Summary
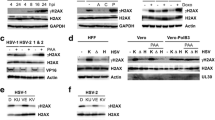
The effect of in vitro infection with herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) on the Interleukin-1 (IL-1) activity of murine keratinocytes was investigated. IL-1α mRNA synthesis was measured by the Northern blot technique, and the IL-1 protein production was measured in terms of the ability of dialysed supernatants from cultures of uninfected and HSV-1 infected keratinocytes to enhance mitogen-induced murine thymocyte proliferation. IL-1α mRNA-synthesis in uninfected keratinocytes was detected 24 h and 48 h after isolation of the keratinocytes. IL-1 protein secretion by these keratinocytes was measureable at 18 h and reached a peak of 73 h, whereas intracellular and membrane-bound IL-1 protein production reached a maximum after 25 h. Keratinocytes, which had been cultured in vitro for 18 h, were infected with HSV-1 for 2 h and further cultured for an additional 4 h or 22 h before IL-1 measurements. A marked reduction of IL-1α gene-expression was noted 6 hours after HSV-1-infection of keratinocytes, and nearly total shut-off was detected after infection for 24 h. Reduced gene-expression was paralleled by a reduction in the IL-1 protein secretion from the HSV-1 infected keratinocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastassakos C, Alexander GJM, Wolstencroft RA, Avery JA, Portmann BC, Panayi GS, Dumonde DC, Eddlseton ALWF, Williams R (1988) Interleukin-1 and Interleukin-2 activity in hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 94: 999–1005
Al-Saadi SA, Gross P, Wildy P (1988) Herpes simplex virus type 2 latency in the footpad of mice: effect of acycloguanosine on the recovery of virus. J Gen Virol 69: 433–438
Ansel JC, Luger TA, Lowry D, Perry P, Roop DR, Mountz JD (1988) The expression and modulation of Interleukin-1 alpha in murine keratinocytes. J Immunol 140: 2274–2278
Ansel J, Perry P, Brown J, Damm D, Phan T, Hart C, Luger T, Hefeneider S (1990) Cytokine modulation of keratinocyte cytokines. J Invest Dermatol 94: 101 S-107 S
Barr RM, Wong E, Mallet A, Olons LA, Greaves MW (1984) The analysis of arachidonic acid metabolites in normal, uninvolved, and lesional psoriatic skin. Prostaglandins 28: 57–60
Basham TY, Nickoloff BJ, Merigan TC, Morhenn V (1985) Recombinant gamma interferon differentially regulates Class II antigen expression and biosynthesis in cultured normal human keratinocytes. J Interferon Res 5: 23–32
Bell TV, Harley CB, Stetsko D, Sauder DN (1987) Expression of mRNA homologous to Interleukin-1 in human epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol 88: 375–379
Ben-Hur T, Rosen-Wolf A, Lamade W, Darai G, Becker Y (1988) HSV-1 DNA sequence determining intraperitoneal pathogenicity in mice is required for transcription of viral immediate-early genes in macrophages. Virology 163: 397–404
Chirgwin JM, Przybyla AE, MacDonald RS, Rutter WS (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonucleases. Biochemistry 18: 5294–5299
Cunningham AL, Noble JR (1989) Role of keratinocytes in human recurrent herpetic lesions: ability to present herpes simplex virus antigen and act as targets for T lymphocyte cytotoxicity in vitro. J Clin Invest 83: 490–496
De Luca D, Mizel SB (1986) Ia-positive nonlymphoid cells and T cell development in murine fetal thymus organ cultures; Interleukin-1 circumvents the block in T cell differentiation induced by monoclonal anti-Ia antibodies. J Immunol 137: 1435–1441
Demczuk S, Baumberger C (1987) Expression of human Interleukin-1 alpha and beta messenger RNAs and IL-1 activity in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Mol Cell Immunol 3: 255–265
Dinarello CA (1988) Biology of Interleukin-1. FASEB J 2: 108–115
Dinarello CA, Clark BD, Puren AJ, Savage N, Rosoff PM (1989) The Interleukin-1 receptor. Immunol Today 10: 49–51
Enk C, Gerstoft J, Moller S, Remvig L (1986) Interleukin-1 activity in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Scand J Immunol 23: 491–497
Goldminz D, Kupper TS, McGuire TS (1988) Keratinocyte membrane associated epidermal cell-derived thymocyte-activating factor (ETAF). J Invest Dermatol 118: 369–376
Granstein RD, Margolis R, Mizel SB, Sauder DN (1986) In vivo inflammatory activity of epidermal cell-derived thymocyte activating factor and recombinant Interleukin-1 in the mouse. J Clin Invest 77: 1020–1027
Gray PW, Glaiser D, Chen E, Goeddel DV, Pennica D (1986) Two Interleukin-1 genes in the mouse: cloning and expression of the cDNA for the murine Interleukin-1 beta gene. J Immunol 137: 3644–3648
Hammerberg C, Fischer G, Voorhees JJ, Cooper KD (1990) Human epidermis processes both Interleukin-1 alpha and Interleukin-1 beta into novel molecular isoforms (abstract). J Invest Dermatol 94: 532
Hill TJ, Blyth WA, Harbour DA (1983) Recurrence of herpes simplex in the mouse requires an intact nerve supply to the skin. J Gen Virol 64: 2763–2765
Kapasi K, Rice GPA (1988) Cytomegalovirus infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells: effects of Interleukin-1 and 2 production and responsiveness. J Virol 62: 3603–3607
