Summary
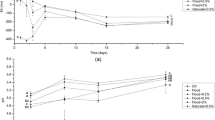
Laboratory experiments were conducted to determine the effects of crop residues, without and withPenicillium urticae Bainer inoculation, on growth of wheat seedlings in soil. Fifty grams of Sharpsburg silty clay loam soil, containing 1% by weight of incorporated alfalfa, sorghum and corn stover residue, were placed in petri dishes, autoclaved, wetted to 40% moisture, and incubated at 24°C. for periods of 2, 3, and 4 weeks. One-half of the petri dishes were inoculated withP. urticae. Germination and seedling-shoot measurements were taken after 7 days of growth.
The results of this study showed that (1) inoculation of soil generally reduced seedling height regardless of the residue treatment; (2) inoculation of soil containing corn and sorghum residues resulted in greater tissue production but reduced height of seedlings as compared to non-inoculated soils; and (3) in the absence of residues, the inoculated control soils were a better growth medium for wheat seedlings than were the non-inoculated control soils. In addition, alfalfa residues, especially in the presence ofP. urticae, were strongly inhibitory to the wheat seedlings, causing curling and reduced wheat-seedling root growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collison, R. C. and Conn, H. J., The effect of straw on plant growth. New York (Geneva) Agr. Expt. Sta. Tech. Bull.114 (1925).
Curtis, R. W., Studies on response of bean seedlings and corn roots to malformin. Plant Physiol.36, 37–43 (1961).
Guenzi, W. D. and McCalla, T. M., Inhibition of germination and seedling development by crop residues. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.26, 456–458 (1962).
Newton, R. and Young, R. S., Nitrification under and after alfalfa, brome, timothy and western rye grass. V. Biological assays of hay crop residues. Can. J. Research18, 374–387 (1940).
Nielsen, K. F., Cuddy, T. F. and Woods, W. B., The influence of the extract of some crops and soil residues on germination and growth. Can. J. Plant Sci.40, 188–197 (1960).
Norstadt, F. A. and McCalla, T. M., A phytotoxic substance from a species ofPenicillium. Science (submitted) (1963).
Patrick, Z. A., The peach replant problem in Ontario. II. Toxic substances from microbial decomposition products of peach root residues. Can. J. Botany33, 461–468 (1955).
Swaby, R. J., Stimulation of plant growth by organic matter. J. Australian Inst. Agr. Sci.8, 156–163 (1942).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Joint contribution from University of Nebraska and Soil and Water Conservation Research Division, Agricultural Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, and Nebraska Agricultural Experiment Station, Lincoln, Nebraska, cooperating. Published with the approval of the Director as Paper No. 1242, Journal Series, Nebraska Agricultural Experiment Station.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behmer, D.E., McCalla, T.M. The inhibition of seedling growth by crop residues in soil inoculated withPenicillium urticae Bainer. Plant Soil 18, 199–206 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347874
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01347874