Summary
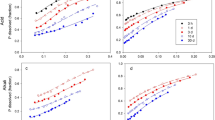
Surface samples of six Ontario soils were selected to provide a range in pH, texture and carbonate content. Phosphorus was added to the soil samples at the rate of 200, and 2000 pounds. P2O5 per acre and the inorganic phosphates associated with aluminum (Al-P), iron (Fe-P) and calcium (Ca-P) were analysed 15, 30, and 335 days after treatment. Samples of the check soils were leached with the equivalent of 7 litres of soil-percolated water and then analysed for phosphate fractions. In 5 soils with added phosphorus the Al-P fraction increased at both rates of added phosphorus, Fe-P increased only at the higher rate of added phosphorus and Ca-P did not increase at either rate. In the sixth soil (69.9% CaCO3 equivalent) Ca-P increased at both rates of added phosphorus, but proportionately less than the water-soluble phosphorus. These changes in phosphorus values existed relatively unchanged for 335 days after the addition of phosphorus. Leaching generally removed phosphorus from all phosphorus fraction. At or below pH 7.1 (soil paste) the Al-P decreased proportionately more than the Fe-P and Ca-P. Above pH 7.1 the Ca-P decreased proportionately more than the other two fractions upon leaching.
Similar content being viewed by others
List of references
Aung, Khin, and Leeper, G. W., Modifications in Chang and Jackson's procedure for fractionating soil phosphorus. Agrochimica4, 246–254 (1960).
Chang, S. C. and Jackson, M. L., Fractionation of soil phosphorus. Soil Sci.84, 133–144 (1957).
Chang, S. C., and M. L. Jackson, 1958. Soil phosphorus fractions in some representative soils. J. Soil Sci.9, 109–119 (1958).
Clarke, J. S. and Peech, M., Solubility criteria for the existence of calcium and aluminum phosphates in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.19, 171–174 (1955).
Cole, C. V. and M. L. Jackson, Solubility equilibrium constant of dihydroxy aluminum dihydrogen phosphate relating to a mechanism of phosphate fixation in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.15, 84–89 (1950).
Fife, C. V., An evaluation of ammonium fluoride as a selective extractant for aluminum-bound soil phosphate: II. Preliminary studies on soils. Soil Sci. 87, 83–88 (1959).
Lindsay, W. L., and Moreno, E. C., Phosphate phase equilibria in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.24, 177–182 (1960).
Mack, A. R. and Barber, S. A., Influence of temperature and moisture on soil phosphorus. I. Effect on soil phosphorus fractions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.24, 381–385 (1960).
MacKenzie, A. F., Inorganic soil phosphorus fractions of some Ontario soils as studied using isotopic exchange and solubility criteria. Can. J. Soil Sci.42, 150–156 (1962).
Scheffer, F., Kloke, A., and Hempler, K., Die Phosphatformen im Boden und ihre Verteibing auf die Korngrossen fraktionen. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Dung. u. Bodenk.91, 240–252 (1960).
Williams, E. G., and Saunders, W. M. H., Distribution of phosphorus in profiles and particle-size fractions of some Scottish soils. J. Soil Sci.7, 90–108 (1956).
Wright, B. C. and Peech, M., Characterization of phosphate reaction products in acid soils by the application of solubility criteria. Soil Sci.90, 32–43 (1960).
Yuang, T. L., Robertson, W. K., and Neller, J. R., Forms of newly fixed phosphorus in three acid sandy soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.24, 447–450 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Contribution from Dept. of Soil Science, O.A.C., Guelph, Canada. Part of thesis submitted by junior author to the Graduate School, University of Toronto, in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the M.S.A. degree.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackenzie, A.F., Amer, S.A. Reactions of iron, aluminum and calcium phosphates in six Ontario soils. Plant Soil 21, 17–25 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01373868
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01373868