Summary
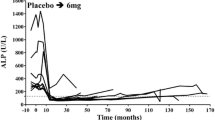
Paget's disease of bone is characterized by primary osteoclastic dysfunction and prolonged treatment with conventional medications including calcitonin and etidronate, results in a number of patients becoming refractory to treatment. We have evaluated the effectiveness of three dosage regimes of aminohydroxypropylidene bisphosphonate (pamidronate) in 15 patients with extensive Paget's disease who had become refractory to conventional therapy. Nine patients had pamidronate (intravenous infusion of 30 mg over 4–5 hours at monthly intervals) for 6 months. A further four patients received 30 mg of pamidronate infusion daily for 6 consecutive days and another two patients, 60 mg on 3 consecutive days (total dose of 180 mg/patient). In all three groups the bone-specific alkaline phosphatase and urinary hydroxyproline excretion both fell by 75% (P < 0.001). All but one patient Showed a marked improvement in clinical symptomatology (pain and mobility) and biochemical parameters indicating decreased bone turnover. Remissions-achieved (> 12 months) with all three regimens were comparable. The pagetic bone pain was reduced and the mobility was Significantly improved after 3 months of therapy and was continued for up to 1 year. Currently, it may be difficult to justify the use of intravenous bisphosphonate as the first line of therapy for Paget's disease, but it does Seem to have a definite place in patients with Severe Paget's disease who do not respond to other therapeutic agents. Here we demonstrate that pamidronate is highly effective in patients with extensive Paget's disease who became refractory to conventional treatment. Further studies are necessary to optimize the dosage and frequency of administration of pamidronate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker DJP, Chamberlain AT, Guyer PB, Gardner MJ (1980) Paget's disease of bone: the Lancashire focus. Br Med J 280:1105–1107
Hamdy RC (1981) Paget's disease of bone. Praeger Press, New York
Evans IM, Banks L, Doyle FH (1980) Paget's disease of bone. The effect of stopping long-term human calcitonin and recommendations for future treatment. Metab Bone Dis Rel Res 2:8791
Wimalawansa SJ (1989) Calcitonin: molecular biology, physiology, pathophysiology and its therapeutic uses. In: Pecile A, Bernard B (eds) Advances in bone regulatory factors: morphology, biochemistry, physiology and pharmacology. Plenum Press, England, pp 121–160
Bijvoet OLM, Sluys Veer JVO, Jansen AP (1967) Thyrocalcitonin in Paget's disease. Lancet ii:471–472
DeRose J, Singer FR, Avramides A, Flores A, Dziadiw R, Baker RK, Wallach S (1974) Response of Paget's disease to porcine and salmon calcitonin. Am J Med 56:858–866
Avramides A (1977) Salmon and porcine calcitonin in the treatment of Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop 127:78–85
Wimalawansa SJ, MacIntyre I (1991) Calcitonin. In: Dollery CT (ed) Therapeutic drugs: a clinical pharmacopia. Churchill Livingstone, UK, pp C18-C22
Haddad JG, Jr, Caldwell JG (1972) Calcitonin resistance: clinical and immunological studies in subjects with Paget's disease of bone treated with porcine and salmon calcitonins. J Clin Invest 51:3133–3136
Wimalawansa SJ, Gunasekera RD, Datta HK (1992) Hypocalcemic actions of amylin amide in human. J Bone Miner Res 7:1113–1116
Drake S, Massie JD, Postlethwaite AE, Palmieri GMO (1989) Pamidronate sodium and calcitonin-resistant Paget's disease: immediate response in a patient. Arch Intern Med 149:401–403
Bijvoet OLM, Frijlink WB, Jie K (1980) APD in Paget's disease of bone. Arthritis Rheum 23:1193–1204
Fleisch H (1983) Bisphosphonates: mechanism of action and clinical applications. In: Peck WA (ed) Bone and mineral research, annual 1. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 319–357
Fraser TRC, King A, Ibbertson HK (1984) Effective oral treatment of severe Paget's disease of bone with APD (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate): a comparison with combined calcitonin and EHDP (1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate). Aust NZ J Med 14:811–818
Harinck HIJ, Papapoulos SE, Blanksma HJ, Moolenaar AJ, Vermeij P, Bijvoet OLM (1987) Paget's disease of bone: early and late responses to three different modes of treatment with aminohydroxypropylidene bisphosphonate (APD). Br Med J 295:1301–1305
Hodgkinson A, Thompson T (1982) Measurement of the fasting urinary hydroxyproline:creatinine ratio in normal adults and its variation with age and sex. J Clin Pathol 35:807–811
Whitaker KB, Whitby LG, Moss DW (1977) Activities of bone and liver alkaline phosphatases in serum in health and disease. Clin Chem Acta 80:209–220
Nagant de Deuxchaisnes C, Rombouts-Lindemans C, Huaux JP, Dovogelaer JP, Malghem J, Maldague B (1979) Roentgenologic evaluation of the actions of the diphosphonate EHDP and combined therapy (EHDP and calcitonin) in Paget's disease of bone. In: MacIntyre I, Szelke M (eds) Molecular endocrinology. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 405–433
Krane SM (1982) Etidronate disodium in the treatment of Paget's disease of bone. Ann Intern Med 96:619–625
Boyce BF, Smith L, Forgleman I, Johnston E, Ralston SH, Boyle IT (1984) Focal osteomalacia due to low dose diphosphonate therapy in Paget's disease. Lancet i:821–824
Singer FR (1977) Human calcitonin treatment of Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop 127:86–93
Wimalawansa SJ (1993) Long- and short-term side effects and safety of calcitonin in man: a prospective study. Calcif Tissue Int 52:90–93
Obie JF, Cooper CW (1979) Loss of calcaemic effects of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone infused continuously into rats using the Alzet osmotic minipump. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 209:422–428
Singer FR, Alfred JP, Neer RM, Krane SM, Potts JT Jr, Bloch KJ (1972) An evaluation of antibodies and clinical resistance to salmon calcitonin. J Clin Invest 51:2331–2336
Singer FR, Fredericks RS, Minkin C (1980) Salmon calcitonin therapy for Paget's disease of bone: the problem of acquired clinical resistance. Arth Rheum 23:1148–1154
Zanelli JM, Salmon DM, Azria M, Zanelli GD (1985) A rat model for clinical resistance to chronic treatment with salmon calcitonin: application of quantitative cytochemistry. In: Pecile A (ed) Calcitonin, 1984: chemistry, physiology, pharmacology and clinical aspects. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 223–230
Tashjian AH Jr, Wright DR, Ivey JL, Pont A (1978) Calcitonin binding sites in bone: relationships to biological response and escape. Recent Prog Horm Res 34:285–334
Ziegler R, Holz G, Raue H, Minne H, Delling G (1976) Therapeutic studies with human calcitonin. In: MacIntyre I (ed) Human calcitonin and Paget's disease. Proc Int Workshop, London, Huber, Vienna, p 167
Kanis JA, McCloskey EV, Paterson AHG (1990) Use of diphosphonate in hypercalcaemia due to malignancy. Lancet i:170–171
Adami S, Bhalla AK, Dorizzo R, Montesant F, Rosini S, Salvagno G, Locascio V (1987) The acute phase response after bisphosphonate administration. Calcif Tissue Int 41:326–331
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wimalawansa, S.J., Gunasekera, R.D. Pamidronate is effective for paget's disease of bone refractory to conventional therapy. Calcif Tissue Int 53, 237–241 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320908
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01320908