Abstract
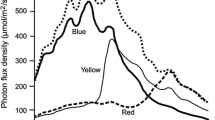
Bioluminescence from the gammarid amphipodCyphocaris faurei Barnard and the hyperiid amphipodsScina crassicornis (Fabricius) andScina borealis (Sars) was measured with a photomultiplier coupled to an integrating sphere, and with a video camera.C. faurei andS. crassicornis were collected in July 1986 and 1987 off Oahu, Hawaii;S. crassicornis was also collected in May 1987 in the northern Sargasso Sea, and in October 1988 north of Hawaii, andS. borealis was obtained in September 1989 off the southern California coast. Emission spectra were obtained with an optical multichannel analyzer. Bioluminescence ofC. faurei appeared as a secretion through integumentary pores on the telson and uropods, and as a glow from a single location on the cephalothorax. The emission spectrum was bimodal or unimodal, with distinct blue-green and orange peaks. In contrast, the bioluminescence ofS. crassicornis andS. borealis was internal and of significantly shorter duration and lower quantum emission, with a unimodal, bluegreen emission spectrum. Appropriate repetitive stimulation in all species induced temporally summated flashes with greater rise times, durations, and total quantum emission than luminescence induced by a single stimulus. The emission spectrum, flash kinetics, quantum emission, and mode of luminescence ofC. faurei are unique compared with those of all other previously investigated amphipod species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ali, M. A., Wagner, J. (1975). Visual pigments: physiology and ecology. In: Ali, M. A. (ed.) Vision in fishes. New approaches in research. Plenum Press, New York, p. 481–516
Bannister, N. J., Herring, P. J. (1989). Distribution and structure of luminous cells in four marine copepods. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 69: 523–533
Barnard, J. L. (1961). Gammaridean Amphipoda from depths of 400–6000 meters. Galathea Rep. 5: 23–128
Barnes, A. T., Case, J. F. (1972). Bioluminescence in the mesopelagic copepod,Gaussia princeps (T. Scott). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 8: 53–71
Biggley, W. H., Lloyd, J. E., Seliger, H. H. (1967). The spectral distribution of firefly light, II. J. gen. Physiol. 50: 1681–1692
Bousfield, E. L., Klawe, W. L. (1963).Orchestoidea gracilis, a new beach hopper (Amphipoda: Talitridae) from lower California, Mexico, with remarks on its luminescence. Bull. Sth. Calif. Acad. Sci. 62(1): 1–8
Bowlby, M. R., Case, J. F. (1989). Endogenous bioluminescent characteristics of a mesopelagic copepod. Am. Zool. 39: 37A
Bowman, T. E. (1967). Bioluminescence in two species of pelagic amphipods. J. Fish. Res. Bd Canada 24(3): 687–688
Bowman, T. E., Phillips, F. (1984). Bioluminescence in the freshwater amphipod,Hyalella azteca, caused by pathogenic bacteria. Proc. biol. Soc. Wash. 97(3): 526–528
Brusca, G. J. (1978). Contributions to the knowledge of hyperiid amphipods of the family Scinidae from near Hawaii, with a description of a new species,Scina hawaiensis. Pacif. Sci. 32(3): 281–292
Childress, J. J., Barnes, A. T., Quetin, L. B., Robison, B. H. (1978). Thermally protecting cod ends for the recovery of living deepsea animals. Deep-Sea Res. 25: 419–422
Dahl, E. (1979). Deep-sea carrion feeding amphipods: evolutionary patterns in niche adaption. Oikos 33: 167–175
Denton, E. J., Gilpin-Brown, J. B., Wright, P. G. (1970). On the ‘filters’ in the photophores of mesopelagic fish and on a fish emitting red light and especially sensitive to red light. J. Physiol., Lond. 208: 72–73
Fernandez, H. R. C. (1978). Visual pigments of bioluminescent and nonbioluminescent deep-sea fishes. Vision Res. 19: 589–592
Frank, T. M., Case, J. F. (1988a). Visual spectral sensitivities of bioluminescent deep-sea crustaceans. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 175: 261–273
Frank, T. M., Case, J. F. (1988b). Visual spectral sensitivity of the bioluminescent deep-sea mysid,Gnathophausia ingens. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 175: 274–283
Gill, C. W. (1986). Suspected mechano- and chemosensory structures ofTemora longicornis (Copepoda: Calanoida). Mar. Biol. 93: 449–457
Harbison, G. R., Biggs, D. C., Madin, L. P. (1977). The associations of Amphipoda Hyperiidae with gelatinous zooplankton. II. Associations with Cnidaria, Ctenophora and Radiolaria. Deep-Sea Res. 24: 465–488
Harvey, E. N. (1952). Bioluminescence. Academic Press, New York
Herring, P. J. (1967). Luminescence in marine amphipods. Nature, Lond. 214: 1260–1261
Herring, P. J. (1981a). Studies on bioluminescent marine amphipods. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 61: 161–176
