Summary
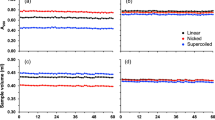
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA sediments homogeneously on a neutral sucrose gradient but heterogeneously on an alkaline sucrose gradient. Several factors that may influence the alkaline sedimentation pattern of HSV DNA were examined: e.g., the host cell, cell density at time of infection, multiplicity of infection, and the starting material for HSV DNA purification (whether HSV-infected cells or cell-free virus). Based on alkaline sedimentation analysis, these factors appear to play little or no role in the amount of intact single-stranded HSV DNA observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenwick, M. Morse, L., Roizman, B.: Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. XI. Apparent clustering of functions effecting rapid inhibition of host DNA and protein synthesis. J. Virol.29, 825–827 (1979).
Geelen, J., Walig, C., Wertheim, P. van der Noordaa, J.: Human cytomegalovirus DNA. I. Molecular weight and infectivity. J. Virol.26, 813–816 (1978).
Howett, M. K.: Personal communication.
Hyman, R. W., Oakes, J. E., Kudler, L.:In vitro repair of the pre-existing nicks and gaps in herpes simplex virus DNA. Virology76, 286–294 (1977).
Iltis, J. P., Oakes, J. E., Hyman, R. W., Rapp, F.: Comparison of the DNAs of varicella-zoster viruses isolated from clinical cases of varicella and herpes zoster. Virology82, 345–352 (1977).
Kieff, E. D., Bachenheimer, S. L., Roizman, B.: Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J. Virol.8, 125–132 (1971).
Pater, M. M., Hyman, R. W., Rapp, F.: Isolation of herpes simplex virus DNA from the “Hirt supernatant”. Virology75, 481–483 (1976).
Roizman, B.: The structure and isomerization of herpes simplex virus genomes. Cell16, 481–494 (1979).
Wilkie, N. M.: The synthesis and substructure of herpesvirus DNA: The distribution of alkali-labile single strand interruptions in HSV-1 DNA. J. gen. Virol.21, 453–467 (1973).
Wilkie, N. M., Clements, J. B., Macnab, J. C. M., Subak-Sharpe, J. H.: The structure and biological properties of herpes simplex virus DNA. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol.39, 657–666 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 4 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ecker, J.R., Hyman, R.W. Variables that may influence the alkaline sedimentation pattern of herpes simplex virus DNA. Archives of Virology 68, 221–228 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314575
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314575