Summary
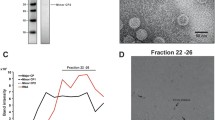
Choroid plexus (GCP-3) cell cultures were prepared from an adult goat with symptoms of visna. The GCP-3 cell layer had partly fused into large multinucleated giant cells and electronmicrographs showed virus particles morphologically indistinguishable from sheep visna virus (SVV). A virus, designated goat visna virus (GVV), was subsequently purified from the GCP-3 cultures. The virus particles have a density of 1.15 g/ml and a high molecular weight RNA similar in size to that of SVV. A virion-associated DNA polymerase was identified which is stimulated to the same extent as the SVV polymerase by different synthetic RNA and DNA template-primer combinations and which shows the same Mg2+ and Mn2+ stimulation optima. Polypeptide analysis by SDS-PAGE revealed that the virion proteins of GVV and SVV had similar molecular weights. By immuno-diffusion tests it was demonstrated that the major internal proteins of GVV and SVV are related. Consequently, we conclude that GVV should be classified as a retrovirus and that it is closely related to visna virus of sheep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cork, L. C., Hadlow, W. J., Crawford, T. B., Gorham, J. R., Piper, R. C.: Infectious leukoencephalomyelitis of young goats. J. inf. Dis.129, 134–141 (1974).
Cork, L. C., Hadlow, W. C., Gorham, J. R., Piper, R. C., Crawford, T. B.: Pathology of viral leukoencephalomyelitis of goats. Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin)29, 281–292 (1974).
Coward, J. E., Harter, D E., Morgan, C.: Electron microscopic observations of visna virus-infected cell cultures. Virology40, 1030–1038 (1970).
Crawford, T. B., Adams, D. S., Cheevers, W. P., Cork, L. C.: Chronic arthritis in goats caused by a retrovirus. Science207, 997–999 (1980).
Dahme, E., Stavrou, D., Deutschländer, N., Arnold, W., Kaiser, E.: Klinik und Pathologie einer übertragbar granulomatösen Miningoencephalomyelitis (g MEM) bei der Hausziege. Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin)23, 59–76 (1973).
Fatzer, R.: Encephalo-Myelitis granulomatosa bei Zicklein in der Schweiz. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilk.121, 329–339 (1979).
Griem, W., Weinhold, E.: Zur Pathologie der Visna der Ziege. Dtsch. Tierärztl. Wschr.82, 385–428 (1975).
Haase, A. T., Baringer, J. R.: The structural polypeptides of RNA slow viruses. Virology57, 238–250 (1974).
Maizel, J. V.: Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of viral proteins. In:Maramorosch, K., Koprowski, H. (eds.), Methods in Virology, 180–244. New York: Academic Press Inc. 1971.
Narayan, O., Griffin, D. E., Chase, J.: Antigenic shift of visna in persistently infected sheep. Science197, 376–378 (1977).
Narayan, O., Clements, J. E., Strandberg, J. D., Cork, L. C., Griffin, D. E.: Biological characterization of the virus causing leukoencephalitis and arthritis in goats. J. gen. Virol. (in press).
O'Sullivan, B. M., Eaves, F. W., Baxendell, S. A., Rowan, K. J.: Leukoencephalomyelitis in goat kids. Aust. vet. J.54, 479–483 (1978).
Pálsson, P. A.: Maedi and visna in sheep. In:Kimberlin, R. H. (ed.), Slow virus diseases of animal and man, 17–43. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publ. Co. 1976.
Scott, J. A., Strowring, L., Haase, A. T., Narayan, O., Vigne, R.: Antigenic variation in visna virus. Cell18, 321–327 (1979).
Sigurdsson, B., Pálsson, P. A., Grímsson, H.: Visna, a demyelinating transmissible disease of sheep. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol.16, 389–403 (1957).
Sigurdsson, B., Pálsson, P. A.: Visna of sheep. A slow, demyelinating infection. Brit. J. exp. Pathol.39, 519–528 (1958).
Stavrou, D., Deutschländer, N., Dahme, E.: Granulomatous encephalomyelitis in goats. J. comp. Pathol.79, 393–396 (1969).
Stowring, L., Haase, A. T., Charman, H. P.: Serological definition of the lentivirus group of lentiviruses. J. Virol.29, 523–528 (1979).
Strand, M., August, J. T.: Structural proteins of ribonucleic acid tumor viruses. Purification of envelope, core and internal components. J. biol. Chem.251, 559–564 (1976).
Sundquist, B., Larner, E.: Phosphonoformate inhibition of visna virus replication. J. Virol.30, 847–851 (1979).
Trowbridge, R. S.: Long-term visna virus infection of sheep choroid plexus cells: Initiation and preliminary characterization of the carrier cultures. Infect. Immun.11, 862–868 (1975).
Weinhold, E.: Visna-Virus-ähnliche Partikel in der Kultur von Plexus chorioideus-Zellen einer Ziege mit Visna-Symptomen. Zentralbl. Veterinärmed.B21, 32–36 (1974).
Weinhold, E., Triemer, B.: Visna bei der Ziege. Zentralbl. Veterinärmed.B25, 525–538 (1978).
Weiss, M. J., Zelon, E. P., Sweet, R. W., Harter, D. H., Spiegelman, S.: Immunological cross-reactions of the major internal protein component from “slow” viruses of sheep. Virology76, 851–854 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 7 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundquist, B. Goat visna virus: Isolation of a retrovirus related to visna virus of sheep. Archives of Virology 68, 115–127 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314441
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314441