Summary
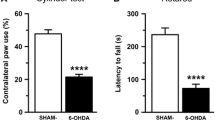
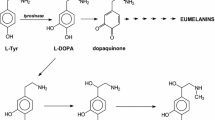
The activity of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylases and of Dopa/ 5-HTP decarboxylase was measured in different structures of the brain of cats administered L-Dopa (100 mg/kg/day,per os) during several consecutive days. The activity of tyrosine hydroxylase which is unchanged after 4 and 7 days of treatment, respectively, is significantly decreased after 21 days of L-Dopa. The activity of tryptophan hydroxylase is normal after 4 days of L-Dopa but it is significantly decreased after 7 and 21 days of L-Dopa, respectively. The activity of decarboxylase is normal after 4 days of L-Dopa but it is significantly increased after 7 and 21 days of L-Dopa, respectively.
Résumé
L'activité des hydroxylases de la tyrosine et du tryptophane et de la décarboxylase de la Dopa et du 5-HTP a été mesurée au niveau de diverses structures du cerveau de chat à la suite d'un traitement chronique à la L-Dopa (100 mg/kg/jour,per os). Après 4 jours de traitement l'activité de ces enzymes demeure normale tandis qu'après 7 et 21 jours, l'activité de Phydroxylase du tryptophane est significativement diminuée et celle de la décarboxylase augmentée. Par ailleurs, l'activité de Phydroxylase de la tyrosine est significativement diminuée après 21 jours de traitement à la L-Dopa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahtee, L., D. F. Sharman, andM. Vogt: Acid metabolites of monoamines in avian brain. Brit. J. Pharm.38, 68–72 (1970).
Anton, A. H., andD. F. Sayre: The distribution of dopamine and dopa in various animals and a method for their determination in diverse biological material. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.145, 326–336 (1969).
Ashcroft, G. W., D. Eccleston, andT. B. B. Crawford: 5-Hydroxyindole metabolism in rat brains. A study of intermediate metabolism using the technique of tryptophan loading. I. Methods. J. Neurochem.12, 483–492 (1965).
Bartholini, G., andA. Pleischer: Cerebral accumulation and metabolism of C14-dopa after selective inhibition of peripheral decarboxylase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.161, 14–20 (1968).
Bertler, A., B. Falck, Ch. Owman, andE. Rosengren: The localization of monoaminergic blood-brain barrier mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 369–385 (1966).
Christenson, J. G., W. Dairman, andS. Udenfriend: On the identity of Dopa decarboxylase and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA)69, 343–347 (1972).
Cicero, T. J., L. G. Sharpe, E. Robins, andS. S. Grote: Regional distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain. J. Neurochem.19, 2241–2243 (1972).
Constantinidis, J., J. C. De La Torre, R. Tissot, andF. Geissbühler: La barrière capillaire pour la dopa dans le cerveau et les différents organes. Psychopharmacol. (Berl.)15, 75–87 (1969).
Dairman, W., J. G. Christenson, andS. Udenfriend: Decrease in liver aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase produced by chronic administration of L-Dopa. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA)68, 2117–2120 (1971).
Dairman, W., J. G. Christenson, andS. Udenfriend: Changes in tyrosine hydroxylase and dopa decarboxylase induced by pharmacological agents. Pharmacol. Rev.24, 269–290 (1972).
Dairman, W., andS. Udenfriend: Decrease in adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase and increase in norepinephrine synthesis in rats given L-Dopa. Science171, 1022–1024 (1971).
Dairman, W., andS. Udenfriend: Studies on the mechanism of the L-3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine induced decrease in tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Mol. Pharmacol.8, 293–299 (1972).
Davidson, L., K. Lloyd, I. Dankova, andO. Hornykiewicz: L-Dopa treatment in Parkinson's disease: Effect on dopamine and related substances in discrete brain regions. Experientia27, 1048–1049 (1971).
Duvoisin, R. C., M. Yahr, andL. D. Côté: Pyridoxine reversal of L-Dopa effects in parkinsonism. Trans. Amer. Neurol. Ass.94, 81–84 (1969).
Freedland, R. A., I. M. Wadznski, andH. A. Waisman: The enzymatic hydroxylation of tryptophan. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.5, 94–103 (1961).
Goldstein, M., andR. Freukel: Inhibition of serotonin synthesis by Dopa and other catechols. Nature New Biol.233, 179–180 (1971).
Goldstein, M., T. H. Joh, andH. Gang: Some aspects of the biosynthesis of catecholamines in adrenal glands and in pheochromocytoma and neuroblastoma tremors. 7th Int. Cong. Clin. Chem.3, 78–84 (1970).
