Abstract
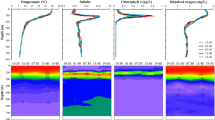
Vertical distribution and nocturnal migration of zooplankton species in relation to the development of the seasonal thermocline in the shallow waters (90 m) of Patraikos Gulf (Ionian Sea, Greece) were investigated using a WP-2 closing net. Juvenile and adult copepods accounted for a mean of 91% of the total collected in three sampling periods, i.e. May, July and September 1985.Ctenocalananus vanus, Paracalanus parvus andOithona plumifera were the dominant copepods. The majority of the zooplankton tend to aggregate at the thermocline layer. Among copepods the two congeneric speciesClausocalanus pergens andC. furcatus exhibited different migratory responses to the development of the thermocline.C. pergens occurred in the lower part of the thermocline andC. furcatus in the upper region or above. The diel vertical migration of all species could be divided into four types: (1) no vertical migration; (2) upward migration at night; (3) occasional migration; and (4) reverse migration (down at night). In July when the strongest thermocline developed, most zooplankters rose close to the surface at night. For most species, temperature discontinuity did not limit their diel migration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Frost, B., Fleminger, A. (1968). A revision of the genusClausocalanus (Copepoda: Calanoida) with remarks on distributional patterns in diagnostic characters. Bull. Scripps Inst. Oceanogr. (New Ser.) 12: 1–235
Greze, V. N. (1963). Zooplankton of the Ionian Sea. Okeanologicheskige Issled. 9: 42–59 [in Russ.]
Hure, J. (1955). Distribution annuelle verticale du zooplancton sur une station de l'Adriatique meridionale. Acta adriat. 7: 1–72
Hure, J. (1961). Daily migration and seasonal vertical distribution in the depths of the Adriatic. Acta adriat. 9: 1–60
Hure, J., Scotto di Carlo, B. (1970). Distribuzione e frequenza delle specie del genereClausocalanus Giesbrecht, 1888 (Copepoda: Calanoida) nel Golfo di Napoli e nell'Adriatico meridionale. Pubbl. Staz. zool. Napoli 38: 289–304
Longhurst, A. R., Williams, R. (1979). Materials for plankton modelling: vertical distribution of Atlantic zooplankton in summer. J. Plankton Res. 1: 1–28
Moraitou-Apostolopoulou, M. (1971). Vertical distribution, diurnal and seasonal migration of copepods in Saronic Bay, Greece. Mar. Biol. 9: 92–98
Paffenhöfer, G. A. (1983). Vertical zooplankton distribution on the northeastern Florida shelf and its relation to temperature and food abundance. J. Plankton Res. 5: 15–33
Raymont, J. E. (1983). Plankton and productivity in the oceans, Vol. 2. Zooplankton, 2nd edn. Pergamon Press, Oxford, p. 824
Scotto di Carlo, B., Ianora, A., Fresh, E., Hure, J. (1984). Vertical zonation patterns for Mediterranean copepods from the surface to 3 000 m at a fixed station in the Tyrrhenian Sea. J. Plankton Res. 6: 1031–1056
Sorokin, Y. I. (1980). Microheterotrophic organisms in marine ecosystems. In: Longhurst, A. R. (ed.) Analysis of marine ecosystems. Academic Press, London, New York, p. 293–342
Vassiere, R., Seguin, G. (1980). Etude preliminaire de peuplements de copepods (Juillet 1977) en relation avec l'hydrologie des mers Tyrrhenienne et Ionienne. Oceanol. Acta 3: 17–29
Vinogradov, M. E. (1970). Vertical distribution of the oceanic zooplankton. Israel Program for Scientific Translations. Keter Press, Jerusalem, p. 338
Williams, R., Conway, D. V. P. (1984). Vertical distribution and seasonal and diurnal migration ofCalanus helgolandicus in the Celtic Sea. Mar. Biol. 79: 63–73
Williams, R., Conway, D. V. P., Collins, N. R. (1987). Vertical distribution of eggs, nauplii and copepodites ofCalanus helgolandicus (Crustacea: Copepoda) in the Celtic Sea. Mar. Biol. 96: 247–252
Williams, R., Fragopoulu, N. (1985). Vertical distribution and nocturnal migration ofNyctiphanes couchi (Crustacea: Euphausiacea) in relation to the summer thermocline in the Celtic Sea. Mar. Biol. 89: 257–262
Williams, R., Robins, D. B. (1982). Effects of preservation on wet weight, dry weight, nitrogen and carbon contents ofCalanus helgolandicus (Crustacea: Copepoda). Mar. Biol. 71: 271–281
Williams, R., Wallace, M. A. (1975). Continuous plankton records: a plankton atlas on the North Atlantic and North Sea. Suppl. 1. The genusClausocalanus (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) in 1965. Bull. mar. Ecol. 8: 167–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Please address all correspondence and requests for reprints to Dr J.J. Lykakis
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fragopoulu, N., Lykakis, J.J. Vertical distribution and nocturnal migration of zooplankton in relation to the development of the seasonal thermocline in Patraikos Gulf. Mar. Biol. 104, 381–387 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314340
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01314340