JAI Press, pp. 371–402
Pintrich, P., and Garcia, T. (1992). ‘An integrated model of motivation and self-regulated learning’. Paper presented at the annual conference of the American Educational Research Association, San Francisco.
Ramsden, P. (1992).Learning to Teach in Higher Education. London: Routledge.
Ramsden, P., and Entwistle, N. (1981). ‘Effects of academic departments on students' approaches to studying’,British Journal of Educational Psychology 51, 367–383.
Resnick, L. (1987). ‘Learning in school and out’,Educational Researcher 16, 13–20.
Reynolds, A.J., and Walberg, H.J. (1991). ‘A structural model of science achievement’,Journal of Educational Psychology’ 83, 97–100.
Rowe, K.G. (1991). ‘The influence of reading activity at home on students' attitudes towards reading, classroom attentiveness and reading achievement: An application of structural equation modelling’,British Journal of Educational Psychology 61, 19–35.
Ryan, R., and Grolnick, W. (1986). ‘Origins and pawns in the classroom: Self-report and projective assessments of individual differences in children's perceptions’Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 50, 550–558.
T & LITE (1992). ‘Teaching and Learning in Tertiary Education’ Research Project coordinated by Research Concentration in Cognition in Learning and Development. Red Hill, Australia: Queensland University of Technology.
Trigwell, K., and Prosser, M. (1991). ‘Relating approaches to study and quality of learning outcomes at the course level’,British Journal of Educational Psychology 61, 265–275.
Van Rossum, E., and Schenk, S. (1984). ‘The relationship between learning conception, study strategy and learning outcome’,British Journal of Educational Psychology 54, 73–83.
Vermunt, J. (1989). ‘The interplay between internal and external regulation of learning, and thedesign of process-oriented instruction’. Paper presented at the third Conference of the European Association of Research on Learning and Instruction, Madrid.
Volet, S., and Chalmers, D. (1992). ‘Investigation of qualitative differences in university students' learning goals, based on an unfolding model of stage development’,British Journal of Educational Psychology 62, 17–34.
Weinstein, R. (1989). ‘Perceptions of classroom processes and student motivation: Children's views of self-fulfilling prophecies’, C. Ames and R. Ames (eds.)Research on Motivation in Education (Vol. 3). San Diego Ca: Academic Press, pp. 187–221.
Wigfield, A., and Eccles, J. (1992) ‘The development of achievement task values: A theoretical analysis’,Developmental Review 12, 265–310.
Zimmerman, B., and Martinez-Pons, M. (1992). ‘Perceptions of efficacy and strategy use in the self-regulation of learning’, in D. Schunk and J. Meece (eds.)Student Perceptions in the Classroom: Causes and Consequences. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dart, B.C. A goal-mediational model of personal and environmental influences on tertiary students' learning strategy use. High Educ 28, 453–470 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01383937
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01383937