Kohl S, Thomas JW, Loo SS (1986) Defective production of anti-herpes simplex virus antibody by neonatal mice. Reconstitution with Ia+-macrophages and T helper lymphocytes from non-immune adult syngeneic mice. J Immunol 136: 3038–3044
Koide S, Steinman RM (1988) Induction of Interleukin-1 mRNA during antigen-dependent interaction of sensitized T lymphoblasts with macrophages. J Exp Med 168: 409–416
Kupper TS, Ballard DW, Chua AO, McGuire JS, Flood PM, Horowitz MC, Langdon R, Lightfoot L, Gubler U (1986) Human keratinocytes contain mRNA indistinguishable from monocyte Interleukin-1 alpha and beta mRNA. J Exp Med 164: 2095–2100
Lepe-Zuniga JL, Mansell PWA, Hersh EM (1987) Idiopathic production of Interleukin-1 in aquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Virol 25: 1695–1700
Lomedico PT, Gubler U, Hellman CP, Dukowitz M, Giri JG, Pan YE, Collier K, Semiononov R, Chua AO, Mizel SB (1984) Cloning and expression of murine Interleukin-1 cDNA inE. coli. Nature 312: 458–462
Luger TA, Stadler BM, Katz SI, Oppenheim JJ (1981) Epidermal cell (keratinocyte)-derived thymocyte activating factor (ETAF). J Immunol 127: 1493–1498
McGuire J, Langdon R, Birchall N, Kupper T (1988) Interleukin-1 alpha mRNA induced by cyclohexamide, PMA, and retinoic acid is reduced by dexamethasone in PAM-212 keratinocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 548: 283–290
Muller C, Godl I, Ahmad R, Wolf HM, Mannhalter JW, Eibl MM (1989) Interleukin-1 production in acute viral hepatitis. Arch Dis Childhood 64: 205–210
Nudel U, Zakut R, Shani M, Neuman S, Levy Z, Yaffe D (1983) The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res 11: 1759–1771
Oakes JE (1975) Role for cell-mediated immunity in the resistance of mice to subcutaneous herpes simplex virus infection. Infect Immun 12: 166–172
Remvig L, Enk C, Svenson M (1985) A standardized human T-lymphocyte proliferation assay for detecting soluble accessory factors from monocytes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C 93: 91–96
Roizman B, Sears AE (1987) An inquiry into the mechanisms of herpes simplex virus latency. Annu Rev Microbiol 41: 543–571
Romeo LI, Ikejima T, Pincus SH (1989) In situ localization of Interleukin-1 in normal and psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol 93: 518–522
Sarmiento M (1988) Intrinsic resistance to viral infection. Mouse macrophage restriction of herpes simplex virus replication. J Immunol 141: 2740–2748
Sauder DN, Carter C, Katz SI, Oppenheim JJ (1982) Epidermal cell production of thymocyte activating factor (ETAF). J Invest Dermatol 79: 34–39
Sauder DN, Ponappan U, Cinader B (1989) Effect of age on cutaneous Interleukin-1 expression. Immunol Lett 20: 111–114
Scala G, Kuang YD, Hall RE, Muchmore AV, Oppenheim JJ (1984) Accessory cell function of human B cells. I. Production of both Interleukin-1 like activity and an Interleukin-1 inhibitory factor by an EBV-transformed human B cell line. J Exp Med 157: 60–65
Schmid DC, Larsen HS, Rouse BT (1982) Role of Ia antigen expression and secretory function of accessory cells in the induction of cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to HSV. Infect Immun 37: 138–1147
Sprecher E, Becker Y (1988) Role of epidermal Langerhans cells in viral infections. Arch Virol 103: 1–14
Sprecher E, Becker Y (1990) Induction of Interleukin-1 beta gene transcription in mouse peritoneal exudate cells after intraperitoneal infection with herpes simplex virus-1. Arch Virol 110: 259–269
Strom T, Frenkel N (1987) Effects of herpes simplex virus on mRNA stability. J Virol 61: 2198–2207
Subak-Sharpe JH, Al-Saadi SA, Clements GB (1984) Herpes simplex type 2 establishes latency in the mouse footpad and in the sensory ganglia. J Invest Dermatol 83 [Suppl]: 67 s-71 s
Tenney DJ, Morahan PS (1987) Effects of differentiation of human macrophage-like U 937 cells on intrinsic resistance to herpes simplex virus type 1. J Immunol 139: 3076–3083
Thomas PS (1980) Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71: 5201–5205
Ulich TR, del Castillo J, Gou K, Souza L (1989) The hematological effects of chronic administration of the monokines tumour necrosis factor, Interleukin-1 and granulocyte-stimulating colony factor on bone marrow circulation. Am J Pathol 143: 149–159
Wahl LM, Corcoran ML, Pyle SW, Arthur LO, Harel-Bellan A, Farrar WL (1989) Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein (gp 120) induction of monocyte arachidonic acid metabolites and Interleukin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 621–625
Wainberg MA, Roy S, Vydelingum S, Grise-Miron L (1985) The role of Interleukins in viral inhibition of lymphocyte mitogenesis. J Clin Lab Immunol 18: 167–174
Wheeler CE (1975) Pathogenesis of recurrent herpes simplex infection. J Invest Dermatol 65: 341–346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enk, C., Sprecher, E. & Becker, Y. Interleukin-1 alpha gene-transcription in murine keratinocytes is inhibited by HSV-1 infection. Archives of Virology 121, 141–151 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01316750
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01316750