Summary
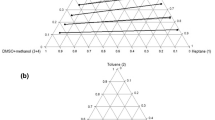
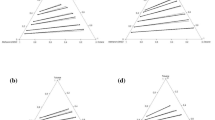
The solubilities of toluene in water-ethylene glycol mixed solvent with or without a hydrotropy agent, urea- or p-toluene-sulfonic acid, were determined at 20 degree intervals from 5–65°C. From the results the thermodynamic parameters for the following processes were calculated: (i) solution process of toluene in water-ethylene glycol mixed solvents and (ii) transfer of one mole of toluene from the mixed solvents to urea- or p-toluenesulfonic acid solutions. From the thermodynamic parameters for the solution process it is concluded that the degree of the order of the structure of mixed solvent would be less than that of water. The. mechanism of hydrotropy in waterethylene glycol was quite different to that in water. In water process (ii) was accompanied by a positive enthalpy and entropy change. On the other hand, in water-ethylene glycol mixed solvents it was accompanied by a negative enthalpy and entropy change. From these results it is concluded that the mechanism of hydrotropy is based on the degree of the ordered structure of solvents.
Zusammenfassung
Die Löslichkeit von Toluol in Wasser-Äthylen-glykol wurde mit oder ohne hydrotrope Verbindungen (Harnstoff oder p-Toluolsulfonsäure) in 20°-Intervallen von 5–65°C bestimmt. Aus den Ergebnissen wurden die thermodynamischen Parameter für folgende Prozesse berechnet: (i) Lösungsprozeß von Toluol im Wasser-Äthylenglykol und (ii) Übergang eines Mols Toluol vom Lösungsmittelgemisch zum Harnstoff oder zur p-Toluolsulfonsäure. Es wird geschlossen, daß der Ordnungsgrad des Lösungsmittelgemischs niedriger als der des Wassers ist. Der Mechanismus der Hydrotropie im Wasser-Äthylenglykol war deutlich verschieden von dem in Wasser. In Wasser war Prozeß (ii)- immer von einer positiven Enthalpie- und Entropieänderung begleitet; im Wasser-Äthylenglykol-Lösungsmittelgemisch war er von einer negativen Enthalpie- und Entropieänderung begleitet. Aus diesen Resultaten wird geschlossen, daß der Mechanismus der Hydrotropie mit dem Grad der Ordnung der Lösungsmittel zusammenhängt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ueda, M., A. Katayama andN. Kuroki, Kolloid-Z. u. Z. Polymere252, 486 (1974).
Bohon, R. L. andW. F. Claussen, J. Amer. Chem. Soc.73, 1571 (1951).
Neméthy, G. andH. A. Scheraga, J. Chem. Phys.36, 3401 (1962).
Ray, A., andG. Neméthy, J. Phys. Chem.75, 809 (1971).
Katayama, A., T. Matsuura, K. Konishi andN. Kuroki, Kolloid-Z. u. Z. Polymere202, 157 (1965).
Katayama, A., T. Takagishi, K. Konishi andN. Kuroki, Kolloid-Z. u. Z. Polymere206, 162 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 2 figures and 3 tables
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, M., Katayama, A., Kuroki, N. et al. Effect of urea and p-toluenesulfonic acid on the solubility of toluene in water-ethylene glycol mixture. Colloid & Polymer Sci 254, 417–420 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01382125
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01382125