Abstract
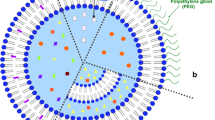
Liposomes are microscopic particles of lipid bilayer membrane that enclose aqueous internal compartments. These drug-delivery systems offer a very interesting opportunity for delivering cytotoxic drugs with equal or improved clinical efficacy and reduced toxicity. The most important clinical application of liposomes until now has been the inclusion of amphotericin B. At the same dose level, liposomal amphotericin B is as effective or slightly less effectivc than the conventional formulation, but much higher dosages, up to 5–7 mg kg−1day−1, can be given with acceptable toxicity. There are three preparations of cytotoxic drugs in an advanced stage of commercial development. Two of these (Doxil and TLD D99) contain doxorubicin and the other (DaunoXome) contains daunorubicin. The cardiac toxicity of the three preparations under clinical evaluation appears to be low in comparison with conventional doxorubicin or daunorubicin. No direct comparisons between the new formulations are available, so it is not yet possible to make any statements concerning their relative efficacy and toxicity. DaunoXome is the only drug that is approved in any country, and is also the best documented. It is too early to make recommendations concerning the place of these drugs in therapy. The marked increase in concentrations at the site of the tumour has yet to lead to increased therapeutic efficacy. These findings need further investigation. The efficacy of liposomal preparations in Kaposi's sarcoma appears to be similar to that of standard therapy and the clinical tolerance is good. Perhaps combination therapy with other cytotoxic agents could result in improved clinical efficacy. Their cost will probably be high in comparison with standard therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogner JR, Kronawitter U, Rolinski R, Truebenbach K, Goebel FD (1994) Liposomal doxorubicin in the treatment of advanced AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma. J Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome 7:463–468
Codde JP, Lumsden AJ, Napoli S, Burton MA, Gray BN (1993) A comparative study of the anticancer efficacy of doxorubicin carrying microspheres and liposomes using a rat liver model. Anticancer Res 13:539–543
Coker RJ, James ND, Stewart JSW (1993) Hepatic toxicity of liposomal encapsulated doxorubicin. Lancet 341:756
De Marie S, Janknegt R, Bakker-Woudenberg IAJM (1994) Clinical use of liposomal and lipid-complexed amphotericin B. J Antimicrob Chemother 33:907–916
Fonseca GA, Valero V, Buzdar A, Walters R, Wiley J (1995) Decreased cardiac toxicity by TLC D-99 (liposomal doxorubicin) in the treatment of metastatic breast carcinoma (abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol Annu Meet 21: Abstract 96
Fonseca GA, Valero V, Buzdar A, Walters R, Wiley J (1995) Phase II study of TLC D99 (liposomal doxorubicin) in patients with metastatic breast cancer (abstract). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol Annu Meet 21: Abstract
Forssen EA, Ross ME (1994) DaunoXome treatment of solid tumors: preclinical and clinical investigations. J Liposome Res 4:481–512
Gabizon A, Catane R, Uziely B, Kaufman B, Sarra T, Cohen R, Martin F, Huang A, Barenholz Y (1994) Prolonged circulation time and enhanced accumulation in malignant exudates of doxorubicin encapsulated in polyethyleneglycol coated liposomes. Cancer Res 54:987–992
Gill PS, Espina BM, Muggia F, Cabriales S (1995) Phase I/II clinical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of liposomal daunorubicin. J Clin Oncol 13:996–1003
Gray A, Morgan J (1991) Liposomes in haematology. Blood Rev 5:258–272
Gregoriadis G (1991) Overview of liposomes. J Antimicrob Chemother 28 [Suppl B]: 39–48
Guaglianone P, Chan K, Delaflor-Weiss E, Hanisch R, Jeffers S, Sharma D, Muggia F (1994) Phase I and pharmacologic study of liposomal daunorubicin (DaunoXome). Invest New Drugs 12:103–110
Harrison M, Tomlinson D, Stewart S (1995) Liposomal-entrapped doxorubicin: an active agent in AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 13:914–920
