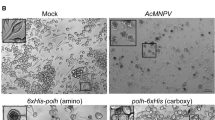
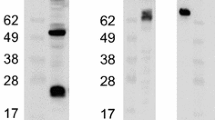
Summary
The DNA sequence encoding the complete herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) glycoprotein D (gD) was inserted into a baculovirus transfer vector under control of the polyhedrin gene promoter of the baculovirusAutographa california nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcNPV). After co-transfection ofSpodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) insect cells with wild-type AcNPV DNA and the recombinant transfer vector DNA, polyhedrin-negative recombinants that expressed high levels of HSV-1 gD were isolated using immunoaffinity selection with antibody coated magnetic particles followed by plaque purification. These recombinant baculoviruses expressed a protein that was slightly smaller than virion HSV-1 gD made in Vero cells. This recombinant protein was expressed at high levels. The expressed protein was glycosylated, was found on the membrane of Sf9 cells, and reacted with gD specific antibodies. Antibodies raised in mice to the recombinant gD neutralized HSV-1 as measured by plaque reduction assays. Mice inoculated with the recombinant baculovirus were completely protected from lethal challenge with HSV-1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman P, Dowbenko D, Lasky LA (1983) Detection of antibodies to herpes simplex virus with a continuous cell line expressing cloned glycoprotein D. Science 222: 524–527
Berman PW, Dowbenko DJ, Simonsen CC, Lasky LA (1984) Production of a subunit vaccine for herpes simplex virus by mammalian cell lines engineered to secrete truncated glycoprotein D. In: Rapp F (ed) Herpesviruses, vol 21. AR Liss, New York, pp 637–649
Campadelli-Fiume G, Arsenakis M, Farabegoli F, Roizman B (1988) Entry of herpes simplex virus 1 in BJ cells that constitutively express viral glycoprotein D is by endocytosis and results in degradation of the virus. J Virol 62: 159–167
Cremer KJ, Mackett M, Wohlenberg C, Notkins AL, Moss B (1985) Vaccinia virus recombinant expressing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D prevents latent herpes in mice. Science 228: 737–740
Desai PJ, Schaffer PA, Minson AC (1988) Excretion of non-infectious virus particles lacking glycoprotein H by a temperature-sensitive mutant of herpes simplex virus type 1: evidence that gH is essential for virion infectivity. J Gen Virol 69: 1147–1156
Eisenberg RJ, Long D, Pereira L, Hampar B, Zweig M, Cohen GH (1982) Effect of monoclonal antibodies on limited proteolysis of native glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by use of monoclonal antibody. J Virol 41: 478–488
Fuller AO, Spear PG (1985) Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit absorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralising antibodies. J Virol 55: 475–482
Garoff H (1985) Using recombinant DNA techniques to study protein targeting in the eucaryotic cell. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1: 403–445
Greenfield C, Patel G, Clark S, Jones N, Waterfield MD (1988) Expression of the human EGF receptor with ligand stimulatable kinase activity in insect cells using a baculovirus vector. EMBO 7: 139–146
Highlander SL, Sutherland SL, Gage PJ, Johnson DC, Levine M, Glorioso JC (1987) Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies specific for herpes simplex glycoprotein D inhibit virus penetration. J Virol 61: 3356–3364
Inumaru S, Ghiasi H, Roy P (1987) Expression of bluetongue virus group specific antigen VP 3 in insect cells by a baculovirus vector: its use for the detection of bluetongue virus antibodies. J Gen Virol 68: 1627–1635
Jarvis DL, Summers MD (1989) Glycosylation and secretion of human tissue plasminogen activator in recombinant baculovirus infected insect cells. Mol Cell Biol 9: 214–223
Johnson DC, Spear PG (1983) O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the golgi apparatus. Cell 32: 987–997
Johnson RM, Lancki DW, Fitch FW, Spear PG (1990) Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D is recognized as antigen by CD 4+ and CD 8+ T lymphocytes from infected mice. J Immunol 148: 702–710
Krishna S, Blacklaws BA, Overton HA, Bishop DHL, Nash AA (1989) Expression of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus type 1 in a recombinant baculovirus: protective responses and T cell recognition of the recombinant infected cell extracts. J Gen Virol 70: 1805–1814
Kuhn JC, Eing BR, Brossmer R, Munk K, Braun RW (1988) Removal of N-linked carbohydrates decreases the infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol 69: 2847–2858