Grahame-Smith, D. F.: The biosynthesis of 5-hydroxy-tryptamine in brain. Biochem. J.105, 351–360 (1967).
Kitsikis, Anne, andAndrée G. Roberge: Behavioural and biochemical effects of L-Dopa in cats. Israel J. Med. Sci. (1972, in press).
Kuczenski, R. T., andA. J. Mandell: Regulatory properties of soluble and paniculate rat brain tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem.247, 3114–3122 (1972).
Kuntzman, R., P. Shore, D. Bogdanski, andB. B. Brodie: Microanalytical procedures for fluorometric assay of brain Dopa-5-HTP decarboxylase, norepinephrine and serotonin, and a detailed mapping of decarboxylase activity in brain. J. Neurochem.6, 226–232 (1961).
Lancaster, G. A., andT. L. Sourkes: Purification and properties of dopa decarboxylase of hog kidney. Can. J. Biochem.50, 7, 791–797 (1972).
Langelier, P., A. Parent, andL. J. Poirier: Decarboxylase activity of the brain capillary walls and parenchyma in the rat, cat and monkey. Brain Res.45, 622–629 (1972).
Leon, A. S., H. E. Spiegel, G. Thomas, Ira Ross, andW. B. Abrams: Effects of pyridoxine on adsorption, metabolism and clinical activity of levodopa in Parkinson's disease. Clin. Pharmacol. and Ther.12, 294–302 (1971).
Lewitt, M., S. Spector, A. Sjoerdsma, andS. Udenfriend: Elucidation of the rate-limiting step in norepinephrine biosynthesis using the perfused guinea pig heart. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.148, 1–8 (1965).
Lison, L.: Statistique appliquée à la biologie expérimentale. Paris: Gauthier Villars. 1958.
Lovenberg, W., E. Jequier, andA. Sjoerdsma: Tryptophan hydroxylation: measurement in pineal gland, brainstem and carcinoid tumor. Science (New York)155, 217–219 (1967).
Lovenberg, W., H. Weissbach, andS. Udenfriend: Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylases. J. Biol. Chem.237, 89–93 (1962).
Lowry, O. H., H. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, andR. J. Randall: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951).
McGeer, E. G., S. Gibson, J. A. Wada, andP. L. McGeer: Distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in adult and developing brain. Can. J. Bioch.45, 1943–1952 (1967).
McGeer, E. G., S. Gibson, andP. L. McGeer: Some characteristics of brain tyrosine hydroxylase. Can. J. Bioch.45, 1557–1563 (1967).
Nagatsu, T., M. Lewitt, andS. Udenfriend: Tyrosine hydroxylase-the initial step in NE biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem.239, 2910–2917 (1964).
Nagatsu, T., andT. Yamamoto: Fluorescence assay of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in tissue homogenate. Experientia24, 1183–1184 (1968).
Peters, D. A. V., P. L. McGeer, andE. G. McGeer: The distribution of tryptophan hydroxylase in cat brain. J. Neurochem.15, 1431–1435 (1968).
Schott, H. F., andW. G. Clark: Dopa decarboxylase inhibition through the interaction of coenzyme and substrate. J. Biol. Chem.196, 449–462 (1952).
Sourkes, T. L.: Dopa decarboxylase: Substrates, coenzymes, inhibitors. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 53–60 (1966).
Sourkes, T. L.: Influence of specifie nutrients on catecholamine synthesis and metabolism. Pharmacol. Rev.24, 349–359 (1972).
Tate, S. S., R. Sweet, F. H. McDowell, andA. Meister: Decrease of the 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (Dopa) decarboxylase activities in human erythrocytes and mouse tissues after administration of Dopa. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (USA)68, 2121–2134 (1971).
Udenfriend, S.: Tyrosine hydroxylase. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 43–51 (1966).
Udenfriend, S., P. Zaltzman-Nirenberg, andT. Nagatsu: Inhibitors of purified beef adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem. Pharmacol.14, 837–845 (1965).
Waalkes, T. P., andS. Udenfriend: A fluorometric method for the estimation of tyrosine in plasma and tissues. J. Lab. Clin. Med.50, 733–736 (1957).
Waymire, J. C., N. Weiner, F. H. Schneider, M. Goldstein, andL. S. Freedman: Tyrosine hydroxylase in human adrenal and pheochromocytoma: localization, kinetics and catecholamine inhibition. J. Clin. Invest.57, 1798–1804 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberge, A.G., Pokier, L.J. Effect of chronically administered L-Dopa on Dopa/5HTP decarboxylase and tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylases in cat brain. J. Neural Transmission 34, 171–185 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01367507
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01367507