Hengge UR, Brockmeyer NH, Rasshofer R, Goos M (1993) Fatal hepatic toxicity with liposomal doxorubicin. Lancet 341:383–384
Huang SK, Stauffer PR, Hong K, Guo JW, Phillips TL, Huang A (1994) Liposomes and hyperthermia in mice: increased tumor uptake and therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin in sterically stabilized liposomes. Cancer Res 54:2186–2191
James ND, Coker RJ, Tomlinson D, Harris JR, Gompels M, Pinching AJ, Stewart JS (1994) Liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil): an effective new treatment for Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS. Clin Oncol R Coll Radiol 6:293–296
Janknegt R, De Marie S, Bakker Woudenberg IAJM, Crommelin DJA (1992) Liposomal and lipid formulations of amphotericin B: clinical pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacokinet 23:279–291
Kanter PM, Bullard GA, Ginsberg RA, Pilkiewicz PG, Mayer LD, Cullis PR, Pavelic ZP (1993) Comparison of the cardiotoxic effects of liposomal doxorubicin (TLC D99) versus free doxorubicin in beagle dogs. In Vivo 7:17–26
Kanter PM, Bullard GA, Pilkiewicz PG, Mayer LD, Cullis PR, Pavelic ZP (1993) Preclinical toxicology study of liposome encapsulated doxorubicin (TLC D99): comparison with doxorubicin and empty liposomes in mice and dogs. In Vivo 7:85–95
Kanter PM, Klaich GM, Bullard GA, King JM, Bally MB, Mayer LD (1994) Liposome encapsulated vincristine: preclinical toxicologic and pharmacologic comparison with free vincristine and empty liposomes in mice, rats and dogs. Anticancer Drugs 5:579–590
Kayyali R, Marriott C, Wiseman H (1994) Tamoxifen decreases drug efflux from liposomes: relevance to its ability to reverse multidrug resistance in cancer cells? FEBS Lett 344:221–224
Kim S (1993) Liposomes as carriers of cancer chemotherapy. Current status and future prospects. Drugs 46:618–638
Ning S, Macleod K, Abra RM, Huang AH, Hahn GM (1994) Hyperthermia induces doxorubicin release from non-circulating liposomes and enhances their anti-tumor efficacy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 29:827–834
24.Ostro MJ, Cullis PR (1989) Use of liposomes as injectable drug-delivery systems. Am J Hosp Pharm 46:1576–1587
Rizzardini G, Vigevani GM, Cremoni L, Pastecchia C, Milazzo F (1995) Liposomal doxorubicin or bleomycin plus vincristine in epidemic Kaposi's sarcoma (abstract). International Congress of Chemotherapy, Montreal, July 1995, abstract 2173
Sharma A, Straubinger RM (1994) Novel taxol formulations: preparation and characterization of taxol-containing liposomes. Pharmacol Res 11:889–896
Sharma A, Mayhew E, Straubinger RM (1993) Antitumor effect of taxolcontaining liposomes in a taxol-resistant murine tumor model. Cancer Res 53:5877–5881
Simpson JK, Miller RF, Spittle MF (1993) Liposomal doxorubicin for treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma. Clin Oncol R Coll Radiol 5:372–374
Uziely B, Jeffers S, Isaacson R, Kutsch K, Wei-Tsao D (1995) Liposomal doxorubicin: antitumor activity and unique toxicities during two complementary phase 1 studies. J Clin Oncol 13:1777–1785
Vaage J, Barbera-Guillem E, Abra R, Huang A, Working P (1994) Tissue distribution and therapeutic effect of intravenous free or encapsulated liposomal doxorubicin on human prostate carcinoma xenografts. Cancer 73:1478–1484
Williams SS, Alosco TR, Mayhew E, Lasic DD, Martin FJ, Bankert RB (1993) Arrest of human lung tumor xenograft growth in severe combined immunodeficient mice using doxorubicin encapsulated in sterically stabilized liposomes. Cancer Res 53:3964–3967
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Presented in part as an invited lecture at the 7th International Symposium: Supportive Care in Cancer, Luxembourg, 20–23 September 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janknegt, R. Liposomal formulations of cytotoxic drugs. Support Care Cancer 4, 298–304 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01358884
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01358884