Summary
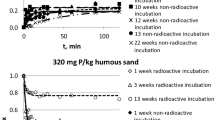
When soils are suspended in solutions of labelled calcium chloride isotopic exchange with the labile soil calcium occurs rapidly. This may be followed by a slow secondary exchange reaction, but its magnitude is not great and equilibrium is nearly, if not completely, attained within 7 days.
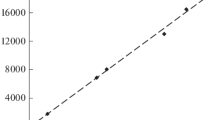
When, however, plants are grown in soil throughout which carrier-free calcium-45 has been thoroughly mixed, it is found that the calcium-45 absorbed by the plants has equilibrated with a quantity of soil calcium larger than that which undergoes isotopic exchange when soils are suspended in solutions of labelled calcium chloride. The analysis of plants grown for varying periods shows that equilibration can continue for several weeks, and that the quantity of soil calcium with which the calcium-45 is associated can be increased both by the addition of electrolytes to the soil and by growing plants under “exhaustion” conditions. In 5 soils the “extra” calcium which equilibrated with calcium-45 in this way never exceeded 3.5 per cent of the total soil calcium, and was usually considerably lower.
The continued equilibration of calcium-45 with soil calcium causes the specific activity (Ca45/stable Ca) of the calcium entering plants to decrease. Because the calcium in plant roots has, on average, been absorbed more recently than that in shoots, the latter show higher specific activities.
The causes of these effects are discussed and consideration is given to their significance in the interpretation of results of experiments involving the use of calcium-45 as a tracer in soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaway, W. H., Availability of replaceable calcium from different types of colloids as affected by degree of calcium saturation. Soil Sci.59, 207–217 (1945).
Blume, J. M. and Smith, D., Determination of exchangeable calcium and cation exchange capacity by equilibration with Ca45. Soil Sci.77, 9–17 (1954).
Biddulph, O.,et al., Circulation patterns for phosphorus, sulphur and calcium in the bean plant. Plant Physiol.33, 293–300 (1958).
Cheng, K. L. and Bray, R. H., Determination of calcium and magnesium in soil and plant. Soil Sci.72, 449–458 (1951).
Larsen, S., The use of P32 in studies on the uptake of phosphorus by plants. Plant and Soil4, 1–10 (1952).
Mason, A. C., The determination of small amounts of calcium in plant material. Analyst77, 529–533 (1952).
McAuliffe, C., Exchange reactions between phosphates and soils: hydroxylic surfaces of soil minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.12, 119–123 (1948).
Mehlich, A. and Colwell, W. E., Absorption of calcium by peanuts from kaolin and bentonite at varying levels of calcium. Soil Sci.61, 369–374 (1946).
Peech, M.et al., Methods of soil analysis for soil fertility investigations. U.S. Dept. Agr. Circ.757 (1947).
Rediske, J. H. and Selders, A. A., Absorption and translocation of strontium in plants. Plant Physiol.28, 594–606 (1953).
Russell, E. J., Soil Conditions and Plant Growth. Longmans, (London), 1961.
Russell, R. S. and Squire, H. M., The absorption and distribution of strontium in plants. I. Preliminary studies in water culture. J. Exp. Botany9, 262–276 (1958).
Russell, R. S., Russell, E. W. and Marais, P. G., Factors affecting the ability of plants to absorb phosphate from soils. I. The relationship between labile phosphate and absorption. J. Soil Sci.8, 248–267 (1957).
Vogel, A. I., Quantitative Inorganic Analysis. Longmans (London), 1951.
Wiersum, L. K., Utilization of soil by the plant root system. Plant and SoilXV, 189–192 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newbould, P., Russell, R.S. Isotopic equilibration of calcium-45 with labile soil calcium. Plant Soil 18, 239–257 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347878
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347878