Herring, P. J. (1981b). Red fluorescence of fish and cephalopod photophores. In: DeLuca, M. A., McElroy, W. D. (eds.) Bioluminescence and chemiluminescence: basic chemistry and analytical applications. Academic Press, New York, p. 527–530
Herring, P. J. (1983). The spectral characteristics of luminous marine organisms. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 220: 183–217
Herring, P. J. (1988). Copepod luminescence. Hydrobiologia 167/168: 183–195
Hessler, R. R., Isaacs, J. D., Mills, E. L. (1972). Giant amphipod from the abyssal Pacific Ocean. Science, N.Y. 175: 636–637
Hiller-Adams, P., Widder, E. A., Case, J. F. (1988). The visual pigments of four deep-sea crustacean species. J. Comp. Physiol. (Sect. A) 163: 63–72
Latz, M. I., Frank, T. M., Bowlby, M. R., Widder, E. A., Case, J. F. (1987). Variability in flash characteristics of a bioluminescent copepod. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 173: 489–503
Latz, M. I., Frank, T. M., Case, J. F. (1988). Spectral composition of bioluminescence of epipelagic organisms from the Sargasso Sea. Mar. Biol. 98: 441–446
Latz, M. I., Bowlby, M. R., Case, J. F. (1990). Mechanical stimulation and recovery of copepod bioluminescence. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 136: 1–22
Lythgoe, J. N. (1972). List of vertebrate visual pigments. In: Dartnall, H. J. A. (ed.) Handbook of sensory physiology, Vol. III, part 1. Photochemistry of vision. Springer, Berlin, p. 604–624
Mauchline, J. (1977). The integumental sensilla and glands of pelagic crustacea. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57: 973–994
Mauchline, J., Ballantyne, A. R. S. (1975). The integumental organs of amphipods. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 55: 345–355
McElroy, W. D., Seliger, H. H., DeLuca, M. (1974). Insect bioluminescence. In: Rockstein, M. (ed.) The physiology of Insecta, Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York, p. 411–460
Mensinger, A. F., Case, J. F. (1988). Dual role of the orbital photophores in the stomiatoid fish,Malacosteus niger. Am. Zool. 28(4): 90A
Moeller, H. W., Bennett, B., Coughlin, S., Getz, D. (1972). Predator prey relationships under luminous conditions. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 1: 257–260
Morin, J. G. (1983). Coastal bioluminescence: patterns and functions. Bull. mar. Sci. 33(4): 787–817
O'Day, W. T., Fernandez, H. R. (1974).Aristostomias scintillans (Malacosteidae): a deep-sea fish with visual pigments apparently adapted to its own bioluminescence. Vision Res. 14: 545–550
O'Day, W. T., Fernandez, H. R. (1976). Vision in the lanternfishStenobrachius leucopsarus (Myctophidae). Mar. Biol. 37: 187–195
Rudyakov, Y. A. (1968). Bioluminescence potential and its relation to concentration of luminescent plankton. Oceanology, Wash. 8: 710–715
Thurston, M. H. (1976). The vertical distribution and diurnal migration of the crustacea amphipoda collected during the Sond cruise, 1965. II. The hyperiidea and general discussion. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 56: 383–470
Tiemann, D. L. (1970). Nature's toy train, the railroad worm. Nat. Hist. Mag. 138: 56–67
Widder, E. A., Hiller-Adams, P., Case, J. F. (1987). A multichannel microspectrophotometer for visual pigment investigations. Vision Res. 27(7): 1047–1055
Widder, E. A., Latz, M. I., Case, J. F. (1983). Marine bioluminescence spectra measured with an optical multichannel detection system. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 165: 791–810
Widder, E. A., Latz, M. I., Herring, P. J. (1986). Temporal shifts in bioluminescence emission spectra from the deep-sea fish,Searsia koefoedi. Photochem. Photobiol. 44: 97–101
Widder, E. A., Latz, M. I., Herring, P. J., Case, J. F. (1984). Far red bioluminescence from two deep-sea fishes. Science, N.Y. 225: 512–514
Wood, K. V., Lam, Y. A., Seliger, H. H., McElroy, W. D. (1989). Complementary DNA coding click beetle luciferases can elicit bioluminescence of different colors. Science, N.Y. 224: 700–702
Young, R. E., Mencher, F. M. (1980). Bioluminescence in mesopelagic squids: diel color change during counterillumination. Science, N.Y. 208: 1286–1288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Grassle, New Brunswick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bowlby, M.R., Widder, E.A. & Case, J.F. Disparate forms of bioluminescence from the amphipodsCyphocaris faurei, Scina crassicornis andS. borealis . Mar. Biol. 108, 247–253 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01344339
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01344339