Kuroda K, Hauser C, Rott R, Klenk HD, Doerfler W (1986) Expression of the influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. EMBO J 5: 1359–1365
Kuroda K, Groner A, Frese K, Drenckhahn D, Hauser C, Rott R, Doerfler W, Klenk HD (1989) Synthesis of biologically active influenza virus hemagglutinin in insect larvae. J Virol 63: 1677–1685
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T 4. Nature 227: 680–685
Lasky LA, Dowbenko D, Simonsen CC, Berman PW (1984) Protection of mice from lethal herpes simplex virus infection by vaccination with a secreted form of cloned glycoprotein D. Bio/Technology 2: 527–532
Lee GTY, Para MF, Spear PG (1982) Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol 43: 41–49
Ligas MW, Johnson DC (1988) A herpes simplex virus mutant in which glycoprotein D sequences are replaced by beta-galactosidase sequences binds to but is unable to penetrate into cells. J Virol 62: 1486–1494
Little SP, Jofre JT, Courtney RJ, Schaffer PA (1981) A virion associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology 115: 149–160
Luckow VA, Summers MD (1988) Trends in the development of baculovirus expression vectors. Bio/Technology 6: 47–54
Luckow VA, Summers MD (1988) Signals important for high level expression of foreign genes in autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus expression vectors. Virology 167: 56–71
Matsuura Y, Possee RD, Bishop DHL (1986) Expression of the S-coded genes of lymphocytic choriomeningitis arenavirus using a baculovirus vector. J Gen Virol 67: 1515–1529
Matsuura Y, Possee RD, Overton HA, Bishop DH (1987) Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol 68: 1233–1250
Matthews JT, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ (1983) Synthesis and processing of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in an in vitro system. J Virol 48: 521–553
McGeoch DJ, Dolan A, Donald S, Rixon FJ (1985) Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol 181: 1–13
Norrild B (1985) Humoral response to herpes simplex virus infections. In: Roizman B, Lopez C (eds) The herpesviruses. Plenum, New York, pp 69–86
Possee RD (1986) Cell surface expression of influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells using a baculovirus vector. Virus Res 5: 43–59
Prehaud C, Takehara K, Flamand A, Bishop DHL (1989) Immunogenic and protective properties of rabies virus glycoprotein expressed by baculovirus vectors. Virology 173: 390–399
Rock DL, Nesburn AB, Ghiasi H, Ong J, Lewis TL, Lokensgard JR, Wechsler SL (1987) Detection of latency related viral RNAs in trigeminal ganglia of rabbits latently infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol 61: 3820–3826
Sarmiento M, Haffey M, Spear PG (1979) Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. III. Role of glycoprotein VP 7 (B 2) in virion infectivity. J Virol 29: 1149–1158
Serafini-Cessi F, Dall'Olio F, Malagolini N, Pereira L, Campa-Delli-Fiume G (1988) Comparative study on O-linked oligosaccharides of glycoprotein D of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Gen Virol 69: 869–877
Spear PG (1985) Glycoproteins specified by herpes simplex virus. In: Roizman B (eds) The herpesviruses. Plenum, New York, pp 315–356
Summers MD, Smith GE (1988) A manual of methods for baculovirus vectors and insect cell culture procedures, 2nd edn. MicroGeneSys, New Haven
Takehara K, Ireland D, Bishop HL (1988) Co-expression of the hepatitis B surface and core antigens using baculovirus multiple expression vectors. J Gen Virol 69: 2763–2777
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedures and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 4350–4354
Van Wyke Coelingh KL, Murphy BR, Collins PL, Lebacq-Verheyden AM, Battey JF (1987) Expression of biologically active and antigenically authentic parainfluenza type 3 virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein by a recombinant baculovirus. Virology 160: 465–472
Watson RJ, Weis JH, Salstrom JS, Enquist LW (1982) Herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression inEscherichia coli. Science 218: 381–384
Zezulak KM, Spear PG (1984) Limited proteolysis of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins that occurs during their extraction from vero cells. J Virol 50: 258–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghiasi, H., Nesburn, A.B., Kaiwar, R. et al. Immunoselection of recombinant baculoviruses expressing high levels of biologically active herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. Archives of Virology 121, 163–178 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01316752
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01316752